![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Hypophosphatasia.
|
|

|
Hypophosphatasia:
Mandible and maxilla - generalized radiolucency, cortex thin, alveolus deficient Lamina dura thin The deciduous teeth (usually anterior) shed early. enamel cap thin and/or hypoplastic. Large pulp chambers and root canals large. |
|
|
Renal Osteodystrophy:
- radiographic appearance: long bones, erosion of cortex -Calvarium: Granular density -Mandible and maxilla - generalized density |
|

|
Renal Osteodystrophy:
- radiographic appearance: long bones, erosion of cortex -Calvarium: Granular density -Mandible and maxilla - generalized density |
|

|
Renal Osteodystrophy
|
|

|
Renal Osteodystrophy:
- This panoramic image reveals areas of radiolucency corresponding to loss of bone mass, loss of distinct lamina dura, and a sclerotic bone pattern around the roots of the teeth. |
|

|
Renal Osteodystrophy: This panoramic image reveals a diffuse sclerotic (radiopaque) bone pattern throughout the jaws. Note the loss of a distinct inferior cortex of the mandible resulting from an increase in radiopacity of the internal aspect of the aspect of the bone.
|
|

|
Simple Rickets:
- Mandible deformed - Cyrpts of teeth and lamina dura attenuated -Hypoplasia of enamel -Delayed eruption and eruption in usual order |
|

|
Hypophosphatemia:
- low level of phosphorus in the blood - Refractory to treatment, resultant rickets severe - Pronounced interglobular dentin Cause: - High renal clearance of phosphate - Results in osteoporotic bone |
|

|
Hypophosphatemia:
- Bone very porotic - Lamina dura absent or attenuated - Crypts thin - Premature loss of teeth - enamel caps thin - Pulp canals wide |
|
|
|
Hypophosphatemia:
- Bone very porotic - Lamina dura absent or attenuated - Crypts thin - Premature loss of teeth - enamel caps thin - Pulp canals wide |
|

|
???
|
|

|
Letter Siwe Disease
- The skull shows multiple areas of radiolucency with irregular outlines - there is saucer-shaped destruction of alveolar process -The teeth become unsupported by bone. - There are multiple lesions. |
|

|
Eosinophilic Granuloma:
- usually in adolescents and young adults - prognosis is good - A radiolucency with an irregular outline (similar to malignancy) in the body of the bone, and sometimes in the alveolus - lesion is usually single - a depositio nof periosteal new bone, usually in the form of a thin line. |
|

|
Hyperadrenalism: Cushing's Syndrome
- many distinctive clinical changes - Radiographic Appearance: generalized osteoporosis - loss of the lamina dura in isolated areas |
|

|
Hyperparathyroidism:
The radiographic signs may precede the clinical signs. Radiographic Appearance: There can be generalized and localized manifestations. |
|

|
Hyperparathyroidism: Example of a Brown Tumor
|
|

|
Hypeparathyroidism:
- The skull shows areas of radiopacity in the region of the basal ganglion. - Increased density of radiopacity in the mandible and maxilla. Rarely there is increased radiolucency. - Hypoplasia of the enamel - Late eruption - Dilaceration - Muliple External Resorption - "Beaten Silver" appearance in Calvarium |
|

|
Hypothyroidism:
Fontanelles late closing Wormian bones General Osteoporosis Mandible and maxilla small Thinning of lamina dura delayed eruption short roots |
|

|
Acromegaly:
- An example of acromegaly manifesting as excessive growth of the mandible, resulting in a Class III skeletal relationship of the jaws. - A portion of a lateral skull view of the same patient demonstrating enlargement of the sella turcica. |
|

|
Agranulocytsis: osteoporotic pattern in bone, granular pattern in bone, loss of lamina dura,slight loss of bone outside the lamina dura.
|
|

|
Sickle Cell Anemia:
* Children seldom affected * Skeleton affected more than the jaws * Skull thickens |
|

|
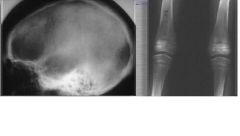
Sickle Cell Anemia
- "Hair-end-end" calvarium - Mandible and maxilla large bone marrow spaces - Vertebrae narrow biconcave - Long bones show osteoporosis, periosteal new bone, and areas of sclerosis |
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia
|
|

|
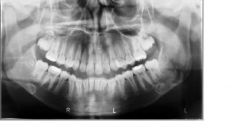
Thalessemia:
- Distinctive radiographic signs: the marrow spaces are larger than in other anemias |
|

|
Thalassemia Radiographic Appearance of the skull:
- very thick, especially in frontal region - inner plate clearly defined - granular pattern - rarely striation in calvarium (hair-on-end) - Maxillary sinuses small |
|

|
Thalassemia
- Premaxilla is prominent - large bone marrow spaces - trabeculae large and coarse - usually overall porosity - Cortex is thin, especially in the region of the angle - lamina dura thin - crypts thin and separated from teeth SOMETIMES THE ROOTS ARE SHORT. |
|

|
Radiographic Appearance of the skull:
- very thick, especially in frontal region - inner plate clearly defined - granular pattern - rarely striation in calvarium (hair-on-end) - Maxillary sinuses small |
|

|
Lymphoma
-Osteolytic Lesions - Diffuse Radiolucency in the alveolar bone |
|

|
Lymphoma CT Appearance.
|
|

|
Multiple Myeloma:
- multiple punched-out radiolucencies - widely disseminated throughout the skeleton - occasionally vertical bone deposition will occur producing a "sunburst" pattern |
|

|
Metastatic Diseases of the Jaw
|
|

|
CBCT Signs of Osteoporosis
- Thinned cortical borders - "Pitting" of cortical bone - Sparse trabecular bone |
|

|
Progressive Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
Generalized connective tissue disease Radiographic Appearance: - Widened PDL - Usually bilateral - Differentiated from osteosarcoma by the uniformity of the widening and the fact that it can be bilateral in scleroderma |

