![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|
|
vvomen with lupus should be screened for
|

|
|
|
q
|

|
|
|
drugs associated with lupus induced SLe
clinical pictures |

|
|
|
what is sensitive marker for drug induced lupus
what drug is exception |

|
|
|
w
|

|
|
|
what is common in pregnant women with SLE
what is the reason for spont abortons in lupus how to tx the placental infarction due to LUPUS what to use during the flares of lupus |

|
|
|
how to screen women with lupus and pregnancy
|

|
|
|
A35-year-old woman is brought for the evaluation of confusion for a day. Her
friends and family inform you that "she did not know how tocome home from work" and that lately "she has not been herself." You find that the patient has elevated blood pressure, decreased air entry on the right lung base with dullness topercussion, and symmetrical joint swelling ofthe wrists and MCPs. Achemistry profile shows an elevated creatinine of 2.4 mgfdl, and there is protein in the urine on the urinalysis. |
Definition. SLEis a systemic disease in which tissues and multiple organs are damaged by
pathogenic autoantibodies and immune complexes |
|
|
Etiology/Pathogenesis
SLEi |
Etiology/Pathogenesis
SLEis of unknown etiology. • Ninety percent of cases are women. • The abnormal immune response probably depends on interactions between a susceptible host and environmental factors. Ultraviolet (UV)-B light is the only environmental factor known to cause flares |
|
|
Presentation. Diagnostic criteria-need four to diagnose.
|
Presentation. Diagnostic criteria-need four to diagnose.
Malar rash Discoid rash Photosensitivity Oral ulcers Arthritis Serositis (pleuritis or pericarditis) Renal involvement Neurologic disorder (seizures or psychosis) Hematologic disorder (hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) Immunologic disorder (anti-ds DNA, anti-SM, and other ANAs) |
|
|
Summary of Criteria
|
Summary of Criteria
• Arthritis is identical to that of RA except that it is non-erosive. • Both the malarrash and photosensitivity rash (diffuse, maculopapular) flare with exposure to UV-Blight (thus are considered photosensitive) and resolve with no scarring of the skin. The discoid lupus (DLE) is a circular rash with a raised rim that occurs over the scalp and face; it can be disfiguring because of central atrophy and scarring. Only5% of patientswith DLBwillgoon to develop SLB. • All patients with renal involvement must undergo renal biopsy before treatment is initiated. • Change of personality and psychosis may be manifestations of eNS lupus. • Libman-Sacks endocarditis is a noninfectious endocarditis that is rarely seen in lupus patients. |
|
|
Diagnosis
|
Diagnosis
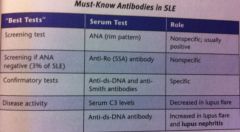
The best screening test for SLEis _ A positive ANAsupports the diagnosis but is not specific for SLE. The and are specific antibodies for lupus (these occur only with lupus so if found, think lupus only). Complement levels (C3, C4, or the more sensitive CH50) are in patients with active lupus. Elevated levels of ds- dNA antibodies are seen with active lupus. Know that the ds-DNA antibodies when positive are very specific for the diagnosis of lupus; they also increase the likelihood of |
|
|
Treatment
|
Treatment. Since there is no cure for SLE, treatment is aimed at controlling symptoms.
NSAIOs are used to treat arthritis and pleurisy. Corticosteroid creams are used to treat skin rashes. Antimalaria drugs (hydroxychloroquine) and oral corticosteroids may also be used for skin and arthritic symptoms. Cytotoxic drugs (azathioprine, cyclophosphamide) are used with severe symptoms (lupus nephritis, heart and lung involvement, hemolytic anemia, central nervous system involvement, etc.), along with corticosteroids. All patients should be advised to wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen when in the sun. |
|
|
Prognosis
|
Prognosis. The prognosis of patients with SLEhas improved significantly in recent years with
a IO-year survival rate greater than 85% People with severe involvement of the CNS, kidney, heart, and lungs have a worse prognosis in terms of overall survival and disability Lupus nephritis is probably the most common cause overall of disability in patients with SLE. |
|
|
s
|

|
|
|
x
|

|
|
|
f
|
|

