![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is acute leukemia?
|
Disease of leukocytes and precursors causing immature and abnormal cells
|
|
|
Where are immature and abnormal leukocytes found in acute leukemia?
|
Bone marrow
Peripheral blood Liver Spleen Lymph nodes |
|
|
What causes acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Accumulation of lymphoblasts in the bone marrow
|
|
|
What are the levels of FAB (French American British) classification for lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
L1
L2 L3 |
|
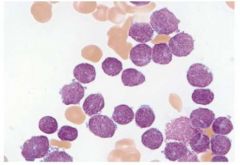
What stage in the FAB (French American British) classification system is this lymphoblastic leukemia slide and what are the characteristics that assign it to this stage?
|
L1:
- Fine chromatin - Small nucleoli - Uniform in size - Little cytoplasm |
|
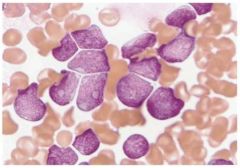
What stage in the FAB (French American British) classification system is this lymphoblastic leukemia slide and what are the characteristics that assign it to this stage?
|
L2:
- Variation in nuclear size - Prominent nucleoli - More cytoplasm |
|
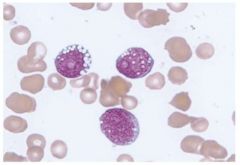
What stage in the FAB (French American British) classification system is this lymphoblastic leukemia slide and what are the characteristics that assign it to this stage?
|
L3:
- Mature chromatin with clumping - Multiple nucleoli - Basophilic and vacuolated cytoplasm |
|
|
What is the current system of classification for lymphoblastic leukemia and by what mechanisms is this done?
|
Cell of origin:
- Type of cell of origin via immunophenotype - Cytogenics - Molecular testing |
|
|
What are the two major mechanisms of oncogenesis?
|
Loss of function of tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes from proto-oncogenes |
|
|
What are some genetic factors that are linked to the incidence of lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Down's syndrome
Bone marrow stimulation Chromosomal breaks Immune dysfunction |
|
|
What are some environmental factors that are linked to the incidence of lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Chemicals
Drugs Radiation Infection |
|
|
What are the two major types of cellular pathways in which mutations must occur in order for lymphoblastic leukemia to occur?
|
Mutation in proliferation and survival (giving advantage)
Mutation in differentiation (impairing differentiation) |
|
|
What are the three classifications of acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Pre-B cell
B cell T cell |
|
|
What are the three most important B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia gene mutations and what do they do for the cell?
|
t(12;21) Tel/AML1
- Increased proliferation t(9;22) BCR-ABL1 - Increased proliferation and survival t(4;11) AF4/MLL - Increased proliferation |
|
|
What is the most frequently mutated tumor suppressor gene in human cancer?
|
p53
|
|
|
How does incidence of acute lymphoblastic leukemia change with age?
|
Decreases with age
|
|
|
What is the peak of incidence for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
2-3 years
(secondary peak after 40) |
|
|
What are clinical symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Bone marrow failure
Organ infiltration |
|
|
What are hematogenous consequences of bone marrow failure?
|
Anemia
Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
What common sites of organ infiltration seen in acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Lymphadenopathy
Bone marrow enlargement Medaistinal masses CNS infiltration Testicular enlargement |
|
|
What are the diagnostic tests commonly performed for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
CBC
Blood smear Bone marrow aspirate CSF sampling Chest X-ray |
|
|
What are diagnostic features of a CBC for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Increased WBC
Decreased Hgb Decreased platelets |
|
|
What is required for a diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia from a bone marrow aspirate?
|
Hypercellular bone marrow with >20% blasts
|
|
|
What are the qualifications for hyperdiploidy and hypodiploidy and how do these conditions affect prognosis?
|
Hyperdiploidy:
- > 50 chromosomes - Good prognosis Hypodiploidy: - <44 chromosomes - Poor prognosis |
|
|
What are common clinical presentations seen with T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
|
Increased WBC
Pleural effusion Mediastinal masses |
|
|
What is the most common pathway that is activated in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
NOTCH pathway
|
|
|
What are the most common genes that are involved in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
TCR genes
|
|
|
When is acute lymphoblastic leukemia considered to be in remission?
|
<5% blasts in bone marrow
Normal peripheral blood count No symptoms or signs of disease |
|
|
What constitutes general supportive therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Central venous line
Blood product support Prevention of tumor lysis syndrome Treatment of infection with prophylactic antibiotics |
|
|
What are consequences of tumor lysis syndrome?
|
Increased uric acid
Increased potassium Increased phosphate Renal failure |
|
|
What are the phases of treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
1. General supportive therapy throughout
2. Remission induction 3. Intensification / Consolidation 4. CNS directed therapy 5. Maintenance and continuation |
|
|
What is the goal of the remission induction phase for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Rapidly kill most leukemia cells
|
|
|
What is the goal of the intensification / consolidation phase of treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Reduce tumor burden to very low levels
|
|
|
What are ways by which CNS directed therapy is administered for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Administer chemotherapy directly into CSF
Cranial radiation (high chance of CNS defects) High dose chemotherapy |
|
|
What are some factors involved with maintenance and continuation of treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Daily oral
Weekly injection Steroid pulses for 5 days / month |
|
|
What is minimal residual disease (MRD) in acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Presence of a small number of tumor cells even in complete remission
|
|
|
What is the optimal cutoff for minimal residual disease (MRD) in acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
.01%
|
|
|
What is the cure rate of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children?
|
85%
|
|
|
What is the difference between good risk patients and poor risk patients in acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Good risk patients are subjected to less intensive treatment
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of relapse for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Sanctuary sites
Leukemic cells remain in G0 Primary resistance Secondary resistance after frontline treatment |
|
|
What are the types of relapse seen in acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
|
Isolated bone marrow relapse
Combined relapse Isolated extramedullary relapse |

