![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
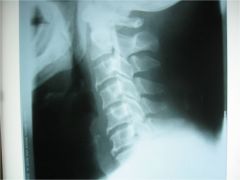
2 OPLL,
lateral cervical spine, thick band of sclerosis posterior to the bodies of C2-3, calcification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, M/C C/S followed by T & L spines, 50% of pt's w/ DISH also have OPLL, anterior osteophytes could represent early DISH changes, OPLL also common among populations from Japanese descent (CONTRAINDICATION to adjusting in the area, OPLL causes significant canal stenosis, disc space preserved) |
ID
|
|
|
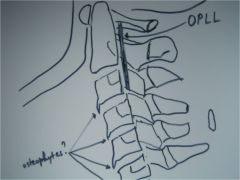
2(2) OPLL,
lateral cervical spine, thick band of sclerosis posterior to the bodies of C2-3, calcification of the posterior longitudinal ligament, M/C C/S followed by T & L spines, 50% of pt's w/ DISH also have OPLL, anterior osteophytes could represent early DISH changes, OPLL also common among populations from Japanese descent (CONTRAINDICATION to adjusting in the area, OPLL causes significant canal stenosis, disc space preserved) |
ID
|
|
|
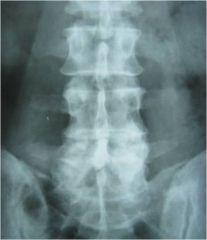
48-1 DISH,
the AP lumbar also demonstrates entesopathy at the upper portion (1/3) of the SI jts (lower 2/3rds synovial = AS, none = OA), clinical consideration: ask pt if they have been checked for diabetes, because of higher incidence (up to 50% of DISH pts develop diabetes), other findings: facet hypertrophy, relative preservation of disc spaces |
ID
|
|
|
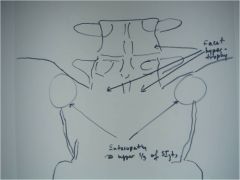
48-1(2) DISH,
the AP lumbar also demonstrates entesopathy at the upper portion (1/3) of the SI jts (lower 2/3rds synovial = AS, none = OA), clinical consideration: ask pt if they have been checked for diabetes, because of higher incidence (up to 50% of DISH pts develop diabetes), other findings: facet hypertrophy, relative preservation of disc spaces |
ID
|
|
|
48-2 DISH,
Lateral Lumbar (and T spine) demonstrates thick flowing calcification anterior to several vertebral bodies (MIDDLE OF BODY AFFECTED at multiple levels, luscencies at level of disc = annular fibers allowing for movement so we can adjust - can adjust DISH as long as no OPLL)(aka dripping candle wax; flame-shaped osteophytes), spared apophyseal joints, relative preservation of disc spaces, Clinical consideration: ask pt if they have been checked for diabetes because of higher incidence with DISH |
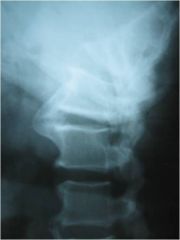
ID
|
|
|
48-2(2) DISH,
Lateral Lumbar (and T spine) demonstrates thick flowing calcification anterior to several vertebral bodies (MIDDLE OF BODY AFFECTED at multiple levels, luscencies at level of disc = annular fibers allowing for movement so we can adjust - can adjust DISH as long as no OPLL)(aka dripping candle wax; flame-shaped osteophytes), spared apophyseal joints, relative preservation of disc spaces, Clinical consideration: ask pt if they have been checked for diabetes because of higher incidence with DISH |
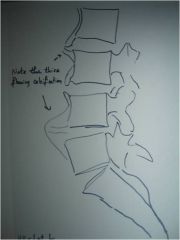
ID
|
|
|
303-1 Ankylosing spondylitis,
Neutral lateral cervical, AS in C-spine = decreased ADI), Fusion in flexion malposition, facet jt. ossification (C2-pelvis), Squaring of the anterior bodies caused by ossification of the ALL with then syndesmophytes, ossification of the Ligamentum flavum (yellow ligament), poor visualization of the upper c-spine, access for upper c-spine instability |
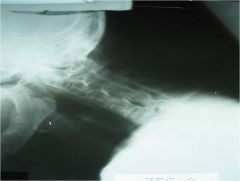
ID
|
|
|
303-1(2) Ankylosing spondylitis,
Neutral lateral cervical, AS in C-spine = decreased ADI), Fusion in flexion malposition, facet jt. ossification (C2-pelvis), Squaring of the anterior bodies caused by ossification of the ALL with then syndesmophytes, ossification of the Ligamentum flavum (yellow ligament), poor visualization of the upper c-spine, access for upper c-spine instability |
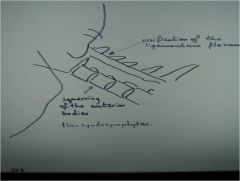
ID
|
|
|
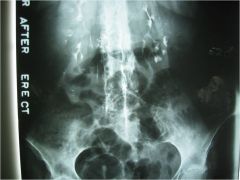
303-2 Ankylosing spondylitis, advanced/late stage AS w/ bilateral SI fusion, no inflammation (no pain), or sclerosis since the jt has been obliterated (ghost sign, star sign), presence of multiple surgical staples in abdomen (GI surgery) w/ unusual, but probably normal for pt gas pattern, note: up to 18% of pts w/ ulcerative collitis and Crohn's disease develop AS, which is a 20 times greater incidence than in the general population, trolley track sign (calcification of facet joint calcification of facet joint capsules), dagger sign (calcification of inter and supraspinous ligaments),
IVP: observe the 2 radiolucencies in the bladder most probably caused by an enlarged prostate pushing against it, Note: remember that chronic prostatitis is ass. in 80% of male pt's w/ AS, adjusting fused joints is a contraindication, check for upper C/S instability |
ID
|
|
|
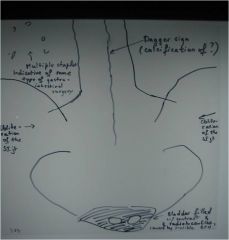
303-2(2) Ankylosing spondylitis, advanced/late stage AS w/ bilateral SI fusion, no inflammation (no pain), or sclerosis since the jt has been obliterated (ghost sign, star sign), presence of multiple surgical staples in abdomen (GI surgery) w/ unusual, but probably normal for pt gas pattern, note: up to 18% of pts w/ ulcerative collitis and Crohn's disease develop AS, which is a 20 times greater incidence than in the general population, trolley track sign (calcification of facet joint calcification of facet joint capsules), dagger sign (calcification of inter and supraspinous ligaments),
IVP: observe the 2 radiolucencies in the bladder most probably caused by an enlarged prostate pushing against it, Note: remember that chronic prostatitis is ass. in 80% of male pt's w/ AS, adjusting fused joints is a contraindication, check for upper C/S instability |
ID
|
|
|
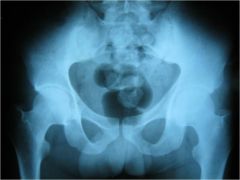
304-2 Ankylosing spondylitis, bilateral & symmetric sclerosis at the inferior 2/3 of the SI joints (upper 1/3rd ok), more pronounced at the iliac part (its cartilage is 3x thinner than on the sacral part), pseudowidening of the SI joints, more prominent on the iliac side, rosary bead erosions, informed consent before treatment, "Taco Bell syndrome" = gas and poop ready to exit
|
ID
|
|
|
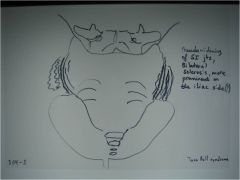
304-2(2) Ankylosing spondylitis, bilateral & symmetric sclerosis at the inferior 2/3 of the SI joints (upper 1/3rd ok), more pronounced at the iliac part (its cartilage is 3x thinner than on the sacral part), pseudowidening of the SI joints, more prominent on the iliac side, rosary bead erosions, informed consent before treatment, "Taco Bell syndrome" = gas and poop ready to exit
|
ID
|
|
|
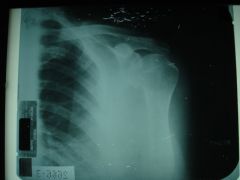
306 CPPD, chondrocalcinosis of the shoulder of unknown cause, inflammatory condition where calcium pyrophosphate crystals deposit in synovial fluid, linings, articular cartilage, degenerative type changes in an unusual location are usually due to CPPD, treatment: maintain good motion
|
ID
|
|
|
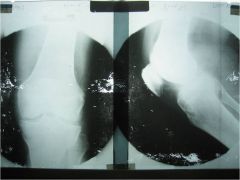
306-1,2 CPPD, chondrocalcinosis of the menisci of unknown cause, inflammatory condition where calcium pyrophosphate crystals deposit in synovial fluid, linings, articular cartilage, degenerative type changes in an unusual location are usually due to CPPD, treatment: maintain good motion
|
ID
|
|
|
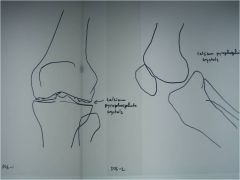
306-1,2(2) CPPD, chondrocalcinosis of the menisci of unknown cause, inflammatory condition where calcium pyrophosphate crystals deposit in synovial fluid, linings, articular cartilage, degenerative type changes in an unusual location are usually due to CPPD, treatment: maintain good motion
|
ID
|
|
|
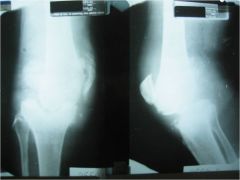
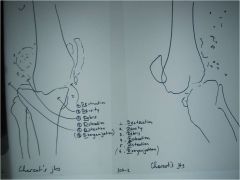
307-1,2 Neurotrophic arthropathy, Charcot's jts,
destructive joint changes due to loss or impairement to joint proprioception, 6 D's: destruction, debris, density, dislocation, distention, disorganization, in weight bearing joints usually caused by diabetes and neurosyphilis (1sr ddx: infection but in infection there will be a fast onset and no floating bones vs Charcot's which has debris and a slow onset, also painless) |
ID
|
|
|
307-1,2(2) Neurotrophic arthropathy, Charcot's jts,
destructive joint changes due to loss or impairement to joint proprioception, 6 D's: destruction, debris, density, dislocation, distention, disorganization, in weight bearing joints usually caused by diabetes and neurosyphilis (1sr ddx: infection but in infection there will be a fast onset and no floating bones vs Charcot's which has debris and a slow onset, also painless) |
ID
|
|
|
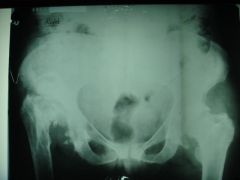
308 Neurotrophic arthropathy, Charcot's jts,
lots of debris in the area of the rt hip, secondary OA on the opposite side |
ID
|
|
|
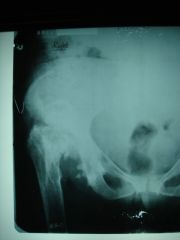
308-1 Neurotrophic arthropathy, Charcot's jts,
lots of debris in the area of the rt hip, thinning of femoral cortex, secondary OA on the opposite side destructive joint changes due to loss or impairement to joint proprioception, 6 D's: destruction, debris, density, dislocation, distention, disorganization, in weight bearing joints usually caused by diabetes and neurosyphilis (1sr ddx: infection but in infection there will be a fast onset and no floating bones vs Charcot's which has debris and a slow onset, also painless) |
ID
|
|
|
308-1(2) Neurotrophic arthropathy, Charcot's jts,
lots of debris in the area of the rt hip, thinning of femoral cortex, secondary OA on the opposite side destructive joint changes due to loss or impairement to joint proprioception, 6 D's: destruction, debris, density, dislocation, distention, disorganization, in weight bearing joints usually caused by diabetes and neurosyphilis (1sr ddx: infection but in infection there will be a fast onset and no floating bones vs Charcot's which has debris and a slow onset, also painless) |

ID
|
|
|
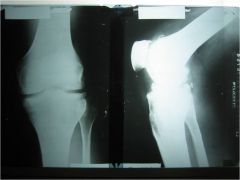
309-1,2 Synovial chondrometaplasia, aka synovial osteochondromatosis,
AP and lateral knee, commonly found at the knee, ankle and hip, metaplasia of the synovium to form cartilage which detaches and then calcifies or ossifies, creates multiple intraarticular, loose bodies (joint mice) that bathe in the synovial fluid, joint locking, surgical resection is often difficult, because of slippery nature of joint mice (monarticular disorder, cartilage can get stuck in facet jt, ossicle mostly around jt) |
ID
|
|
|
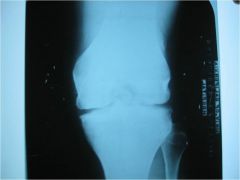
309-3 Synovial chondrometaplasia, aka synovial osteochondromatosis,
Tunnel view knee, commonly found at the knee, ankle and hip, metaplasia of the synovium to form cartilage which detaches and then calcifies or ossifies, creates multiple intraarticular, loose bodies (joint mice) that bathe in the synovial fluid, joint locking, surgical resection is often difficult, because of slippery nature of joint mice (monarticular disorder, cartilage can get stuck in facet jt, ossicle mostly around jt) |
ID
|
|
|
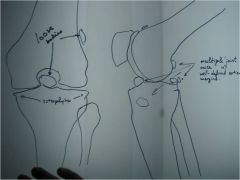
309-1,3(2) Synovial chondrometaplasia, aka synovial osteochondromatosis,
Tunnel view and lateral knee, commonly found at the knee, ankle and hip, metaplasia of the synovium to form cartilage which detaches and then calcifies or ossifies, creates multiple intraarticular, loose bodies (joint mice) that bathe in the synovial fluid, joint locking, surgical resection is often difficult, because of slippery nature of joint mice (monarticular disorder, cartilage can get stuck in facet jt, ossicle mostly around jt) |
ID
|
|
|
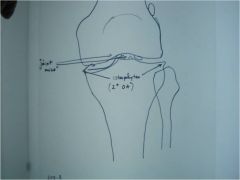
309-2(2) Synovial chondrometaplasia, aka synovial osteochondromatosis,
AP knee, commonly found at the knee, ankle and hip, metaplasia of the synovium to form cartilage which detaches and then calcifies or ossifies, creates multiple intraarticular, loose bodies (joint mice) that bathe in the synovial fluid, joint locking, surgical resection is often difficult, because of slippery nature of joint mice (monarticular disorder, cartilage can get stuck in facet jt, ossicle mostly around jt) |
ID
|
|
|
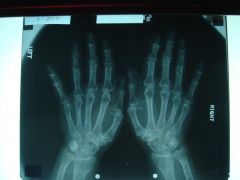
310 Osteoarthritis hand,
Decrease in jt space at the DIP's and PIP's of the 2nd and 3rd digits, 1st carpo-metacarpal (CMCP) joint changes, radial subluxation of the 1st metacarpal (metacarpals sliding to radial side), triangular extension off of the articular surface of the trapezium (osteophyte), Unaffected MCP's |
ID
|
|
|
310 hand(2) Osteoarthritis hand,
Decrease in jt space at the DIP's and PIP's of the 2nd and 3rd digits, 1st carpo-metacarpal (CMCP) joint changes, radial subluxation of the 1st metacarpal (metacarpals sliding to radial side), triangular extension off of the articular surface of the trapezium (osteophyte), Unaffected MCP's |
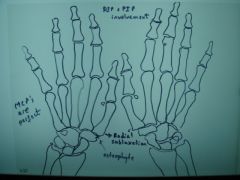
ID
|
|
|
310 Osteoarthritis knee,
decrease in the medial joint space (expect because weight bearing), osteophytes, prominent intercondylar eminences, patellar tendon calcification (common and insignificant, significant if in muscle belly) |
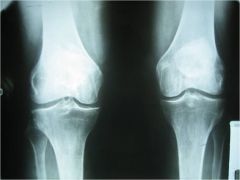
ID
|
|
|
310 Osteoarthritis knee,
decrease in the medial joint space (expect because weight bearing), osteophytes, prominent intercondylar eminences, patellar tendon calcification (common and insignificant, significant if in muscle belly) |
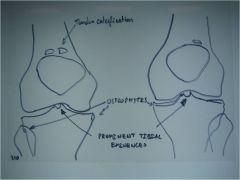
ID
|
|
|
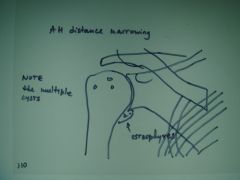
310 Arthritis shoulder,
Osteophytes off of medial surface of the humeral head (glenoid lip - on cartilage that surrounds the bone), narrowing of the A-H distance most likely caused by chronic rotator cuff tendonitis, multiple cysts in humeral head, again most likely due to chronic rotator cuff inflammation, note: remember that degenerative type changes in an unusual location are usually due to CPPD, the shoulder has the greatest range of motion of all joints so we wouldn't usually expect to see OA here |
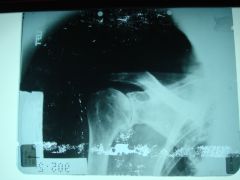
ID
|
|
|
310 Arthritis shoulder,
Osteophytes off of medial surface of the humeral head (glenoid lip - on cartilage that surrounds the bone), narrowing of the A-H distance most likely caused by chronic rotator cuff tendonitis, multiple cysts in humeral head, again most likely due to chronic rotator cuff inflammation, note: remember that degenerative type changes in an unusual location are usually due to CPPD, the shoulder has the greatest range of motion of all joints so we wouldn't usually expect to see OA here |
ID
|
|
|
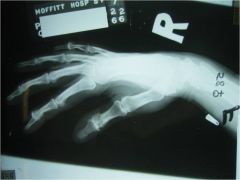
313-F Osteoarthritis hand,
degenerative changes at the DIP joints, joint narrowing, osteophyte formation - more prominent on the dorsal surface, subchondral sclerosis, degenerative changes at the first CMCP joint |
ID
|
|
|
313-F(2) Osteoarthritis hand, degenerative changes at the DIP joints, joint narrowing, osteophyte formation - more prominent on the dorsal surface, subchondral sclerosis, degenerative changes at the first CMCP joint
|
ID
|
|
|
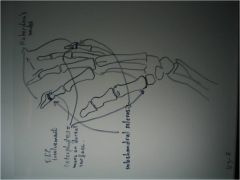
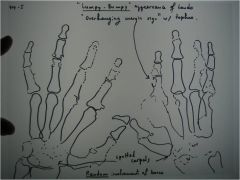
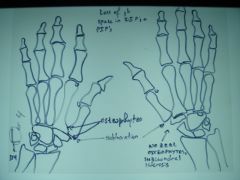
314-I Gout,
lumpy-bumpy appearance, pancarpal involvement (universal), random involvement (not symmetrical), marginal and intraarticular erosions (see R 2nd digit), overhanging margin sign (bone growth around the tophi) (unique to gout - eroding and pushing), relative preservation of the joint spaces, treatment: allopurinal (inhibits xanthine oxidase), indomethacin or colchicine for acute episodes, Spotty carpal sign = loss of cortical margin |
ID
|
|
|
314-I(2) Gout,
lumpy-bumpy appearance, pancarpal involvement (universal), random involvement (not symmetrical), marginal and intraarticular erosions (see R 2nd digit), overhanging margin sign (bone growth around the tophi) (unique to gout - eroding and pushing), relative preservation of the joint spaces, treatment: allopurinal (inhibits xanthine oxidase), indomethacin or colchicine for acute episodes, Spotty carpal sign = loss of cortical margin |
ID
|
|
|
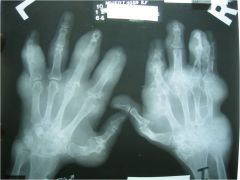
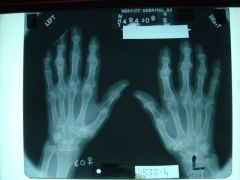
314-L Osteoarthritis hand,
B/L study of hands (like 310), DIP and PIP involvement, jt narrowing, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, 1st CMCP involvement, radial subluxation of the 1st MC, osteophyte formation, (OA in MCP - CPPD) at MCP jt osteophytes called "hook" |
ID
|
|
|
314-L(2) Osteoarthritis hand,
B/L study of hands (like 310), DIP and PIP involvement, jt narrowing, osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, 1st CMCP involvement, radial subluxation of the 1st MC, osteophyte formation, (OA in MCP - CPPD) at MCP jt osteophytes called "hook" |
ID
|
|
|
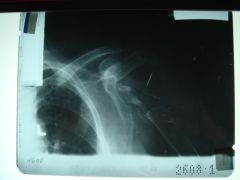
317-1 Neurotrophic arthropathy, Charcot's jt,
Shoulder, Destruction of humeral head and glenoid fossa, Shoulder jt not weight bearing so no density change, tent-like end of bone = "licked candycane appearance" (if perfectly straight = "pseudoamputation appearance"), debris, upper extremity charcot's jt could indicate syringomyelia (present with cervical anomalies - Arnold Chiari malformation) |
ID
|
|
|
323-1 Gout,
erosions at the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP), hallux valgus deformity, intra-articular erosion, overhanging margin sign, relative preservation of the joint space, asymmetry, the last 2 help to differentiate from RA, soft tissue swelling, cystic lucencies - crystal balls of monosodium urate pressing, pressure erosions around outside bones = Periarticular erosions (Gout is a lack of protein, collect monosodium urate, deposit around jt, pt no pain most of life, pain triggered with diet and stress (overload to system), crystals cross synovial membrane into jt space which is very painful, untreated it lasts for 14-21 days, self-resolving, acute inflammation - contraindication to adjust that jt, mediate pain with antiinflammatories (diarrhea), xray features directly proportional to length of deposit and number of attacks, erosions take months to years, avoid red wine, beer, and aspirin) |
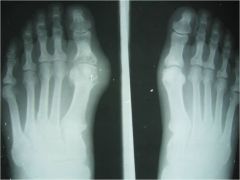
ID
|
|
|
323-1(2)Gout,
erosions at the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP), hallux valgus deformity, intra-articular erosion, overhanging margin sign, relative preservation of the joint space, asymmetry, the last 2 help to differentiate from RA, soft tissue swelling, cystic lucencies - crystal balls of monosodium urate pressing, pressure erosions around outside bones = Periarticular erosions (Gout is a lack of protein, collect monosodium urate, deposit around jt, pt no pain most of life, pain triggered with diet and stress (overload to system), crystals cross synovial membrane into jt space which is very painful, untreated it lasts for 14-21 days, self-resolving, acute inflammation - contraindication to adjust that jt, mediate pain with antiinflammatories (diarrhea), xray features directly proportional to length of deposit and number of attacks, erosions take months to years, avoid red wine, beer, and aspirin) |
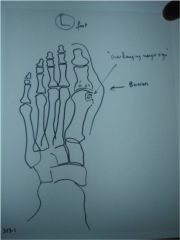
ID
|
|
|
951-1 Scaphoid fx, upper left,
4 film study, fx at proximal pole of the scaphoid on initial evaluation |
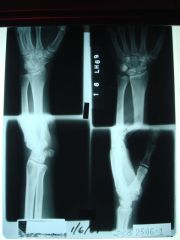
ID
|
|
|
951-1(2) Scaphoid fx, upper left,
4 film study, fx at proximal pole of the scaphoid on initial evaluation |
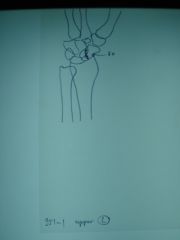
ID
|
|
|
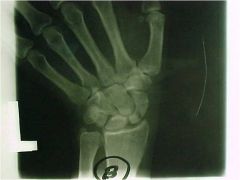
951-2 Scaphoid fx,
Ulnar deviation, fx at proximal pole of the scaphoid on initial evaluation, follow up demonstrates non-union, and evidence of AVN at the proximal fragment = Preiser's dx, last follow up shows evidence of healing (inc density = dead trabeculae with new calcified osteoid - bone can collapse) |
ID
|
|
|
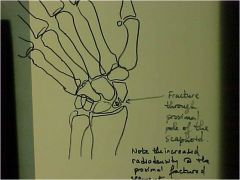
951-2(2)Scaphoid fx,
Ulnar deviation, fx at proximal pole of the scaphoid on initial evaluation, follow up demonstrates non-union, and evidence of AVN at the proximal fragment = Preiser's dx, last follow up shows evidence of healing (inc density = dead trabeculae with new calcified osteoid - bone can collapse) |
ID
|
|
|
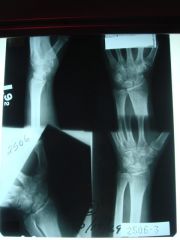
951-3 Scaphoid fx,
4 film study, normal position of lunate on lateral, very subtle hair-line radiolucency visible at the proximal pole of the scaphoid in oblique, fx at proximal pole of the scaphoid on initial evaluation |
ID
|
|
|
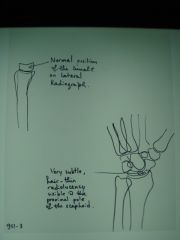
951-3(2)Scaphoid fx,
4 film study, normal position of lunate on lateral, very subtle hair-line radiolucency visible at the proximal pole of the scaphoid in oblique, fx at proximal pole of the scaphoid on initial evaluation |
ID
|

