![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oxidation |
Loss of Electrons |
|
|
Reduction |
Gain of electrons. |
|
|
Oxidizing Agent |
Causes another atom to undergo oxidation, and is itself reduced. |
|
|
Reducing Agent |
Causes another atom to be reduced, and is itself Oxidized. |
|
|
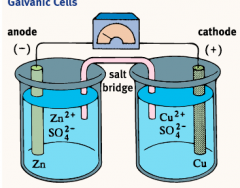
Galvanic Cells |
|
|
|
Galvanic Cells |
A redox reaction occurring in a galvanic cell has a negative Delta G and is therefore a spontaneous reaction. Galvanic Cell reactions supply energy and are used to do work. This energy can be harnessed by placing the oxidation-reduction half-reactions in separate containers called half-cells. The half-cells are then connected by an apparatus that allows for the flow of electrons. |
|
|
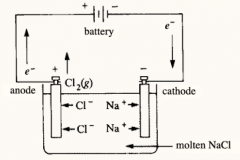
Electrolytic Cells |
|
|
|
Electrolytic Cells |
A redox reaction occurring in an electrolytic cell has a positive delta G and is therefore non-spontaneous. In electrolysis, electrical energy is required to induce a reaction. The oxidation and reduction half-reactions are usually placed in one container. |
|
|
Reduction Potential |
Is defined as the tendency of a species to acquire electrons and be reduced. Standard reduction potential is measured under standard conditions: 25 Degrees Celsius, 1 M concentrations for each ion in the reaction, a partial pressure of 1 atm for each gas and metals in their pure state. |
|
|
Standard Reduction Potentials |
Used to calculate the standard EMF of a reaction, the difference in potential between two half-cells. EMF = Ecathode - Eanode |
|
|
Gibbs Free Energy (Delta G) |
Is the thermodynamic criterion for determining the spontaneity of a reaction. Delta G = -n*F*Ecell |

