![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the iliac crest correspond to? What does the PSIS correspond to? What does the inferior angle of scapula correspond to? |
iliac crest - S4 PSIS - S1 Inferior angle of scapula - T7 |
|
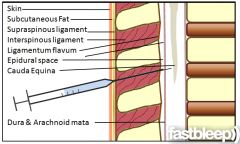
identify the structures |
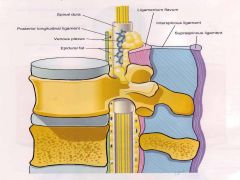
|
|
|
describe epidural anaesthesia
|
|
|
|
describe spinal anaesthesia |
|
|
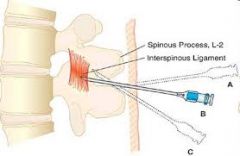
What is midline approach? |
needle is placed midline, perpendicular to spinous process, aimed slightly cephalad |
|
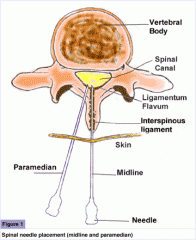
What is paramedian approach? |
needle placed 1.5cm laterally and slightly caudad to the center of interspinous space, needle is aimed medially and slightly cephalad, passed lateral to supraspinous ligament. if lamina is contacted, redirect needle medial and cephalad |
|
|
What medications are injected into the subarachnoid/epidural space? |
Shorter duration, faster onset Chloroprocaine Lidocaine Longer duration, slower onset Bupivacaine Ropivacaine |
|
|
Side effects of spinal and epidural anaesthesia
|
1. Cauda equina syndrome - a/w high dose of anaesthesia - permanent bowel,bladder dysfunction, paralysis of lower limb 2. Transient neurologic symptoms - a/w lithotomy position and lidocaine - resolves within days 3. Cardiovascular changes - hypotension, treated with ephedrine/phenylephrine - bradycardia if T1-4 affected 4. Post dural puncture headache (epidural>spinal) 5. Urinary retention 6. Intravascular injection (requires emergent surgical decompression) 7. Epidural abscess 8. Total spinal anaesthesia - Needs intubation, since respiratory centers are affected - watch out for hypotension |
|
|
Contraindications of neuraxial anaesthesia |
Absolute: - Injection in area of needle puncture - Elevated intracranial pressure - Uncontrolled bleeding Relative: - Bacteraemia - pre-existing neurologic disease - Cardiac disease - Abnormal coagulation studies |

