![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
which side is the xray tube located at? high voltage side or low voltage?
|
High voltage.
|
|
|
what are the two types of xray tubes?
|
1. stationary anode
2. rotating anode |
|
|
Which end of the x-ray tube is the positive end?
|
Anode
|
|
|
what are some problems with early rotating anode disk made only out of one material, tungsten?
|
-limited heat storage capacity
-wobbling -pitting -causes early aging of xray tubes |
|
|
RTM anode disk
|
-90% tungsten 10% rhenium
Fewer rotational problems Resistance to aging Greater heat storage capacity Less target roughening High and uniform dose |
|
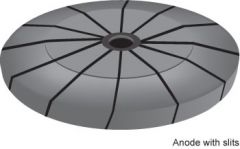
RTM Anode Disk with Slits
|
-slits angled 20 degrees to the axis of rotation.
-prevent the electrons from passing through the anode and hitting the glass envelope - Adding the slits to the anode also prevents cracking and helps keep the anode from distorting. |
|
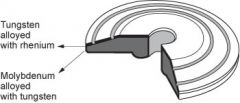
Anode Disk with Grooves
|
-alternative to slits
-surface of this disk is composed of tungsten alloyed with rhenium -base of molybdenum alloyed with tungsten. |
|
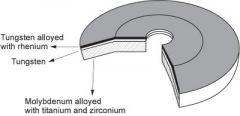
TZM Anode Disk
|
-pure tungsten sandwiched between a surface layer of tungsten alloyed with rhenium
-base is molybdenum alloyed with titanium and zirconium |
|
|
anode rotation from ball bearings. what do they use now?
|
replaced with a liquid metal lubricant, using hydroplaning principles.
|
|
|
as the anode angle increases, the field size?
as the SID increases, the field size? |
the field size also increases for both
|
|
|
what does the protective housing or envelope do?
|
contains the x-rays produced, protects the x-ray tube, insulates the technologist from electrical shock and acts as a thermal conductor to dissipate the heat that is produced in x-ray production.
|
|
|
what are the two basic types of envelopes for the x-ray tubes?
|
Metal-glass envelopes
Metal envelopes with ceramic insulators |
|
|
tubes with metal-glass envelopes
|
-two windows, one made of beryllium, and the other aluminum.
-large volume anode disk 100mm diameter + cathode Functions of metal envelope: -Encases the electron optical field between the cathode and anode -Lengthens tube life, as the metal is unaffected by tungsten deposits so there is no arcing |
|
|
Tubes with Metal Envelopes and Ceramic Insulators
|
-better thermal and electrical properties than glass
-more mechanically stable -direct oil cooling of the spiral groove bearing. -accommodate a large diameter anode disk (120 mm) with improved cooling and more loadability, allowing the tube to produce more x-rays over a specific time. functions of metal envelope: -Encase the electron optical field between cathode and anode and maintain a constant electric potential between electrons and the envelope -Prevent arcing, as the metal is unaffected by tungsten deposits |
|
|
mammography tubes
|
-tungsten/molybdenum or rhodium target is used
-no aluminum filter |
|
|
grid controlled xray tube
|
-used in digital radiography, digital subtraction angiography and mobile x-ray machines
-designed to turn on and off quickly |
|
|
Special X-ray Tube for Multi-Slice CT Scanning
|
-specially designed for the best heat dissipation
- run for up to 60 seconds continuously |
|
|
The Straton tube
|
-developed to dissipate heat faster
-anode is in direct contact with the cooling oil -fast heat exchange. |
|
|
What is the main purpose for using a rotating anode?
|
better heat dissipation, longer life.
|
|
|
What is the best anode angle for doing barium studies?
|
15 degrees. why? :(
|
|
|
What is an advantage of an x-ray tube with a metal envelope with ceramic insulator?
|
better thermal properties, accomodates larger anode
|
|
|
What is the best filter for a mammography unit?
|
molybdenum
|
|
|
Why is the rhodium target used in a mammography unit?
|
23 kev produced
|
|
|
Why is a grid-controlled x-ray tube used for specialized radiography?
|
turns on and off quickly
|
|
|
Which x-ray tube has the anode in direct contact with the cooling oil?
|
stranton tube
|
|
|
What is the main advantage of the Stranton tube?
|
no wait times for anode to cool
|
|
|
What is the purpose of slits in the anode?
|
prevents the anode from cracking
|
|
|
What problems are associated with a pure tungsten anode?
|
Limited heat storage capacity
Wobbling Pitting |

