![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
X-rays differ due to |
Shorter wavelengths |
|
|
|
X-rays packet |
Of energy |
|
|
|
Electrons are |
Negatively charged |
|
|
|
How much energy produced is heat |
99% |
|
|
|
How much energy produced is x-ray |
1% |
|
|
|
Medically correct term for x-ray |
Radiograph |
|
|
|
Table mount used for |
Small animal |
|
|
|
Ceiling mount used for |
Large animal |
|
|
|
Stationary table top |
Most common |
|
|
|
What are the 2 x-ray machine tables |
Stationary and floating |
|
|
|
kVp dial major range |
10-12 |
|
|
|
kVp dial minor |
1-2 |
|
|
|
Cathode |
- electrode |
|
|
|
Anode |
+ electrode |
|
|
|
Glads envelope prevents |

Oxidation of elements |
|
|
|
Tungsten filament similar to |
Filiment in light bulb |
|
|
|
When the Tungsten filament is heated |
It emits electrons |
|
|
|
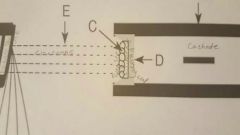
Focusing cup contains |
Filament |
|
|
|
Focusing cup controls |
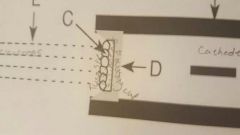
Size of electron beam |
D |
|
|
Primary x-ray beam created |
After electrons cross over |
|
|
|
Tungsten target contained |
In anode |
|
|
|
Beryllium window is |
An exit portal for x-ray beams |
|
|
|
Aluminum filter absorbs |
Soft (lazy) x-rays |
|
|
|
Excessive anodes |
Cause heat damage |
|
|
|
2 types of anode machines |
Stationary and rotating |
|
|
|
Stationary anode utilized |
In low output |
|
|
|
Rotating anode |
Dissipates heat preventing damage |
|
|
|
mA x sec = |
mAs |
|
|
|
mAs controls |
Quantity of x-rays |
|
|
|
Larger body areas |
Require higher mAs |
|
|
|
Head of patients should face |
Anode side of machine |
|
|
|
kVp penetrates |
Through more |
|
|
|
kVp controls |
Quality of x-ray beams |
|
|
|
Grids are between |
The patient and film |
|
|
|
Grids are used when radiographs |
> 10 cm |
|
|
|
< 10 cm is called |
Table top grid |
|
|
|
Focal spots major function is to |
Distribute electron stream over larger area |
|
|
|
As focal spot gets bigger |
Clarity decreases |
|
|
|
Smaller focal spot is |
Less heat dissipation |
|
|
|
Heel effect is caused by |
Uneven absorption of x-rays in tungsten target |
|
|
|
Repeated tube overload |
Will crack anode (mAs) |
|
|
|
Tube saturation aka |
Arching |
|
|
|
Tub saturation occurs when |
kVp not high enough to pull electrons |
|
|
|
Cathode failure (Filiment evaporation ) |
Most common cause of tube failure |
|

