![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of Cerebral Oedema |
Vasogenic (↑ cap permeability): trauma, tumour, ischaemia, infection Cytotoxic: e.g. from hypoxia Interstitial: e.g. obstructive hydrocephalus, ↓Na+ |
|
|
Causes |
Haemorrhage Tumours Infection: meningitis, encephalitis, abscess Hydrocephalus Status Cerebral oedema |
|
|
Signs and Symptoms |
Headache n/v Seizures Drowsiness → coma Cushing’s reflex: ↑BP, ↓HR, irregular breathing 6th CN palsy (may be false localising) Cheyne-Stokes respiration Pupils: constriction → dilatation Papilloedema, loss of venous pulsation @ disc |
|
|
Herniation SyndromesTonsillar (Coning) |
↑ pressure in posterior fossa → displacement of cerebellar tonsils through foramen magnum → compression of brainstem and cardioresp centres in medulla CN6 palsy, upgoing plantars → irregular breathing → apnoea |
|
|
Transtentorial / Uncal |
Lateral supratentorial mass → compression of ipsilateral inferomedial temporal lobe (uncus) against free margin oftentorium cerebelli. Ipsilateral CN3 palsy: mydriasis (dilation) then down-and-out Ipsilateral corticospinal tract: contralateral hemiparesis May → compression of contralateral corticospinal tracts → ipsilateral hemiparesis (Kernohan’s Notch: False Localising) |
|
|
Subfalcine |
Frontal mass Displacement of cingulate gyrus (medial frontal lobe) under falx cerebri Compression of ACA → stroke Contralateral motor/sensory loss in legs>arms Abulia (pathological laziness) |
|
|
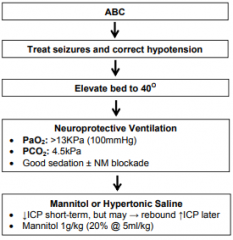
Acute Management |
|

