![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Wilhelm Roentgen
Basic Facts |

- Born March 27 1845
- Discovered X-Rays on November 8, 1895 - Awarded first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901 |
|
|
Wilhelm Roentgen
link to Modern use |
Reason we use Roentgen to determine the amount of intensity or radioactivity a source has per hour
|
|
|
Roentgen to Miliroentgen
|
1 R (Roentgen) = 1000 MR (Miliroentgen)
1R/hr = 1000 mr/hr |
|
|
First X-ray
|
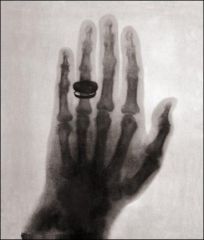
Taken by Roentgen of wife's hand
|
|
|
Mr. Becquerel
|
- Born December 15, 1852
- Discovered Radioactivity in 1896 - Uranium Salts - Film -Awarded Nobel Prize in 1903 |
|
|
Mr. Becquerel Cont
|
- Is the reason we use the European Measurement of Becquerel to determine strength of source
- Rest of the world uses Becquerel as strength of source |
|
|
What did Becquerel discover
|
X-ray of Metal Cross on film after being exposed to radiation from uranium salts
|
|
|
Ernest Rutherford
|

Born 1871
Made contributions towards the discovery of the nature of radiation 1908 Nobel Prize "Father" of Nuclear Physics |
|
|
Marie Curie
|

Born November 7 1867
Worked with her husband discovering Radium and Radon Awarded nobel prize in 1903 and 1911 |
|
|
Curie
|
Reason we use the measurement Curie or Curies to determine Strength of a source in the US
|
|
|
Albert Einstein
|

Born March 14, 1979
1921 Awarded Nobel Prize Discovered "Photo-electric effect" |
|
|
describe an Atom
|
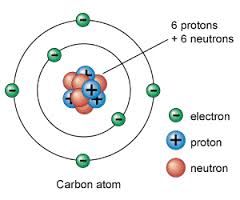
Nucleus
Protons Neutrons Orbital Electrons |
|
|
Are Unstable Elements and Unstable Isotopes Radioactive
|
Yes, not all isotopes are unstable so not all are radioactive. Only unstable Isotopes are Radioactive
|
|
|
Xray Machines-
What is mostly Produced |
Heat
|
|
|
Are X-rays a bi-product of Xray Machines?
|
Yes, Heat is the main thing produced by X-ray Machines
|
|
|
What is the difference between an Anode and a Cathode
|
an Anode is Positively Charged and a Cathode is negatively charged.
X-rays are released from the Cathode |
|
|
On X-ray Machines what is the "Target" Made of
|
Tungsten is the most common target
|
|
|
KV
|
Is the voltage used to control x-ray energy. The higher the Kv, the shorter the wavelength and the more penetrating Power (Like going from Iridium to Cobalt
|
|
|
MA
|
Is Filament Current. Remember that the higher the MA, the more electrons you produce, the higher the activity. (The same as using a hotter source, more curies)
|
|
|
Which has the highest Penetrating Power
|
Cobalt - Can penetrate 3"-8" of steel
|
|
|
Iridium or Cobalt have the longer wavelength
|
Iridium - can penetrate 1/4"-3" of steel
|
|
|
Which source has the least power
|
Selenium - Can penetrate 0"-1 3/4" of steel
|
|
|
Which type of Radiation is Positive
|
Alpha
|
|
|
Which type of radiation is Negative
|
Beta
|
|
|
How are items made radioactive
|
Only through the bombardment of neutron flux can something be made radioactive or activated. The process of irradiation is cell activation
|
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation
|
Energy that is transmitted in waves that show electric and magnetic effects
Energy of electromagnetic radiation is indirectly proportional to its wavelength The penetrating power of radiation is directly proportional to its wavelength |
|
|
What happens to a material when Radiation passes through it
|
Ionization
|
|
|
Characteristics of X-Ray & Gamma Rays
|
- No mass, weight, polarity or charge
- Not affected by electric or magnetic fields - create ionization in all forms of matter - can be harmful to body tissue and cells - not detectable by the senses |
|
|
Characteristics of X-ray & Gamma Rays
|
- Part of the electro-magnetic "EMR" Spectrum
- Travel in straight lines at the speed of light - Penetrates all forms of matter - Can be absorbed by all forms of matter - can be scattered |
|
|
Characteristics of Alpha Particles
|
2 Protons & 2 Neutrons (+2 Charge) 4-10 MEV (Energy)
|
|
|
Characteristics of Beta Particles
|
Nothing more than an electron (+1 Charge) 0.025 - 3.15 MEV (Energy)
|
|
|
Characteristics of Gamma & Xray particles
|
A packet of electromagnetic energy-a photon. Gamma rays (gamma photons) are emitted from the nucleus of some unstable (radioactive) atoms 0 Mass 0 Charge
Gamma 0.04 - 3.2 MEV (Charge) X-ray Up to 30 MEV (Charge) |
|
|
Characteristics of Alpha Beta & Neutron Radiation
|
- Has Mass
- Sub-light speed - Causes Ionization - limited penetration - Not detectable by the senses |
|
|
Photoelectric effect
|
Gamma photon interacts with and transferes its energy to an atomic electron, ejecting that electron from the atom. the kinetic energy of the resulting photoelectron is equal to the energy of the incident gamma photon minus the binding energy of the electron
|
|
|
How to get GBQ
|
Curies x 37
|
|
|
Half Life
|
Time required to reduce the activity by half
|
|
|
Cobalt 60 Half Life
|
5.3 Years
|
|
|
Iridium 192 Half Life
|
75 Days
|
|
|
Selenium 75 Half Life
|
120 Days
|
|
|
R refers to what
|
Symbol for Roentgen
|
|
|
rad refers to what
|
Radiation Absorbed Dose
Animals |
|
|
Q Refers to what
|
Quality Factor
|
|
|
rem refers to what
|
Roentgen Equivalent Man (TLD Badge Measures in rem)
|
|
|
Describe Roentgen (R)
|
Unit of Measurement of gamma or x-ray radiation in air. Specifically, the amount of gamma or x-ray radiation that will produce 1 electrostatic unit (ESU) in 1 cc of air at STP
|
|
|
Describe rad
|
measures absorbed dose in animal tissue
|
|
|
Describe Quality Factor
|
Different types of radiation have different biological effects for the same rad - the quality factor makes them comparable
|
|
|
describe rem
|
product or rad *Q. measures biological effect of radiation on humans
|
|
|
Standard International units
|
1 Gray = 1 joule/kilogram or 100 rads
1 rad = 100 ergs/gram or 0.01 joules/kilogram, or 0.01 gray 1 roentgen = 2.58 x 10^4 coulombs/kilogram air 1 sievert = 100 rems 1 rem = 0.01 sievert |
|
|
Activity
|
the quantity of radioactive material present at a given time
|
|
|
x-ray has what quality factor value
|
1
|
|
|
Gamma Ray has what quality factor value
|
1
|
|
|
Beta Particles have what quality factor value
|
1
|
|
|
Neutrons have what quality factor value
|
5-10
|
|
|
Alpha particles have what quality factor value
|
20
|
|
|
Calculating rem
RAD times the Quality Factor |
Gamma Ray Rad is 3x1 = 3 rem
beta rad 3x1 = 3 rem Alpha rad 3x20 = 60 rem |
|
|
What is most affected by radiation
|
White Blood cells
|
|
|
What is the least affected by radiation
|
Extremities
|
|
|
Exposure limiits
|
Eyes 15R/yr
extremities 50 R/yr Whole body 5R/yr |
|
|
Other exposure limits
|
<18 Dose <10 % of dose limit
same with Pregnant and embryo |
|
|
Cell sensitivity
|
1. White Blood Cells
2. Immature Red Blood Cells 3. Digestive system lining cells 4. Cells of the Gonad 5. Blood Vessel Cells 6. Bone, Muscle and Nerve Cells |

