![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
117 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a bony protuberance or hypertosis or exostoses that occurs in the middle third of the midline of the hard palate?
|
palatine tori
|
|
|
True or false, normal mucosa covers palatal tori
|
True
|
|
|
True or False, platal tori may be superimposed over periapical area of teeth
|
True
|
|
|
Palatal tori are (not/very) well defined radiographically
|
very
|
|
|
What treatment must be used for palatal tori?
|
none (may have to modify dentures)
|
|
|
What two things can cause tori on the mandible?
|
genetic
mastacatory forces |
|
|
What is a hyperostosis protruding from the lingual aspect of the mandibular alveolar process usually near premolars?
|
mandibular tori
|
|
|
Tori appear (RL/RO) on a radiograph
|
RO
|
|
|
Mandibular tori appear to be better defined in the (anterior/posterior)
|
anterior
|
|
|
Random hyperostosis or exostoses will typically have a (rough/smooth) outline
|
smooth
|
|
|
Proliferation of normal bone on alveolar ridge beneath a fixed bridge is called what?
|
subpontic hyperstosis
|
|
|
What causes subpontic hyperstosis?
|
unknown
|
|
|
True or False, subpontic hyperostosis usually cases the patient great pain
|
False, typically asymptomatic
|
|
|
What is the term for anatomic variation characterized by an apparent increase in the height of the alveolar bone on the distal of the last molar in mandible?
|
distal mandibular pseudohyperostosis
|
|
|
What causes distal mandibular pseudohyperostosis?
|
extraction distal to the tooth or mesial tipping due to loss of tooth
|
|
|
distal mandibular pseudohyperostosis is a small bony (protuberance/indentation)
|
protuberance
|
|
|
What is a begnin tumor characterized radiographically and histologically by the production of mature enamel, dentin, cementum and pulp tissue?
|
odontoma
|
|
|
A (complex/compound) odontoma consists of non-descriptive masses of dental tissue
|
complex
|
|
|
A (complex/compound) odontoma consists of multiple well-formed teeth (denticles)
|
compound
|
|
|
(males/females) are more susceptible to odontomas
|
Neither! Same rate
|
|
|
True or False, Odontoma can interfere with the eruption of secondary teeth
|
True
|
|
|
Which is more common, compound or complex odontoma?
|
compound
|
|
|
True or False, there is jaw expansion and cortical boundary is lost with an odontoma
|
False, it is maintained
|
|
|
__% of compound odontoma occur in anterior maxilla with impacted canine
|
62
|
|
|
__% of complex odontoma are in mandibular 1st and 2nd molar area
|
70
|
|
|
The odontoma periphery is (poorly/well) defined, (noncorticated/corticated) with soft tissue capsule
|
well, corticated
|
|
|
True or False, odontomas contain tooth-like materials
|
True
|
|
|
True or False, odontomas are typically isolated and have no effect on surrounding area
|
False, they can cause impaction, diastemas, and malpositioning
|
|
|
An osteoma is a (benign/malignant) mesodermal tumor
|
benign
|
|
|
Osteomas are common in what 2 sinuses?
|
frontal and ethmoid
|
|
|
(compact/cancellous) osteomas are more common in males
|
compact
|
|
|
(compact/cancellous) osteomas are more common in females
|
cancellous
|
|
|
Osteomas are most common in people over the age of ___
|
40
|
|
|
True or false, the mucosa covering an osteoma is normal
|
True
|
|
|
Osteomas grow (fast/slow)
|
slow
|
|
|
Osteomas are more common in (anterior/posterior) mandible on (facial/lingual) side
|
posterior, lingual
|
|
|
The periphery of an osteoma is (poorly/well) defined
|
well
|
|
|
What disease consists of multiple enostosis and osteomas?
|
Gardner's Syndrome
|
|
|
What do we call it when a root fragment is in the bone with a full LD and PDL but no crown?
|
root remnant
|
|
|
True or false, root remnants may have root canal spaces
|
True
|
|
|
What surface anatomical feature on incisors is commonly mistaken for caries?
|
shovel-shaped incisors
|
|
|
Small, normal, developmental bumps on incisors are called
|
mamelons
|
|
|
Horizontal root fractures occur most often in the (mand/max) central incisors
|
max
|
|
|
What portion of the root do horizontal fractures typically occur?
|
midline
|
|
|
True or False, all horizontal fractures are easy to see radiographically
|
False, if there is not much displacement, it may be hard to tell
|
|
|
(horizontal/vertical) fractures run from apex of root to crown
|
vertical
|
|
|
Vertical cracks are usually oriented in what plane?
|
facial-lingual
|
|
|
True or False, vertical root fractures are difficult to see radiographically
|
yes, unless you already know they are there and can align the bean accordingly
|
|
|
vertical door fractures usually have (sharp/dull) pain
|
dull
|
|
|
Vertical root fractures may have periodontal lesions associated with them, T or F
|
T
|
|
|
When a tooth rotates, contact becomes (lost/increased)
|
lost (typically)
|
|
|
When a tooth rotates, the pulp canals appear (narrower/wider) mesiodistally
|
wider
|
|
|
A space between teeth is a ____
|
diastima
|
|
|
Blockage of secretory ducts of seromucus glands OR cystic degeneration within an inflammed sinus lining can both cause what?
|
mucus retention pseudocyst
|
|
|
mucus retention pseudocyst appear (corticated/noncorticated)
|
noncorticated
|
|
|
Fluid accumulation in a mucus retention pseudocyst can appear (RL/RO)
|
RO
|
|
|
In mucus retention pseudocyst, what happens to floor of sinus
|
remains intact
|
|
|
CBCT stands for what type of imagine technology?
|
cone beam computed tomography
|
|
|
When tonsilar crypts are enlarged over and over again due to inflammation damage, this is called what?
|
dystrophic calcification of tonsils
|
|
|
What are the typical clinical findings of dystrophic calcification of tonsils?
|
there are usually none at all!
|
|
|
In dystrophic calcification of tonsils, you have a (RL/RO) area that overlaps the mandibular ramus where dorsal surface of ___ crosses ramus in the GP airspace
|
RO, tongue
|
|
|
Plaque buildup in the arteries can be seen on radiograph, and we call this what?
|
arterial calcification arthrosclerosis
|
|
|
arterial calcification arthrosclerosis develop at what area in arteries?
|
bifurcation
|
|
|
arterial calcification arthrosclerosis may be visible by C__ and C__
|
C3, and C4
|
|
|
What is the term for a stone found in the salivary duct glands?
|
sialolith
|
|
|
Sialoliths are most common in what gland?
|
submandibular
|
|
|
Half of all sialoliths lie in (mesial/distal) portion of what duct?
|
distal, Wharton's
|
|
|
What symptoms are assocuated with sialoliths?
|
usually none
|
|
|
Ossification of the stylohyoid ligament often occurs (uni-,bi-) lateraly
|
bilaterally
|
|
|
The normal styloid process measures __-__ cm
|
0.5-2.5
|
|
|
Stylohyoid syndrome is also known as ___ syndrome
|
Eagle's
|
|
|
Linear ossification extending from region of mastoid process and crosses posterior-inferior aspect of ramus toward the hyoid bone is probably what?
|
ossification of stylohyoid ligament
|
|
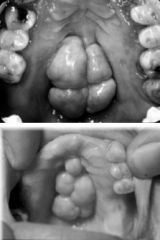
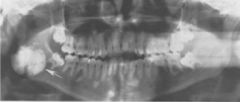
What is this condition known as?
|
palatal tori
|
|
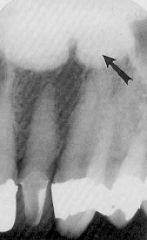
This radiograph shows what object?
|
palatal tori
|
|
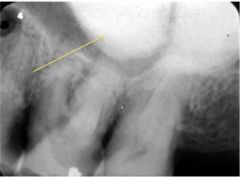
The RO mass is what?
|
palatal tori
|
|
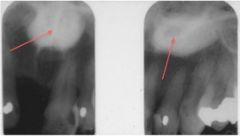
Both of these images show a RO mass known as what?
|
palatal tori
|
|
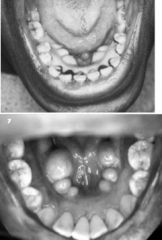
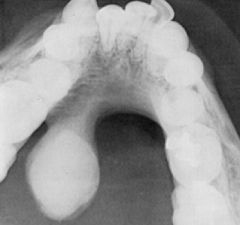
Is this palatal or mandibular tori?
|
mandibular
|
|
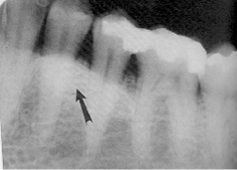
This radiograph show what RO mass?
|
mandibular tori
|
|
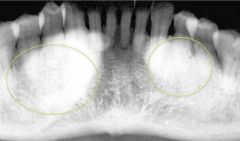
What are the two RO masses?
|
mandibular tori
|
|
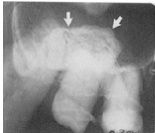
The general term for this RO mass is what?
|
exostoses or hyperostosis
|
|
This is known as what?
|
exostoses
|
|
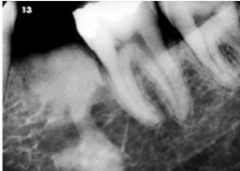
What is this known as?
|
exostoses
|
|
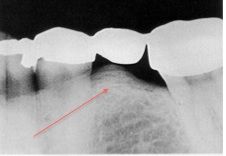
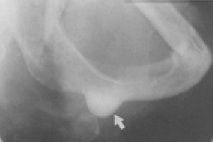
What is this bony mass called?
|
subpontic hyperostosis
|
|
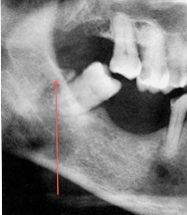
What is this small bony mass called?
|
distal mandibular pseudohyperostosis
|
|
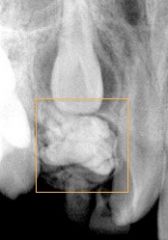
What is this?
|
COMPOUND odontoma
|
|
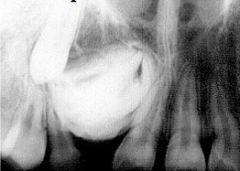
What is this?
|
Complex odontoma
|
|
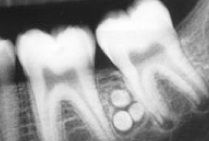
These little RO balls are known generally as what?
|
odontoma
|
|
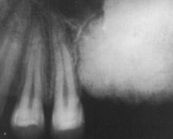
What is this RO mass known as?
|
odontoma
|
|
|
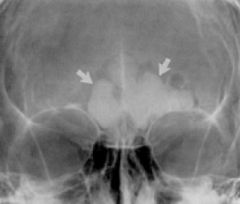
What is the pathology here?
|
osteoma
|
|
What is the pathology here?
|
osteoma
|
|
What is the pathology here?
|
osteoma
|
|
What is the pathology here?
|
osteoma
|
|
What view is this and what is the pathology?
|
PA view, osteoma
|
|
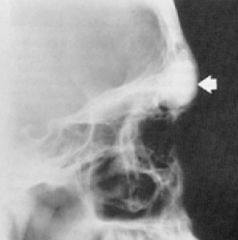
What is the view here and what is the pathology?
|
Lateral view, osteoma
|
|
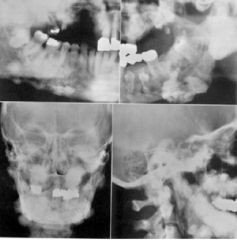
All of these show ___ syndrome
|
Gardner's
|
|
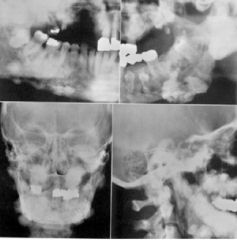
All of these show ___ syndrome
|
Gardner's
|
|
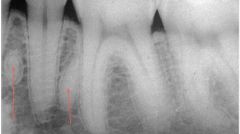
The small RO areas are what?
|
root remnants
|
|
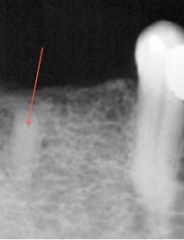
This small RO mass is what?
|
root remnant
|
|
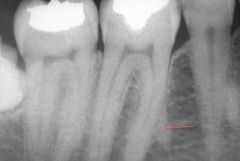
This image shows small RO masses called what?
|
root remnants
|
|
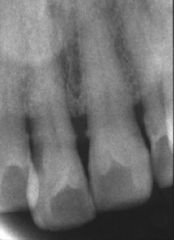
These incisors are not carious, but are said to be ___ shaped
|
shovel
|
|
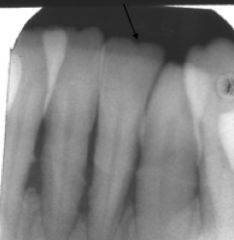
These small "bumps" on top of these teeth are called what?
|
mamelons
|
|
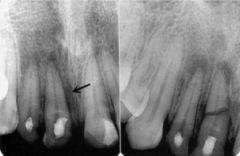
The image on the right shows what? (different than left image)
|
horizontal root fracture
|
|
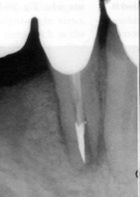
This is a (horizontal/vertical) root fracture
|
vertical
|
|
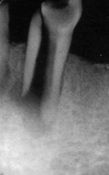
What is wrong with this tooth?
|
vertical root fracture
|
|
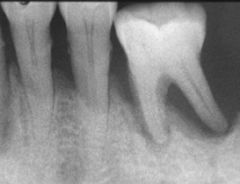
What is wrong with the pulp?
|
calcified
|
|
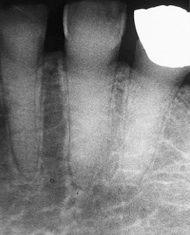
What is wrong with the root of this tooth?
|
pulpal calcification
|
|
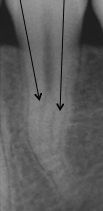
What is unique about this root canal?
|
it is bifurcated
|
|
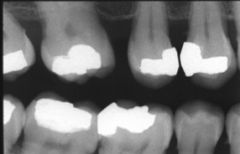
These spaces are known as what?
|
diastimas
|
|
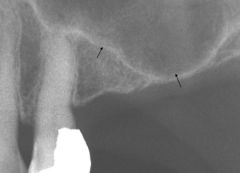
This maxillary sinus is said to have undergone what?
|
pneumatization
|
|
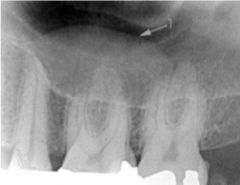
This image shows what?
|
a mucus retention pseudocyst
|
|
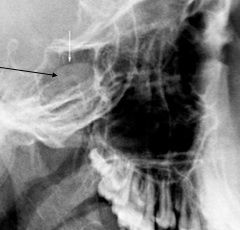
The arrow is pointing to what?
|
a mucus retention pseudocyst
|
|
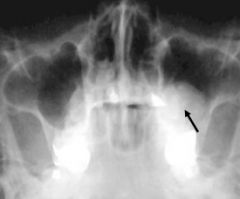
What three things might these RO masses be?
|
mucus retention cyst
osteoma polyp in max sinus |
|
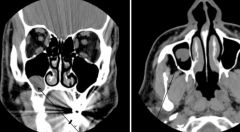
The image on the left is in the ___ view and the right is in the ___ view. Both are indicating what type of cyst?
|
Left, coronal
Right, Axial mucus retention cyst |
|
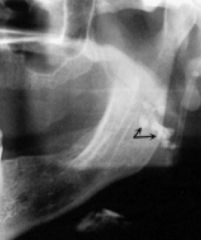
This is known as calcification of what structure?
|
tonsils
|
|
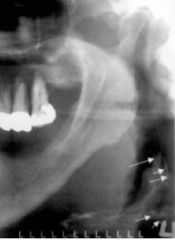
What is calcified in this image? (that we DON'T want)
|
artery
|
|
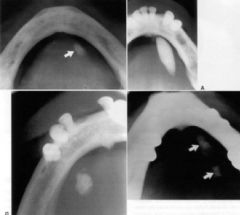
These little RO balls are called what?
|
sialoliths
|
|
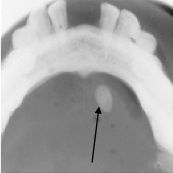
This is a stone in what?
|
salivary gland stone
|

