![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Name some components associated with primary and secondary haemostasis. |
Primary - platelets + VWF (platelet plug formation) and blood vessels (reflex vasoconstriction) Secondary - clotting factors |
there are three for primary and one for secondary |
|
|
Which clotting factors are vitamin k dependent? |
2, 7, 9, 10 |
|
|
|
Which clotting factor isn't synthesised in the liver? |
7 |
|
|
|
Exposure to collagen or tissue factor activates the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway, which activates which pathway? |
tissue factor - extrinsic collagen - intrinsic |
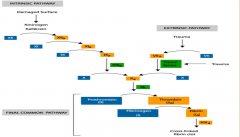
|
|
|
Name three congenital haemorrhagic clotting disorders. |
Haemophilia A Haemophilia B Von Willebrands disease |
|
|
|
How can haemorrhagic disorders be acquired? |
antiplatelet therapy anticoagulant therapy - warfarin/heparin platelet dysfunction due to drugs thrombocytopenia |
|
|
|
What is hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia/osler-rendu-weber syndrome? |
A vascular defect that rarely causes serious bleeding. Autosomal dominant condition leading to abnormal blood vessel formation. Seen as telangiectasia on skin + mucous membranes. |
|
|
|
What is von willebrands disease, how does it cause a vascular problem? |
An inherited tendency to produce less VWF than required. VWF has three jobs: 1. mediates platelet adhesion to damaged endothelium 2. stabilises and tranports FVIII 3. mediates platelet aggregation therefore there is a clotting difficulty |
|
|
|
How is von willebrands disease treated? |
desmopressin/vasopressin to stimulate release of factor VIII, vwf and tPa OR Factor concentrate/cryoprecipitate with FVIII, VWF and fibrinogen |
antidiuretic drug and replacement therapy |
|
|
What is Bernard Soulier syndrome? |
Rare autosomal coagulopathy (bleeding disorder) causes a deficiency of glycoprotein 1b (GP1b) which is the platelet receptor for VWF |
GP1B |
|
|
What sort of things might cause platelet deficiency? |
chemotherapeutic agents or viruses (HIV/mumps) may cause megakaryocyte suppression Bone marrow may have failed due to aplastic anaemia/leukaemia/metastases splenomegaly may cause platelet sequestration and lead to a thrombocytopenic state |
|
|
|
which conditions cause splenomegaly? |
blood cancers i.e. hodgkins lymphoma, leukaemia haemolytic anaemia endocarditis mononucleosis |
|
|
|
What is idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura? |
Low platelet count causing a purpuric rash with an increased bleeding tendency. It is autoimmune, with antibodies against platelets being clearly seen. |
|
|
|
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is often the first manifestation of which condition? |
systemic lupus erythematosus and can be brought about by malaria |
|
|
|
Which 4 drugs cause platelet dysfunction? |
NSAIDS, clopidogrel and dypyridamole and asprin (reversible) |
|
|
|
What are the clinical signs of platelet dysfunction? |
easy bruising and bleeding petechiae (pin point haemorrhagic lesions) ecchymosis |
|
|
|
What would a dentist have to consider for a patient with suspected thrombocytopenia/platelet deficiency? |
Investigate platelet count/FBC Stop antiplatelet drugs 7 days prior except NSAIDs > 24hrs prior |
|
|
|
How would a FBC indicate risk of spontaneous bleeding in a platelet deficient patient? |
if the PC <20,000/mm^3 = risk |
think about the platelet count |
|
|
Give examples of local haemostatic agents that dentists may use |
moist tea bag (tannic acid) compressive packing absorbable haemostatic agents (oxidised regenerated cellulose - surgicel) |
surgicel cotton wool tannic acid what are these things |
|
|
What systemic conditions might result in a clotting disorder? |
liver disease malabsorption problems disseminated intravascular coagulation |
|
|
|
What is disseminated intravascular coagulation? |
aka "consumptive coagulopathy" is a pathological widespread activation of the clotting cascade to form clots in small blood vessels of the body |
|

