![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
173 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
real estate licensing requirements |
18 or older -Us citizen (or noncitizen national or qualified alien under fed. Law) -not required to be resident of NC -75 hr prelicensing course passed -background check passed -state exam passed -commission determines person possesses "requisite character" after passing
|
|
|
Pocket card |
Issued with license by the board. Agents are required to produce upon being asked while engaging in brokerage activities |
|
|
A NC real estate license is required when: |
LLBEANS (brokerage activities) Lists, leases, buys, exchanges, auctions, negotiates, sells Three prong test: ****real property for compensation for others |
|
|
Difference between broker (non provisional status), broker (provisional status) and broker in charge (BIC): |
Broker (nonprovisional) has: -completed all post licensing requirements -May except commissions directly from parties other than the BIC -May associate with multiple BICs (with the full knowledge and consent of all BICs) -May operate independently as the sole proprietor -may or may not qualify for being A BIC
Broker provisional status: -completed 75 hr approved coursework (or what commission deems equivalent) -passes state exam -background check submitted - initial license issued ***** must complete 90 hours of post license education within 3 years of license being issued to remove provisional status Can do all at once but a minimum of 1 course (30 hours) each year for 1st 3 years to be active status. Will be placed on inactive status until education requirements met. ****** must have a broker in charge to be on active status ****** must not except commissions from anyone except for the supervising broker in charge ****** must immediately convey all trust funds into the possession of the supervising BIC (e.g earnest $) ****** must complete eight hours of continuing education each license year (in addition to post licensing ed.) following the first license renewal date |
|
|
How does one become a BIC |
2 years full time experience actively engaged in brokerage and actively supervising other brokers |
|
|
License status: Current and expired relate to ——— Active and inactive relate to ——— |
Current and expired relate to money Active and inactive relate to education |
|
|
$——renewal fee to commission must be paid on/before —— (date) to remain current.
Continuing ed must be completed by —— (date) or will be placed on inactive status on —— |
$45 on/before June 30th or expired status on July 1st. 8 hrs continuing ed completed by June 10th or placed inactive on July 1st |
|
|
All name changes (personal or business) or address changes (personal or business) must be submitted in writing within — |
10 days of the change |
|
|
Criminal convictions (felonies or misdemeanors) or when another professional licensing board disciplines a broker this must be reported within–– days of final judgement |
60 days (must use NCREC report form) |
|
|
CE requirements begin for the 2nd license renewal and are —hours per year with —hrs being GENUP (general update) or BICUP (BIC update) plus —— hrs of an elective course |
8 hrs total, 4 general update and 4 elective. General update has to be in a classroom in person but the 4 hr elective can be online |
|
|
Inactive status: Automatic for provisional brokers who are not supervised by a BIC or who have not completed 90 hrs post lic. Ed. Can be requested in writing but still have to pay renewal fees each year. May have to complete max. Of 16 hrs CE and pay renewal fees (or meet edu. Requirements) plus late fee before reinstated |
See front of card |
|
|
License reinstatement If license is expired less than 6 months then..., |
May submit request to activate and pay renewal fee. If greater than 6 moths must file regular license application |
|
|
A license is issued on December 2nd. In what order are the educational and renewal requirements due. |
License renewal by June 30th, post licensing ed by dec 2nd and cont ed by the following June 10 |
|
|
What is the primary purpose of the North Carolina real estate commission? |
To protect the public in their dealings with real estate brokers |
|
|
What are the powers of the North Carolina real estate commission |
Licensing real estate brokers and firms *Registering timeshare projects Approving real estate schools & instructors Educating/ informing the public and brokers Regulating the real estate business activities of brokers |
|
|
How many board members are on the real estate commission and are requirements |
There are nine total At least three must be brokers and at least two must not be brokers or in any related field They each serve 3 year terms and each year a new chairperson is elected |
|
|
Real property defined |
Is immovable Includes the land, fixtures/improvements affixed to the land & rights/interests in the land. Transferred by deed |
|
|
Appurtenances |
Improvements, fixtures, rights and privileges that run with the land and transfer via deed |
|
|
Types of Land rights |
Surface, sub-surface, air rightd |
|
|
Types of Land rights |
Surface, sub-surface, air rightd |
|
|
Improvements |
Items attached to land with intent of being permanent (fence, road, house, landscaping) |
|
|
Types of Land rights |
Surface, sub-surface, air rights |
|
|
Improvements |
Items attached to land with intent of being permanent (fence, road, house, landscaping) |
|
|
3 forms of land rights |
Rights in land like air, water mineral rights Rights of ownership, such as right of owner to possess, transfer and control the property Government rights (land use, taxes, escheat, eminent domain) |
|
|
Air rights |
Rights extend as high as can reasonably be used Government controls airspace Others may not interfere |
|
|
Air rights |
Rights extend as high as can reasonably be used Government controls airspace Others may not interfere |
|
|
Water rights & doctrine of prior appropriation |
Doctrine of prior appropriation: The government controls water rights and grants permits for beneficial use of water such as irrigation. |
|
|
Riparian rights |
Flowing water (think R is for river). If navigable the property line is the edge of the water, if nonnavigable the property line is the center of the river or stream |
|
|
Riparian rights |
Flowing water (think R is for river). If navigable the property line is the edge of the water, if nonnavigable the property line is the center of the river or stream |
|
|
Littoral rights |
Non flowing or standing body of water. Think L for lake. The property line is the average high watermark |
|
|
Boundary shifts occur as a result of accretion, reliction, erosion and avulsion. Explain each |
Accretion: addition of land by gradual accumulation through natural causes Reliction: land required by receeding water Erosion: gradual wearing away of land Avulsion: sudden loss of land through being washed away or other violent acts ******Property line is maintained even if the land is no longer there |
|
|
Boundary shifts occur as a result of accretion, reliction, erosion and avulsion. Explain each |
Accretion: addition of land by gradual accumulation through natural causes Reliction: land required by receeding water Erosion: gradual wearing away of land Avulsion: sudden loss of land through being washed away or other violent acts ******Property line is maintained even if the land is no longer there |
|
|
If an owner has water rights would right of accessing the water be included? |
No! The owner does not have the right to cross another's property and would need to obtain an easement |
|
|
Rights of land support |
Owners of adjacent property cannot excavate their property in a way that will cause loss of support to another's property Lateral support is to the property sides by neighboring properties Subadjacent support of surface is from below |
|
|
Personal property or chattel |
Is movable, not permanently attached, typically does not transfer with real estate (must be included in the purchase offer to convey with the real property) and is transferred by a bill of sale |
|
|
Law of fixtures |
An object that was once personal property which has been attached to an improvement so as to become real estate (window unit, chandelier, Jacuzzi that is recessed into deck) once attached it becomes an appurtenances and automatically transfers in deed |
|
|
What do these terms mean (in regards to a rectangular/ government survey): Meridian and base lines Township Ranges Bases Section |
Meridians are large imaginary lines that run north to south Baselines large imaginary lines that run east to west
Township: square formed by meeting of ranges and tiers and each township is 6 miles by 6 miles (36 sq miles) Each section is 1 mile x 1 mile and contains 640 acres
Ranges are vertical rows of townships (north to south) Bases are Horizontal row of townships (east to west) |
|
|
Recorded map plat (Aka lot, block, subdivision, or lot and block system) |
A plat is a map showing the location and boundaries of individual lots in a land subdivision. Once the final approved map is complete and before building the plat is recorded in the county's recorders office.**** Recording a subdivision plat is a common way for streets and developments to become dedicated for public use |
|
|
Reference to a prior recorded deed can be used in North Carolina (uses a previously recorded deed as a reference for the property. Metes and bounds description would appear in the prior recorded deed though it might not appear in the new deed |
See front |
|
|
Survey and ILC (improvement location certificate) |
Onsite measurement of property lines and locations of houses, easements, encroachments, etc. both use monuments Survey more detailed than ILC Survey used to create/confirm legal description but ILC not used to set legal boundaries just improvements Both reveal encroachments & zoning violations (i.e. Setback requirements) |
|
|
Math facts: Sq foot formula Triangle area Volume or cubic feet ___cubic feet = 1 cubic yard 1 acre = _ feet 1 section or 1 mile = __acres |
Square/rectangle area or street footage: l x w Triangle area= 1/2 (b x h) Volume/cubic feet= l x w x h 27 cubic feet = 1 cubic yard 1 acre= 43560 feet 1 section/1 mile= 640 acres |
|
|
Purpose of government Master development plan (like land and economic surveys) |
Used to control growth |
|
|
Land use classifications |
Residential Commercial Industrial/ manufacturing Agricultural Mixed |
|
|
Buffer zone |
Area of land separating 2 significantly different land use zone. E.g., parks and open spaces used as buffer zones |
|
|
Purpose of land use restrictions tied to police power |
Protect against uncontrolled growth, protect public health and preserve compatibility |
|
|
Building permit |
The First step in new building and many renovations Building permit ensures that property owners are in compliance with building codes. the state sets minimal construction safety requirements and city or county codes baby more restrictive than the states. Which ever is stricter is the one that is used. Primarily concerned with structural integrity and Public Safety of buildings Set standard for types of materials and how they are used. There are separate codes for plumbing electrical fire etc. |
|
|
Total circumstances test for fixtures |
IRMA 1)Intent: was the object affixed or installed with the apparent intent of improving the land?
2)Relationship of the annexor (person attaching) to the property: if it was the owner then it is a fixture, if it was a tenant then personal property
3) Method of attachment (the permanence of method: if it was built-in it is a fixture;if it is freestanding it is personal property
4)Adaption: specific to the individual property such as house keys, garage door opener, landscaping, *****fructus naturales (natural growing vegetation requiring no annual cultivation) 5) Agreement: the written agreement regarding the item (e.g offer to purchase) creates the final decision about what is conveyed |
|
|
Certificate of occupancy |
Obtained after all requirements of the building permit are fulfilled and show that buildings are ready and fit for occupancy they provide evidence of compliance with building codes |
|
|
Zoning laws |
Set at a local level (city or county) Specifies type of construction allowed (like single-family, multi family or mixed-use) also specify style, height and types of construction.zoning laws also set setbacks required for improvements |
|
|
Illegal use, building codes, zoning violations do not become legal through passage of time/cannot be grandfathered in |
See front |
|
|
Spot zoning |
Possibly illegal because it is the practice of granting special zoning treatment to one or a group of properties that is inconsistent with the master plan surrounding uses |
|
|
Non-conforming use |
An Amendment is a zoning change for an entire area which can cause nonconforming use. It allows the owner to continue a present use that no longer complies with current zoning laws (grandfathered in)***** owner cannot enhance improvements or rebuild improvements if destroyed. Transfer of title may or may not require new owner to meet current zoning use |
|
|
Variance |
Allow individual owners to deviate from strict compliance with zoning in order to relieve or prevent economic hardship An example would be allowing a home to be built into a setback |
|
|
Conditional use or a special use permit |
Allows a particular property to be used for a special purpose that's in the public's best interest. for example a church or daycare in a residential zoning. So undue hardship not required |
|
|
PUD (planned unit devlp) & nc planned community act |
PUD's created after January 1, 1999 fall under the North Carolina planned community act. Gives association powers not available under the traditional subdivision form of development. These powers include: Power of covenants, restrictions, rules, and annual assessments. Power to fine, suspend use of common areas, liens and even foreclosure |
|
|
Cluster zoning |
Typical in a PUD. it utilizes flexible zoning to maximize open space in the project |
|
|
Overlay zoning |
Overlay zoning for exceptional or special uses are created at the city, county or regional level. School, tax or utility districts, airport or flight paths, cluster, aesthetic or historical preservation |
|
|
Trade fixtures, emblements or fructus industriales |
Trade fixtures: Tenant installed additions that are a necessary part of the tenants trade or business remains personal property, these items are to be removed before the lease termination or they will belong to the landlord emblements or fructus industrials (annually cultivated crops) are personal property Trade fixtures or emblements are transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Interstate land sales full disclosure act |
Federal law that regulates the sale or lease of 25 or more lots of unimproved land across state lines. The developer is required to provide a property report to buyers three days before excepting an offer. |
|
|
Restrictive covenants |
Not set by government (town or state) but by communities |
|
|
Disclosure by brokers regarding property |
Brokers should explain to the buyers that the buyer is responsible for verifying: zoning use and rules, that the property is not in a floodplain, that the property has proper access to and from highways and streets, That the building permits were pulled and completed if required, Street status of subdivisions, the access or lack of access to public roads or if access is changing |
|
|
How is property frontage always listed? |
Always listed 1st (w x l) so if a lot is 70' x 209' the street front footage is 70' |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Review |
|
|
When does a manufactured or mobile home become real property? When are modular homes considered real property? |
Mobile homes: Must be on land owned by the person who is placing the mobile home; must be attached to a permanent foundation; must have the hitch and axles removed; and must have a canceled DMV title *Mobile homes must meet HUD building requirements Modular housing: immediately considered real property once assembled on the lot and attached to the foundation *modular housing must meet State construction regulations |
|
|
Physical characteristics of land & Economic characteristics of land |
Physical characteristics: Immobile (can't be moved); Indestructable Unique
Economic characteristics: Scarcity (limited supply in area affects value) Improvements (placing improvements on a parcel of land affects the value and use of neighboring parcel's) Permanence of investment (Land is not a liquid asset!!!!Sale of a particular parcel may take considerable time) Area preference (people's preferences and desires for a given area make one site more desirable than another) |
|
|
Interstate land sales full disclosure act |
Federal law that regulates the sale or lease of 25 or more lots of unimproved land across state lines. The developer is required to provide a property report to buyers three days before accepting an offer. |
|
|
Legal descriptions do not describe improvements only the land (improvements are automatically included) street addresses can change and are not considered adequate legal descriptions to convey ownership ***but can be used in a lease |
See front |
|
|
Metes and bounds |
Most accurate method of land description and most used in North Carolina. Metes are measured in feet and compass degrees. Bounds is the shape, boundaries or directions. Monuments are fixed objects that can serve as a reference points. Must begin and end at POB (or point of beginning) Descriptions must completely enclose the property or are considered incomplete or imperfect. Metes and bounds are measured in a clockwise direction. is the only legal description that states "starting beginning or commencing at" the point of beginning |
|
|
Rectangular or government survey |
Developed by US government locates a parcel of land within a grid system based on its location with reference to meridians and ranges (which run north to south) and baselines & tiers (which run east to west) |
|
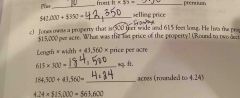
Front (Term) |
Review |
|
|
Police power |
Implements public control for land use for the protection , health and safety of the public
|
|
|
Police power and examples |
Right to enact and enforce laws governing land use ( for the protection , health and safety of the public) Examples: Zoning, property taxes and special assessments, immanent domain, escheat
|
|
|
Eminent Domain vs condemnation |
Eminent domain is the power of the government to take private land for public use and condemnation is the process that exercises the right. Eminent domain is an example of involuntary alienation. Compensation is fair market value plus damages. Tenants leases terminated by condemnation process |
|
|
Which type of liens always take priority |
Real property taxes (aka ad valorem taxes) they are specific liens |
|
|
Which type of liens always take priority |
Real property taxes (aka ad valorem taxes) they are specific liens |
|
|
How is tax bill calculated |
Assessed value X tax rate (mil rate) Mil rate is expressed as either dollars per hundred or per a thousand. A rate of $4 per $100 would be expressed .04, a rate of $4 per $1000 would be expressed .004 |
|
|
Example of calculating property tax |
What is the assessed value of a property with an actual value of 425,000 when the state sets the assessment rate at 29% 425,000 x .29 = 123,250 Now what is the annual tax on the same property with the mill rate of $50 per thousand 50/1000 = .05 so 123,250 x .05 = 6262.50 is prop tax |
|
|
Define special assessments and how are they often determined |
Special assessments are charges against specific properties that benefit from a public improvement (such as sidewalks or streetlights) Are often charged on a front footage basis If not paid they can create a specific lien with the right of foreclosure Though property tax liens have priority over special assessment liens the special assessment liens have priority over other liens |
|
|
Define special assessments and how are they often determined |
Special assessments are charges against specific properties that benefit from a public improvement (such as sidewalks or streetlights) Are often charged on a front footage basis If not paid they can create a specific lien with the right of foreclosure Though property tax liens have priority over special assessment liens the special assessment liens have priority over other liens |
|
|
Government's rights/powers defined by PETE |
Police power eminent domain taxation Escheat ****Escheat is when government takes property that has been abandoned or when an owner dies intestate (without will and no heirs) |
|
|
Estate 2 types: freehold vs leasehold (aka non freehold) |
Freehold estates are ownership for a lifetime or longer (an undetermined duration) Leasehold or non-freehold possession lasts less than a lifetime |
|
|
Estate 2 types: freehold vs leasehold (aka non freehold) |
Freehold estates are ownership for a lifetime or longer (an undetermined duration) Are inheritable and transferable Leasehold or non-freehold possession lasts less than a lifetime |
|
|
Types of freehold estates: Fee simple absolute
defeasible fee or qualified fee (2 types are fee simple determinable and fee simple subject to a condition subsequent)
conventional life estate
life estate for the life of another (pur autre vie) |
Fee simple absolute is the highest and most desirable form of ownership and you get the complete bundle of rights
defeasible fee or qualified fee estates are conditional There are 2 types: feesimple determinable (which is if the deed condition is violated property automatically reverts to grantor) then with fee simple subject to a condition subsequent (if deed condition is violated ownership may revert to grantor if action is taken) All 3 types above are transferable and inheritable |
|
|
Conventional life estate |
The life tenant (or grantee) is the owner. These estates cannot be willed and upon the death of the life tenant the estate reverts to the grantor or goes to the remainderman fee simple absolute. The life tenant may sell or lease the property but upon the death of the tenant the buyer or lessee's interest ends |
|
|
Conventional life estate |
The life tenant (or grantee) is the owner. These estates cannot be willed and upon the death of the life tenant the estate reverts to the grantor or goes to the remainderman fee simple absolute. The life tenant may sell or lease the property but upon the death of the tenant the buyer or lessee's interest ends |
|
|
Life estate for the life of another (pur surer vie) |
As long as someone else is alive the life tenant has ownership, if the life tenant dies first, the heirs of the life tenant inherit the property. ****so can be willed/ is inheritable (unlike the conventional life estate) Then upon the death of the person who has the measuring life, the estate goes back to the grantor or a remainderman fee simple |
|
|
Leasehold estates |
Tenant has the right to possess the leased property of the landlord Tenant holds a leasehold estate where as the landlord holds a leased fee is state and has a reversionary interest Amount of notice needed is set by lease terms or state law
|
|
|
Leasehold estates |
Tenant has the right to possess the leased property of the landlord Tenant holds a leasehold estate where as the landlord holds a leased fee is state and has a reversionary interest Amount of notice needed is set by lease terms or state law
|
|
|
Statute of frauds |
All transfers of an interest (either freehold or leasehold) in real estate must be in writing to be enforceable except a lease of less than three years |
|
|
Types of leasehold estates: Estate (tenancy) for years Periodic estate Estate (tenancy) at will Estate (tenancy) at sufferage |
Estate for years: there is a specific termination date, no advance notice required, the death of the lessor or lessee does not terminate the lease. The estate will pay the rent or I. The case of the sale of the property, the lease does not terminate until the lease is up
Periodic estate: renews automatically upon payment of rent. example is month-to-month. Can be terminated by advance notice of either party
Estate at will: indefinite duration, tenant occupies at the landlords discretion, lease terminated by notice or death
Estate at sufferance: holdover after legal tenancy expires. Owner can evict tenant or accept rent. if rent is accepted from tenant at sufferance the estate becomes a periodic estate |
|
|
Encumbrances and types |
An encumbrance is any claim, right, or interest held by a party who is not the legal owner of the property. Examples include easements, deed restrictions, and encroachments. Encumbrances may effect value or even may cloud the title |
|
|
Easements and types |
Easements are the right to use the lands of another for a specific purpose. Runs with the land (apurtanent) unless released and will transfer with the deed |
|
|
Easements and types |
Easements are the right to use the lands of another for a specific purpose. Runs with the land (apurtanent) unless released and will transfer with the deed |
|
|
Appurtenant easement |
Involves two properties or owners and includes a dominant estate and a subservient estate. Dominent estate is the property that gets the easement from the subservient estate. Easement transfers or "runs with the land". does not increase dominent estate's lot size but may increase its value |
|
|
Easements and types |
Easements are the right to use the lands of another for a specific purpose. Runs with the land (apurtanent) unless released and will transfer with the deed |
|
|
Appurtenant easement |
Benefits the land. Involves two properties or owners and includes a dominant estate and a subservient estate. Dominent estate is the property that gets the easement from the subservient estate. Easement transfers or "runs with the land". does not increase dominent estate's lot size but may increase its value |
|
|
Easement in gross |
It benefits an individual. may be personal or commercial |
|
|
Personal easement in gross |
Cannot be assigned or inherited. Continues until the holder either dies or releases the easement. If recorded would transfer to the buyer of the property until the original holder died) example would be if a property owner grants John the right to fish in his farm pond, once John dies the easement automatically terminates |
|
|
Commercial easement in gross |
Given to a business such as a railroad or utility company. The easement is lengthy or indefinitely. these easements may be a assigned,conveyed or inherited. example: utility co. has a 5 foot easement in the rear of the property to maintain and run powerlines |
|
|
Easement by necessity |
Granted by the court to a private owner to remedy land locked property only if there is no other access. Only available to private owners not public utilities or government |
|
|
How are easements created and how are they terminated? |
Created by agreement, prescription or necessity. Express easement agreement is an interest in real property and is transferred by deed and typically recorded. Not revocable once given
How terminated: Easements are terminated three ways: 1) merger: one property acquires the other property 2) release: the holder of the dominant interest releases his rights it then no longer transfers with deed 3)abandonment: this is not automatic. It happens over time & must be proven in court |
|
|
Deed restrictuons |
Privately created limitations that protect property values/interests -Binding restrictions for present and future property - they run with the land -Owners may be subject to injunction or monetary damages for violating -HOAs must go to court to obtain injunction -the restriction must be for lawful purposes (not restrict blacks for example) -the strictest rule zoning or date prevails |
|
|
Liens, lien classifications and how released |
Lien: A claim on land to secure payment of a debt by taking and selling property if not paid Types Voluntary vs involuntary specific vs general Specific liens attach to specific real or personal property. Examples is specific liens property taxes/assessment liens (involuntary) take priority over all others (1st prop tax, 2nd assessments) mechanics or construction lien (involuntary) contractor must have contract with the owner of the property. Tenant cannot obligate the landlord to a contractor for repairs. **Priority dates back to the delivery of materials. mortgage or deed of trust (voluntary) voluntary pledge of lands to secure payment of debt |
|
|
General liens and types |
Attached to an individual and impact all personal and real property owned -Judgment lien (involuntary): court ordered claim against an individual and all the individual owns like unpaid hospital bills and child support ***Life of a judgment in North Carolina is typically 10 years -IRS or State lien (involuntary) -personal property tax lien (involuntary) has priority over other non-tax liens |
|
|
General liens and types |
Attached to an individual and impact all personal and real property owned -Judgment lien (involuntary): court ordered claim against an individual and all the individual owns like unpaid hospital bills and child support ***Life of a judgment in North Carolina is typically 10 years -IRS or State lien (involuntary) -personal property tax lien (involuntary) has priority over other non-tax liens |
|
|
Writ of attachment |
Used to create an encumbrance against real property. created by court order until a lawsuit can be settled would be followed by a rid of execution to sell the property if needed to satisfy the judgment |
|
|
General liens and types |
Attached to an individual and impact all personal and real property owned -Judgment lien (involuntary): court ordered claim against an individual and all the individual owns like unpaid hospital bills and child support ***Life of a judgment in North Carolina is typically 10 years -IRS or State lien (involuntary) -personal property tax lien (involuntary) has priority over other non-tax liens |
|
|
Writ of attachment |
Used to create an encumbrance against real property. created by court order until a lawsuit can be settled would be followed by a rid of execution to sell the property if needed to satisfy the judgment |
|
|
Homestead rights |
Homestead exemption is created by state statute to protect a primary residence against creditors. Protects against judgments and debits for personal loans and credit cards but typically does not protect against mortgage liens or property tax liens North Carolina standard exemption is $35,000 which increases to $65,000 for homeowners older than 65 All states differ who may receive homestead rights and the value of the rights |
|
|
Encroachments |
Unauthorized use of another's land; physical object intruding onto neighboring property Any buyer that finds an encroachment before or after closing should consult an attorney as this may make title to both properties unmarketable. Survey or ILC will reveal encroachments |
|
|
Encroachments |
Unauthorized use of another's land; physical object intruding onto neighboring property Any buyer that finds an encroachment before or after closing should consult an attorney as this may make title to both properties unmarketable. Survey or ILC will reveal encroachments |
|
|
Licenses |
Revocable unassignable permission granting privilege to use a property usually granted to an individual. Example... Jon has license to fish on Jim's land as long as Jim does not wish to revoke license |
|
|
Estate in severalty |
1) Ownership is by an individual 2)Upon death goes to heirs or devisees (by Will) 3)a legal entity can own in severalty A syndication is 2 or more people or firms joining together as a single entity Examples are: corporation, partnership, trust, REIT (real estate investment trust) |
|
|
Estate in severalty |
1) Ownership is by an individual 2)Upon death goes to heirs or devisees (by Will) 3)a legal entity can own in severalty A syndication is 2 or more people or firms joining together as a single entity Examples are: corporation, partnership, trust, REIT (real estate investment trust) |
|
|
Forms of Concurrent or multiple ownership
concurrent ownership is two or more persons or entities that share ownership with undivided interests. Because their shares are fractional but undivided they have equal rights of possession. No co-owner has a right to any specific part of the property |
Tenancy in common No survivorship (interests go to heirs/devisees) individuals can sell or will their part. The default in most states is equal ownership unless specified in deed (but unequal shares is possible) Distribution subject to probate Joint tenancy has right of survivorship (if one dies the other gets the dead partners portion) Can sell but cannot will Always equal shares unless 1 sells out. ***If one owner sells, joint tenancy is broken and it becomes tenants in common. Not typically recognized in nc. Joint tenancy must be specified in deed. A partition lawsuit can divide property amount co-owners. No probate, overrides will, death certificate and joint tendency affidavit must be recorded. Tenancy by the entirety Form of ownership available exclusively to married couples in some states. The favored form of ownership in North Carolina. Each spouse owns equal, undivided interest, regardless of the financial contribution. There is the right of survivorship, if one spouse dies the surviving spouse become his owner in severalty. No probate, overrides a will. Is terminated by death, mutual agreement of husband and wife, and divorce *** 1 to buy and 2 to sell |
|
|
Types of common interest community ownership |
Condos, town homes, cooperatives, timeshares |
|
|
Do common interest communities have the right to levy mandatory assessments on its owners for the maintenance of common elements? |
YES |
|
|
Do common interest communities have the right to levy mandatory assessments on its owners for the maintenance of common elements? |
YES |
|
|
Condominium |
Real estate, portions of which are designated for separate ownership and the remainder of which is designated for common ownership of common elements. Can be commercial or residential. Owners own from paint to paint. Created by recording a declaration which describes the legal and physical structure along with any restrictions in use. Common elements are owned by all unit owners as tenants in common. A limited common element is any common element reserved for the use of one or more unit owners at exclusion of other owners. Examples: assigned parking spaces, storage units and balconies Each member of each unit is a member of the HOA (homeowners association) The HOA functions to: -manage common elements -set rules regulations & budgets -adopting/amending bylaws -collects assessments/dues (can create a specific lien on unit if dues unpaid) -holds annual meeting -maintains insurance on common elements (contents of units are not covered) separate title and taxation of each unit: **Deed transfers fee simple plus undivided interest in common elements **all unit owners share ownership of common elements as tenants in common **** seller is required to give buyer full disclosure including the declaration, bylaws, financial reports etc. |
|
|
Townhomes |
Horizontal units (row houses) the ownership includes the dirt under the unit Similar to the condo, has HOA However unlike with condos, common elements are not owned by unit owners but rather by the association owns the common elements (owned in severalty) |
|
|
Cooperative |
Building is owned by a corporation which is allows owners or stockholders occupancy. A cooperative corporation or tenants association owns the real estate. Buyers receive membership and association, shares of stock and a proprietary lease, which gives them right of possession but there is no deed and no ownership of units Stockholder/tenants pay assessments and association fees |
|
|
Time shares |
Purchasers buy interest in real estate and receive a right to use the property for certain periods of time. ** no set number of days or years required unless created by state law -Purchasers may own the land or the developer may own the land and contract for its use -purchasers of units own units as tenants in common with other purchasers Timeshares are most common for resort properties |
|
|
Time shares |
Purchasers buy interest in real estate and receive a right to use the property for certain periods of time. ** no set number of days or years required unless created by state law -Purchasers may own the land or the developer may own the land and contract for its use -purchasers of units own units as tenants in common with other purchasers Timeshares are most common for resort properties |
|
|
What are Advantages of business ownership for investment purposes (Corporation, LLC, partnership, general partnership, limited partnership, syndicate, REIT) |
Advantages of investment ownership by entities include: -separate legal identities for members limits liability -investment enhanced by individual strengths and talents -favorable tax regulation -consolidation of $ resources |
|
|
Corporation |
the legal entity is a company owned by shareholders but regarded under law as having an existence separate from the shareholders |
|
|
Corporation |
the legal entity is a company owned by shareholders but regarded under law as having an existence separate from the shareholders |
|
|
LLC (Limited liability company) |
LLC offers the following advantages: -limited liability tax advantages (no double taxation) - flexible management structure without corporation requirements or restrictions on limited partnership |
|
|
Corporation |
the legal entity is a company owned by shareholders but regarded under law as having an existence separate from the shareholders |
|
|
LLC (Limited liability company) |
LLC offers the following advantages: -limited liability tax advantages (no double taxation) - flexible management structure without corporation requirements or restrictions on limited partnership |
|
|
Partnership (general vs limited partnerships, syndicates and REIT) |
Association of 2 or more to carry out Business for profit as co-owners, some are formed for the main reason of owning real estate. General partnerships: all partners participate in operation and management, all partners have full liability for business losses and obligations Limited partnership: General partners run the business while limited partners do not participate in the running of the business and are liable for losses only up to the amount that they have invested Syndicate syndicate as a business venture in which participants pool resources to own or develop property REIT Real estate investment trust does not pay Corporate income tax as long as 95% of its income is distributed to shareholders |
|
|
Corporation |
the legal entity is a company owned by shareholders but regarded under law as having an existence separate from the shareholders |
|
|
LLC (Limited liability company) |
LLC offers the following advantages: -limited liability tax advantages (no double taxation) - flexible management structure without corporation requirements or restrictions on limited partnership |
|
|
Partnership (general vs limited partnerships, syndicates and REIT) |
Association of 2 or more to carry out Business for profit as co-owners, some are formed for the main reason of owning real estate. General partnerships: all partners participate in operation and management, all partners have full liability for business losses and obligations Limited partnership: General partners run the business while limited partners do not participate in the running of the business and are liable for losses only up to the amount that they have invested Syndicate syndicate as a business venture in which participants pool resources to own or develop property REIT Real estate investment trust does not pay Corporate income tax as long as 95% of its income is distributed to shareholders |
|
|
Alienation and 3 types of transferring title |
Alienation is the act of conveying real estate ownership/transferring title private grant is from individuals using a deed public grant is from government to individuals using land patent dedication is from individuals to the government |
|
|
Corporation |
the legal entity is a company owned by shareholders but regarded under law as having an existence separate from the shareholders |
|
|
LLC (Limited liability company) |
LLC offers the following advantages: -limited liability tax advantages (no double taxation) - flexible management structure without corporation requirements or restrictions on limited partnership |
|
|
Partnership (general vs limited partnerships, syndicates and REIT) |
Association of 2 or more to carry out Business for profit as co-owners, some are formed for the main reason of owning real estate. General partnerships: all partners participate in operation and management, all partners have full liability for business losses and obligations Limited partnership: General partners run the business while limited partners do not participate in the running of the business and are liable for losses only up to the amount that they have invested Syndicate syndicate as a business venture in which participants pool resources to own or develop property REIT Real estate investment trust does not pay Corporate income tax as long as 95% of its income is distributed to shareholders |
|
|
Alienation and 3 types of transferring title |
Alienation is the act of conveying real estate ownership/transferring title private grant is from individuals using a deed public grant is from government to individuals using land patent dedication is from individuals to the government |
|
|
7 essential elements of a valid Deed |
1) competent grantor (18, sane & sober) 2) identifiable grantee (buyer) (does not need to be competent) 3) words of conveyance/granting clause. Clause states that the seller is making a grant that conveys the warranties of the deed i.e.. what creates The difference between a general warranty in a quick claim deed ****Habendum clause (conveys a freehold estate) "to have and hold forever" conveys fee simple absolute ownership 4) legal description of property (describes only the land not apertinences which are presumed to transfer with the land) 5) consideration this can be money or anything of value "a dime, a dollar, a donut" 6) execution by the grantors (must be signed by all owners to convey the property) 7) delivery to an acceptance by the grantee (title passes upon acceptance by grantee) |
|
|
Corporation |
the legal entity is a company owned by shareholders but regarded under law as having an existence separate from the shareholders |
|
|
LLC (Limited liability company) |
LLC offers the following advantages: -limited liability tax advantages (no double taxation) - flexible management structure without corporation requirements or restrictions on limited partnership |
|
|
Partnership (general vs limited partnerships, syndicates and REIT) |
Association of 2 or more to carry out Business for profit as co-owners, some are formed for the main reason of owning real estate. General partnerships: all partners participate in operation and management, all partners have full liability for business losses and obligations Limited partnership: General partners run the business while limited partners do not participate in the running of the business and are liable for losses only up to the amount that they have invested Syndicate syndicate as a business venture in which participants pool resources to own or develop property REIT Real estate investment trust does not pay Corporate income tax as long as 95% of its income is distributed to shareholders |
|
|
Alienation and 3 types of transferring title |
Alienation is the act of conveying real estate ownership/transferring title private grant is from individuals using a deed public grant is from government to individuals using land patent dedication is from individuals to the government |
|
|
7 essential elements of a valid Deed |
1) competent grantor (18, sane & sober) 2) identifiable grantee (buyer) (does not need to be competent) 3) words of conveyance/granting clause. Clause states that the seller is making a grant that conveys the warranties of the deed i.e.. what creates The difference between a general warranty in a quick claim deed ****Habendum clause (conveys a freehold estate) "to have and hold forever" conveys fee simple absolute ownership 4) legal description of property (describes only the land not apertinences which are presumed to transfer with the land) 5) consideration this can be money or anything of value "a dime, a dollar, a donut" 6) execution by the grantors (must be signed by all owners to convey the property) 7) delivery to an acceptance by the grantee (title passes upon acceptance by grantee) |
|
|
Types of deeds (General warranty, special/limited, quitclaim, correction) |
General warranty deed Includes the most promises or covenants, greatest protection for the grantee. Contains five covenants and warranties of title: Covenant of Seisin (owner owns and has right to convey) Covenant of quiet enjoyment (Grantee will not be disturbed by others claiming an interest) Covenant against encumbrances (no unspecified encumbrances) Covenant of further assurance Cooperation in signing additional documents Warranty forever guarantee of defense of title against claims such as liens or easements Special/limited warranty deed Only warrants against defects or encumbrances arising during grantors ownership/there is no protection against previous claims. Frequently used by banks and municipalities to transfer title to foreclosed property Quit claim deed This date is best for the seller/grantor. No covenants or warranties "what I got you got" Used to clear clouds on title and to release interest in property such as a divorce settlement. Would use when grantor wants no future claims/liability Correction deed Used to make corrections such as errors in previous deeds like misspellings usually not used to release interest in property |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Testate versus intestate succession, to devise vs to bequest |
Testate: transfer by Will, intestate: there is no will. Determined by state laws of descent Devise refers to real estate transfered by deed Bequest refers to personal property transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Testate versus intestate succession, to devise vs to bequest |
Testate: transfer by Will, intestate: there is no will. Determined by state laws of descent Devise refers to real estate transfered by deed Bequest refers to personal property transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Adverse possession |
Ownership recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open (visible) continuous, exclusive (distinct), actual, notorious (hostile) possession of another's land for certain period Set by state law |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Testate versus intestate succession, to devise vs to bequest |
Testate: transfer by Will, intestate: there is no will. Determined by state laws of descent Devise refers to real estate transfered by deed Bequest refers to personal property transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Adverse possession |
Ownership recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open (visible) continuous, exclusive (distinct), actual, notorious (hostile) possession of another's land for certain period Set by state law |
|
|
Easement by prescription/prescriptive easement |
An easement recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open, continuous, exclusive actual, and notorious use of another's land for certain period Adverse possession =possession prescriptive easement = use |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Testate versus intestate succession, to devise vs to bequest |
Testate: transfer by Will, intestate: there is no will. Determined by state laws of descent Devise refers to real estate transfered by deed Bequest refers to personal property transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Adverse possession |
Ownership recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open (visible) continuous, exclusive (distinct), actual, notorious (hostile) possession of another's land for certain period Set by state law |
|
|
Easement by prescription/prescriptive easement |
An easement recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open, continuous, exclusive actual, and notorious use of another's land for certain period Adverse possession =possession prescriptive easement = use |
|
|
If all parties know and agree to the possession or use of land can it be adverse possession or prescriptive easement? |
NO! A quiet title suit is typically used to grant title by a party claiming ownership through adverse possession. Must show the possessor met all the criteria of (ocean) in particular position that was continuous for the amount of time required **** then North Carolina it is 20 years required for both adverse possession an easement by prescription |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Testate versus intestate succession, to devise vs to bequest |
Testate: transfer by Will, intestate: there is no will. Determined by state laws of descent Devise refers to real estate transfered by deed Bequest refers to personal property transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Adverse possession |
Ownership recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open (visible) continuous, exclusive (distinct), actual, notorious (hostile) possession of another's land for certain period Set by state law |
|
|
Easement by prescription/prescriptive easement |
An easement recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open, continuous, exclusive actual, and notorious use of another's land for certain period Adverse possession =possession prescriptive easement = use |
|
|
If all parties know and agree to the possession or use of land can it be adverse possession or prescriptive easement? |
NO! A quiet title suit is typically used to grant title by a party claiming ownership through adverse possession. Must show the possessor met all the criteria of (ocean) in particular position that was continuous for the amount of time required **** then North Carolina it is 20 years required for both adverse possession an easement by prescription |
|
|
Sellers disclosure statement |
All states have an option for a sellers property disclosure In North Carolina it is a specific form Disclosure covers land/soil & environ'tl issues structural issues condition of fixtures lot size, encroachments & easements All material defects tax liens or special assessments **** sellers never brokers complete the disclosure to the best of their current knowledge |
|
|
Other types of deeds |
Bargain and sale deed no warranties against liens or encumbrances but does want the grantors right to come by tile Trustees deed/sheriffs deed/certificate to sell transfer the title at the end of a foreclosure proceeding or statutory redemption. Reconveyance deed used wgrn botrower pays off the loan secured by a deed of trust Nc special purpose deeds: Timber deed, mineral deed, tax deed (given at tax foreclosure sale) deed of gift **** must be recorded within two years or it is void |
|
|
Testate versus intestate succession, to devise vs to bequest |
Testate: transfer by Will, intestate: there is no will. Determined by state laws of descent Devise refers to real estate transfered by deed Bequest refers to personal property transferred by bill of sale |
|
|
Adverse possession |
Ownership recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open (visible) continuous, exclusive (distinct), actual, notorious (hostile) possession of another's land for certain period Set by state law |
|
|
Easement by prescription/prescriptive easement |
An easement recognized by the courts after (OCEAN) open, continuous, exclusive actual, and notorious use of another's land for certain period Adverse possession =possession prescriptive easement = use |
|
|
If all parties know and agree to the possession or use of land can it be adverse possession or prescriptive easement? |
NO! A quiet title suit is typically used to grant title by a party claiming ownership through adverse possession. Must show the possessor met all the criteria of (ocean) in particular position that was continuous for the amount of time required **** then North Carolina it is 20 years required for both adverse possession an easement by prescription **** A group of people may use tacking to gain a prescriptive easement or adverse possession, this allows the adding together of successive periods of use or possession by more than one person to meet the statutory period required |
|
|
Sellers disclosure statement |
All states have an option for a sellers property disclosure In North Carolina it is a specific form Disclosure covers land/soil & environ'tl issues structural issues condition of fixtures lot size, encroachments & easements All material defects tax liens or special assessments **** sellers never brokers complete the disclosure to the best of their current knowledge |
|
|
Material fact/defect vs latent defect |
A material fact or defect is one that if known might change a decision A latent defect is a hidden fact that is not easily discovered by inspection *** buyer should receive the disclosure before or shortly after making an offer **Buyers may be able to resend the contract if they can prove the seller or broker knew and did not disclose the material defect **Most states require a broker to do a visual inspection of the property **Brokers if aware must share defect must be immediately disclosed upon discovery to all parties of the transaction ** brokers should recommend that buyers have a property inspection |

