![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
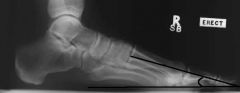
1st Met Declination Angle
Normal: 20-30 degrees -Angle between first metatarsal axis and plane of support |
|
|
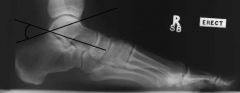
Boehlers Angle
Normal: 28-40 degrees - angle always taken with calcaneal fractures and indicates relative declination of the posterior facet |
|
|
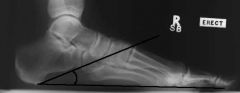
Calcaneal Inclination Angle
Normal: 18-22 degrees -Angle decreases with pronation |
|
|
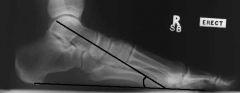
Talar Declination Angle
Normal: 21 degrees, increases with increased pronation |
|
|
What is the talar axis, how is it drawn?
|
line joining bisection of distal regular neck and proximal regular neck of talus
|
|
|
Talar declination angle
|
Norm: 21°
Angle formed by collum tali axis and plane of support. Angle increase with pronation. |
|
|
Plane of support
|
Formed by a line joining the plantar most aspect of the plantar calcaneal tuberosity to the most plantar aspect of the head of the fifth metatarsal
|
|
|
Calcaneal inclination axis
|
Formed by a line joining the most plantar aspect of the calcaneal tuberosity and the most distal plantar aspect of the calcaneus
|
|
|
First metatarsal axis
|
Formed by a bisection of the shaft of the first metatarsal. Care needs to be taken not to bisect the base or head of the first metatarsal
|
|
|
Calcaneocuboid Angle
Norm: 0-5 degrees -angle increases with pronation |
|
|
Forefoot angle
Norm: 8 degrees 12-14 FF adductus <12 straight rectus foot |
|
|
HAV Angle
Norm: < 15 |
|
|
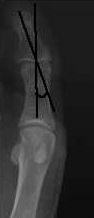
IM Angle
Norm: 8-12 Rectus >14 degrees Metatarsus adductus/forefoot adductus = 12 degrees |
|
|
Hallux Interphalangeal Angle
Norm: 8-10 |
|
|
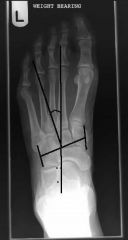
Lesser Tarsus Angle
|
|
|
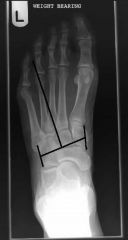
Lesser Tarsus Axis
(1) line joining distal medial point of medial cuneiform and proximal medial portion of navicular. (2) line joining distal lateral point of cuboid and proximal lateral point of cuboid (3) line joining bisection of (1) and (2) (4) Line perpendicular to bisection of line (3) |
|
|
Tibial Sesamoid Position
-determined by the position of the tibial sesamoid relative to the 1st metatarsal axis |
|
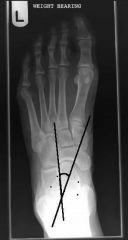
|
TaloCalcaneal
Norm: 17-20 Angle increases above 21 degrees when foot is pronated further from a resting position Angle decreases below 16 degrees when foot is supinated further from a resting position |
|
|
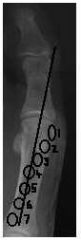
Tibial Sesamoid Position
|
Position of sesamoid relative to a bisection of the first metatarsal
1) Sesamoid is medial to axis 2) Sesamoid is touching the axis (laterally) 3) Sesamoid overlaps the axis (laterally) 4) Sesamoid is bisected by the axis 5) Sesamoid overlaps the axis (medially) 6) Sesamoid is touching the axis (medially) 7) Sesamoid is lateral |
|
|
Axial Calcaneal view
|
- Central beam aimed 45 degrees at calcaneus
- Used to visualise posterior calcaneus |
|
|
Harris Beath
|
- For posterior and middle facets of STJ
- Central ray aimed from 30 to 50 degrees at posterior calcaneus - May need serial x-rays |
|
|
Anterior posterior Ankle xray view
|
- Standing in angle base of gait, posterior aspect of calcaneus against x-ray film, central ray horizontal and aimed at middle of ankle
|
|
|
Ankle Mortise xray view
|
- Same as ankle AP, but leg internally rotated 15 degrees
|
|
|
Ankle MO and LO xray views
|
- MO - leg externally rotated 45 degrees
- LO - leg internally rotated 45 degrees (for view of tibofibular syndesmosis) |
|
|
RF longitudinal axis
|
Formed by a line that bisects the posterior aspect of calcaneus and continues anteriorly to the anterior medial edge of the calcaneus. Often the posterior aspect of the calcaneus is not visible, so a line parallel to the anterior lateral edge of the calcaneus is usually used
|
|
|
Metatarsus Longitudinal axis
|
Formed by a longitudinal bisection of the shaft of the second metatarsal.
|
|
|
FF Angle
|
- Angle between long axis of rearfoot and metatarsus axis
|
|
|
Met Adductus Angle
|
- Angle between metatarsus axis lessor tarsus axis
- Normally 16-18 degrees adducted |
|
|
Lesser Tarsus Angle
|
Angle between lessor tarsus axis and rearfoot axis
|
|
|
IM angle
|
- Angle between bisections of first and second metatarsals
- Normally 8 - 12 degrees |
|
|
Hallux Angle
|
- Angle between bisections of first metatarsal and proximal phalanx
|
|
|
Normal DP xray
|
1) MTJ is continuous cyma line
2) Head of talus bound close to anterior calcaneus 3) Proximity of sustentaculum tali to navicular 4) Long axis of rearfoot - relationship to forefoot 5) Direction of head of talus 6) 75% of head of talus articulates with navicular 7) Lateral border of calcaneus parallel with long axis of foot |
|
|
Normal Lateral Xray
|
1) Midtarsal joint cyma line continuos
2) Sinus tarsi visible 3) Body of talus parallel with plane of support 4) Normal calcaneal inclination 5) Height of foot 6) Space at posterior aspect of STJ 7) Plantar tuberosities densities superimposed 8) Dense area for sustentaculum tali 9) Cuboid articular facet evenly aligned with calcaneal 10) Peroneal groove delineated by added density |
|
|
Flat/Pronated Foot xray
|
1) Break in cyma line
2) Sinus tarsi diminished 3) Talus moved distally and plantarly 4) Lower of calcaneus inclination 5) Lower height of foot 6) Eversion of calcaneus 7) Lateral tuberosity raised 8) Less density of sustentaculum tali 9) Cuboid lower and everted 10)No groove visible in plantar cuboid |
|
|
cavus/Supinated foot xray
|
1) High pitch to calcaneus
2) High declination to 5th metatarsal 3) Normal cyma line of MTJ 4) Sinus tarsi accentuated 5) Acute angle between STJ and long axis of calcaneus |
|
|
FF Angle
|
Ideal average measurement:(8 degrees)-Angle formed by metatarsal axis (line joining bisection of distal and proximal regular shaft of 2nd metatarsal) and the longitudinal axis of the rearfoot (line joining distal middle portion of calcaneus and center posterior aspect of calcaneus.
|
|
|
Calcaneocuboid Angle
|
Ideal average measurement:(0-5 degrees)
(1) line along lateral distal margin of calcaneus (2) line along lateral distal margin of cuboid Angle increases with foot pronation |
|
|
HAV Angle
|
Ideal average measurement: <15°
Angle formed bisection of 1st metatarsal and proximal phalanx |
|
|
IM Angle
|
Ideal average measurement: 8-12°
Line joining bisection of distal and proximal regular shafts of metatarsals one and two. The lesser intermetatarsal angles are not usually measured. Rectus >14 degrees Metatarsus adductus/forefoot adductus = 12 degrees |
|
|
PASA
|
Ideal average measurement: 0-8°
(1) Line joining edges of the proximal articular facet of the proximal phalanx (2) Bisection of proximal phalanx • Subtract 90° from angle |
|
|
DASA
|
Ideal average measurement: 0-6°
(1) line joining edges of distal articular facet of 1st metatarsal. (2) Bisection of 1st metatarsal • Subtract 90° from angle. NB: The PASA and DASA should add up to equal the HAV angle |
|
|
Met Break Angle
|
Ideal average measurement: 142°
(1) Line joining distal centre 1st and 2nd metatarsals (2) Line joining distal center 2nd and 5th metatarsals Metatarsal Formula: 2>1=3>4>5 |
|
|
Boehlers Angle
|
- (28-40 degrees)
(1) line joining anterior process and posterior calcaneal facets (2) line joining most posterior process and posterior facets - angle always taken with calcaneal fractures and indicates relative declination of the posterior facet |
|
|
1st Met Declination Angle
|
(20-30 degrees)
(1) line joining bisection of distal and proximal regular shaft of 1st metatarsal. (2) Plane of support. |

