![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Q001. (3) causes of viral Esophagitis
|
A001. HSV; VZV; CMV
|
|
|
Q002. (5)* causes of Bacterial Esophagitis
|
A002. My Pnew Strep Lacts Crypt:; Mycobacterium TB;; Pneumocystis Carnii;; Strep;; Lactobacillus;; Cryptospordium
|
|
|
Q003. *When is a Barium Esophagram the best initial test?; when is it the most accurate?; (3)
|
A003. Dysphasia (that shows no signs of obstruction...for obstruction it would be Upper Endoscopy); most accurate:; 1. Esoph Webs; 2. Esoph Rings; 3. Esoph Diverticuli
|
|
|
Q004. Dx: Odynophagia (pain with swallowing), dysphagia, esophageal bleeding, N/V, chest pain, (or asymptomatic)
|
A004. Infectious Esophagitis
|
|
|
Q005. Dx: Infectious esophagitis with nodular filling defects on barium esophagram; Tx?
|
A005. Candida; Tx: Fluconazole PO
|
|
|
Q006. Causes: Infectious esophagitis with vesicles and descrete erosions on endoscopy; (2); Tx?
|
A006. HSV or VZV; Tx: Acyclovir for HSV
|
|
|
Q007. Dx: Infectious esophagitis with intranuclear inclusions on biopsy via endoscopy; Tx?
|
A007. CMV; Tx: Ganciclovir IV
|
|
|
Q008. Who should upper endoscopy screening be offered to?; (2)
|
A008. 1. Patients with GERD and Symptom for > 5 years (to check for Barrett's esophagus); 2. Patients with Esophageal varices
|
|
|
Q009. Dx: A Full-thickness tear usu in the weak left posterolateral wall of distal esophagus; (3) causes?
|
A009. Boerhaave's Syndrome; Causes:; Forceful vomiting;; Cough;; Trauma
|
|
|
Q010. Dx: A Partial-thickness tear usu in the right posterolateral wall of the distal esophagus and results in bleeding that resolves spontaneously; Cause?
|
A010. Mallory-Weiss syndrome; Cause: Forceful vomiting
|
|
|
Q011. medical Tx for non-bleeding Esophageal Varices
|
A011. Propranolol
|
|
|
Q012. What is the next step in the Tx of a patient with GERD that has persistent Symptom after 4 weeks of Tx with a PPI?
|
A012. 24-hour Esophageal pH recording
|
|
|
Q013. If patient has mediastinal and subcutaneous emphysema, what esophageal problem do they have?
|
A013. Full-thickness tear; (Boerhaave's syndrome)
|
|
|
Q014. Dx sign: "Crunching sound" heard with heartbeat; what is it due to?
|
A014. "Hammon's crunch" (Mediastinal emphysema); From: Full-thickness esophageal tear (Boerhaave's syndrome)
|
|
|
Q015. *What is the Diagnostic test of choice for Boerhaave's syndrome or a partial esophageal perforation?; What is the most accurate test?
|
A015. Dx test: Gastrograffin (water-soluble contrast); most accurate: CT scan
|
|
|
Q016. Tx for esophageal tear; (1 for each type)
|
A016. Partial-thickness (Mallory-Weiss): may resolve spontaneously; Full-thickness (Boerhaave's): Surgery
|
|
|
Q017. Definition: Pharyngeal or esophageal pouch due to a defect in the muscular wall of the posterior hypopharynx
|
A017. Zenker's Diverticulum
|
|
|
Q018. Dx: Halitosis, regurgitation of food after eating it, frequent aspiration, esophageal obstruction
|
A018. Zenker's Diverticulum
|
|
|
Q019. Dx test for Zenker's Diverticulosis; (2 possible); Tx (2 possible)
|
A019. Tests: Barium swallow;; Endoscopy; Tx:; Surgical removal;; Cricopharyngeal myotomy
|
|
|
Q020. Dx: 56-yo man complains of food feeling "stuck" on its way down and vomiting food he ate days ago
|
A020. Zenker's Diverticulum
|
|
|
Q021. Definition: Neurogenic disorder of esophageal motility with absence of normal peristalsis and impaired relaxation of the LES
|
A021. Achalasia
|
|
|
Q022. Definition: Esophageal motility disorder with frequent non- peristaltic contractions
|
A022. Diffuse Esophageal Spasms; (DES)
|
|
|
Q023. What esophageal problem affects 70% of people with Scleroderma?
|
A023. Achalasia
|
|
|
Q024. What type of problem does dysphagia to solids and liquids indicate?; (2 examples); To just solids?; (3 examples)
|
A024. Solids + Liquids: Motility problem (Achalasia; DES); Solids only: Mechanical problem (Tumor; Schatzki's ring; Plummer-Vinson syndrome)
|
|
|
Q025. Dx: weight loss, cough, dysphagia of both solids and liquids, "bird's beak" on CXR; Tx options?; (2 drugs and 2 procedures)
|
A025. Achalasia; Tx options:; Nitroglycerin;; Local Botulinum toxin;; Balloon Dialation;; Sphinctor Myotomy
|
|
|
Q026. Dysphagia to both solids and liquids, diffuse chest pain, "corkscrew" appearance on CXR; DES Drug Tx options? (2 possible)
|
A026. Diffuse Esophageal Spasms (DES); Tx options:; 1. Nitroglycerin;; 2. Anticholinergics
|
|
|
Q027. When is an Esophageal Manometry the test of choice?; (2)
|
A027. 1. an Inconclusive Barium or upper endoscopy; 2. Description of a Motility problem (Achalasia, DES, Nutcracker esophagus)
|
|
|
Q028. Etiology of Achalasia; (2)
|
A028. Scarring of Auerbach's plexus from: Chagas Disease; or Ganglionic degeneration
|
|
|
Q029. Definition: Hypopharyngeal webs (thin mucosal structures protruding into lumen of the esophagus) associated with iron deficiency anemia
|
A029. Plummer-Vinson Syndrome
|
|
|
Q030. Definition: Narrow lower esophageal ringlike outgrowth associated with dysphagia
|
A030. Schatzki's Ring
|
|
|
Q031. Etiology of GERD; (4)*
|
A031. HIDE:; Hiatal hernia;; Incompetent LES tone; Delayed Gastric emptying;; Esopageal motility decreased
|
|
|
Q032. (5)* causes of Delayed Gastric Emptying
|
A032. Delayed Food GAG: DM;; Fatty foods;; Gastroparesis;; Anticholinergics;; Gastric outlet obstruction
|
|
|
Q033. (8)* causes of a decreased LES tone
|
A033. Coffee CAN Cause Esophageal Sphinctor Problems:; Coffee;; Chocolate;; Alcohol;; Nitrates;; Calcium channel blockers;; Estrogen;; Smoking;; Progesterone
|
|
|
Q034. Differential of Chronic Cough; (3)*
|
A034. GAP in breathing:; GERD;; Asthma / Chronic Bronchitis;; Post-nasal drip
|
|
|
Q035. Dx: Substernal chest pain, dysphagia, hypersalivation, cough, wheezing
|
A035. GERD
|
|
|
Q036. What (3) lifestyle modifications should be told to patients with GERD?
|
A036. Discontinue foods that lower LES tone;; Elevate head of bed;; No food < 3 hours before bed
|
|
|
Q037. (2) drug Tx options for GERD; What can be done if medication doesn't work?
|
A037. Proton Pump Inhibitor (1st);; H-2 Blocker; Final solution: Surgical fundoplication
|
|
|
Q038. Definition: Esophageal damage, bleeding and friability due to prolonged exposure to gastric contents
|
A038. Esophagitis
|
|
|
Q039. (4)* complications of GERD
|
A039. BEEP:; Barrett's Esophagus;; Esophagitis;; Esophageal cancer;; Peptic stricture
|
|
|
Q040. (2) types of esophageal cancers and where each is formed in esophagus
|
A040. Squamous: Upper 2/3 of esophagus; Adenocarcinoma: Lower 1/3 of esophagus
|
|
|
Q041. Risk factors for CA of the esophagus; (7)*
|
A041. ABCDEF:; Alcohol;; Barrett's esophagus;; Cigarettes;; Diverticuli (Zenker's);; Esophageal web (P-V synd), Esophagitis (reflux or irritants);; Familial
|
|
|
Q042. What causes Barrett's?; What can it become?; How often should a patient with Barrett's have an upper endoscopy?
|
A042. BARRett's: Becomes Adenocarcinoma, Results from Reflux; UE: Barrett's: every 2 - 3 years
|
|

|
ggg
|
|

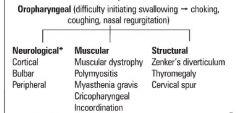
what types
|

|
|

what types
|
|
|

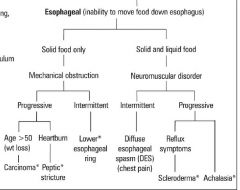
what type
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
odinophagia
|

|
|
|
d/d of dysphagia
|

|
|
|
key questions in dysphagia
|

|
|
|
odinophagia
|

|
|

ds
|

|

