![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What stimulus do pacinian corpuscle respond to? |
Mechanical pressure |
|
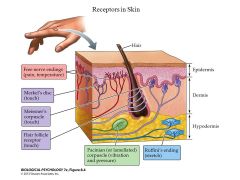
Where are pacinian corpuscles found? |
Deep in the skin and are most abundant on the fingers and soles of the feet. They also oocur in joints, ligament and tendons. |
|
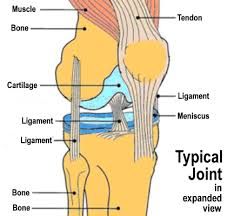
Why do pacinian corpuscles occur in joints, ligaments and tendons? |
They enable the organism to know which joints are changing direction. |
|
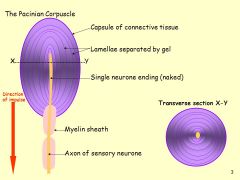
Describe the structure of a pacinian corpsucle: |
Single sensory neurone of pacinian corpsucle is at the centre of lamellae: layers of connective tissue each separated by a viscous gel. |
|
|
What is the special type of sodium channel that the sensory neurone at the centre of the pacinian corpsucle has? |
stretch mediated sodium channel. These change the permeability of sodium ions when they are deformed. |
|
|
During resting state what is the charge of the inside of the membrane of the sensory nerve ending? |
the inside of the membrane is negatively charged compared to the outside. |
|
|
What is the state of the stretch mediated sodium channnels of the membrane in the sensory nerve endings resting state? |
The stretch mediated sodium channels are too narrow to allow sodium ions to pass through. |
|
|
What happens to pacinian corpuscle when pressure is applied? |
It becomes deformed and the membrane around the neurone becomes stretched. This widens the sodium channels. |
|
|
What happens when the membrane around the neurone becomes stretched in the pacinian corpuscle? |
The sodium channels widen and allows sodium ions to diffuse into the neurone. This changes the potential and depolarises the membrane producring a generator potential. |
|
|
What depolarises the membrane of the neurone in the pacinian? |
The influx of sodium ions through the widen stretch mediated sodium channels. |
|
|
What does a generator potential produce? |
action potential. |
|

What are the two types of photoreceptors? |
rods and cones |
|
|
What do rods and cones act as? |
transducers as they convert light energy into electrical energy. |
|
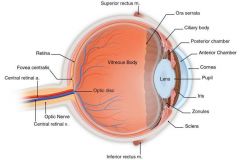
What doesn't contain receptors in the eye? |
Optic nerve |
|
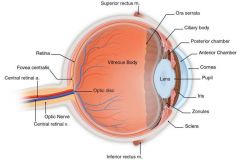
What contains many cones and no rods? |
Favea |
|
What kind of image do rods produce? and why. |
Rods cannot distinguish different wavelengths of light so image is black and white. |
|

Which ones are more numerous rods or cones and how many are there in each eye? |
120 million rods |
|
|
How are rods different to cones i terms of the number connected to a single neurone? |
Whilist cones have their own separate bipolar cell connected to one sensory neurone in the optic nerve many rods are connected to a single neurone in the optic nerve. |
|
|
What is retinal convergence? |
a number of rod cells are connect to a single bipolar cell. |
|
|
What must be reached before a generator potential is created in bipolar cells? |
certain threshold value (of light intensity) |
|
|
Why do rods allow us to see in low light intensities? |
many rod cells are connected to a single bipolar cell so there is much greater chance that a threshold value will be exceeded, to create a generator potential (and therefore action potential) than if only a single rod cell were connected to each bipolar cell. |
|
|
How is a generator potential created in a rod cell? |
The pigment rhodopsin is broken down, there is enough energy from low light intensity to do this. |
|
|
What is visual acuity? |
The ability to tell apart points that are close together. |
|
|
Why do rods give low visual acuity? |
Light recieved by rod cells sharing the same neurone will only generate a single action potential. The brain cannot distinguish the separate sources of light that stimulated them. |
|

how many different types of cone cells are there? |
Three |
|
|
How many cone cells are there in the eye? |
6 million. |
|
|
Why do cone cells only respond to high light intensoties? |
They have their own separate bipolar cell connected to a sensory neuron in the optic nerve. Stimulation of cones cells cannot be combined to reach a threshold value. Pigment iodopsin requires high light intensity to break it down. |
|
|
Why do cone cells have good visual acuity? |
Each cell has its own connection to a single bipolar cell. |
|
|
Why do different types of cone cells respond to different types of light intensity?
|
The three different types have different types of iodopsin which is sensitive to different wavelengths |

