![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
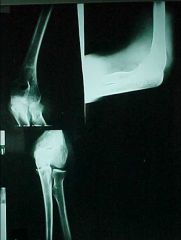
801-1,2, Chisel fx, Lateral and AP view, Alteration at the anterior fat pad causing sail shape (normally present as teardrop hugging the humerus), Posterior fat pad present (abnornal) which is indicative of intraarticular fx, Subtle fx line visible at the radial head on AP view, MOI: fall on outstretched arm causing radial head snap against the capitelum, UNSTABLE as all elbow fx's, refer to ortho surgeon, M/C fx of the elbow in ADULTS
|
Identify
|
|
|
801-1,2(2), Chisel fx, Lateral and AP view, Alteration at the anterior fat pad causing sail shape (normally present as teardrop hugging the humerus), Posterior fat pad present (abnornal) which is indicative of intraarticular fx, Subtle fx line visible at the radial head on AP view, MOI: fall on outstretched arm causing radial head snap against the capitelum, UNSTABLE as all elbow fx's, refer to ortho surgeon, M/C fx of the elbow in ADULTS
|
Identify
|
|
|
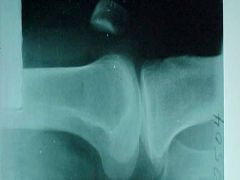
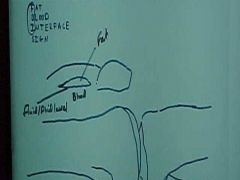
806-1, Bumper, aka Fender fx, FBI (fat (radioluscent)-blood interface) sign (intraarticular fx) on Cross Table Lateral of the knee (cassette between knees), View identifies by femur straight on tibia
|
Identify
|
|
|
806-1(2), Bumper, aka Fender fx, FBI (fat (radioluscent)-blood interface) sign (intraarticular fx) on Cross Table Lateral of the knee (cassette between knees), View identifies by femur straight on tibia
|
Identify
|
|
|
806-2, Bumper, aka Fender fx, Internal rotation (patella opposite fibula) and External rotation (patella same side as fibula) of the knee shown, Depressed fx along the articular surface of the tibial plateau (PROXIMAL TIBIA), Zone of condensation, Valgus injury
|
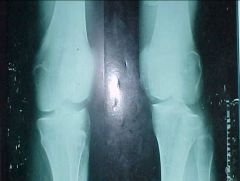
Identify
|
|
|
806-2(2), Bumper, aka Fender fx, Internal rotation (patella opposite fibula) and External rotation (patella same side as fibula) of the knee shown, Depressed fx along the articular surface of the tibial plateau (PROXIMAL TIBIA), Zone of condensation, Valgus injury
|
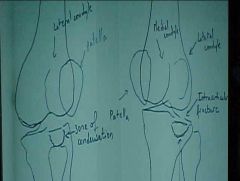
Identify
|
|
|
807-1, Femoral neck fx, AP view of pelvis (acceptable for AP view of hip), Subtle interruption of the cortex of the superior portion of the femoral neck in subcapital location, intracupsular fx, area of poor vascularization, MOI: non-specific, person is ambulatory with positive ortho tests, fx was initially missed and 2 wks later the neck of the femur projects superior (those are also usually posterior), needs to be pinned in young, hip replacement in old (fx easier with age,osteoporosis)
|
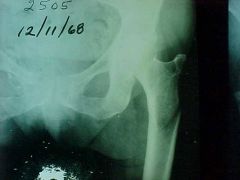
Identify
|
|
|
807-1(2), Femoral neck fx, AP view of pelvis (acceptable for AP view of hip), Subtle interruption of the cortex of the superior portion of the femoral neck in subcapital location, intracupsular fx, area of poor vascularization, MOI: non-specific, person is ambulatory with positive ortho tests, fx was initially missed and 2 wks later the neck of the femur projects superior (those are also usually posterior), needs to be pinned in young, hip replacement in old (fx easier with age,osteoporosis)
|
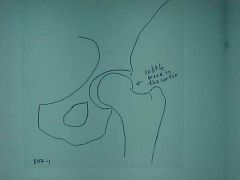
Identify
|
|
|
808-2
|
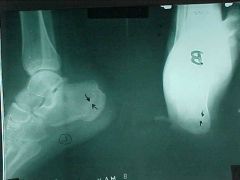
ID
|
|
|
808-2(2)
|
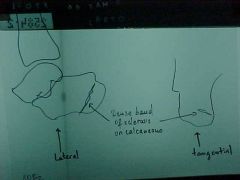
ID
|
|
|
808-4, Stress fx, Fatigue fx, (bilateral study) bilateral and symmetrical at the shaft of the tibia with endosteal and periosteal callus, mimics tumor or infection but is bilateral
|
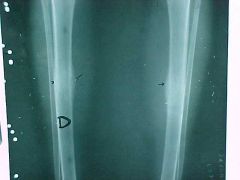
Identify
|
|
|
808-4(2), Stress fx, Fatigue fx, (bilateral study) bilateral and symmetrical at the shaft of the tibia with endosteal and periosteal callus, mimics tumor or infection but is bilateral
|

ID
|
|
|
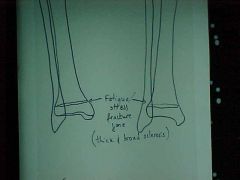
808-5, Stress fx, Fatigue fx at the distal tibia, same leg - 2 different views (opposite leg will look same)broad sclerotic rim mimicking an epiphyseal growth center but much denser (location of injury poor for bone scan in young)
|
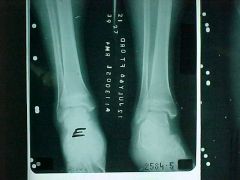
Identify
|
|
|
808-5(2), Stress fx, Fatigue fx at the distal tibia, same leg - 2 different views (opposite leg will look same)broad sclerotic rim mimicking an epiphyseal growth center but much denser (location of injury poor for bone scan in young)
|
ID
|
|
|
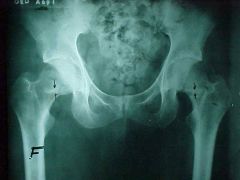
808-6, Stress fx, Fatigue/Insufficiency fxs at the femoral necks, bands of radiodensity across femoral neck (stress fx zone), rare, check for underlying bone softening disease, NOTE: always correlate with pt's history
|
Identify
|
|
|
808-6(2), Stress fx, Fatigue/Insufficiency fxs at the femoral necks, bands of radiodensity across femoral neck (stress fx zone), rare, check for underlying bone softening disease, NOTE: always correlate with pt's history
|

ID
|
|
|
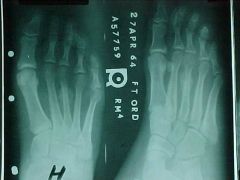
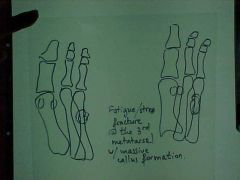
808-8, Stress fx, March fx -Classic stress fx in foot, Solid periosteal callus at the 3rd metatarsal indicative of new bone formation
|
Identify
|
|
|
808-8(2), Stress fx, March fx -Classic stress fx in foot, Solid periosteal callus at the 3rd metatarsal indicative of new bone formation
|
ID
|
|
|
811-1,2, Monteggia fx, Hyperextension/hyperflexion injury with fx of the FOREARM - PROXIMAL 1/3 of the ULNA, non-comminuted, recent (jagged edges), transverse fx - indicates possibility of underlying pathology, overriding aka imbrication aka foreshortening aka telescoping of the 2 segments, radial and palmar displacement of the distal segment, posterior dislocation of the radial head, if angulation is greater than 10 degrees immediate referral to an orthopedic surgeon, complications: radial n. palsy from anterior displacement of radial head
|
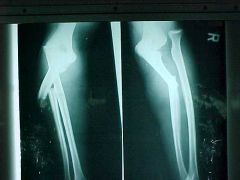
Identify
|
|
|
811-1,2(2), Monteggia fx, Hyperextension/hyperflexion injury with fx of the FOREARM - PROXIMAL 1/3 of the ULNA, non-comminuted, recent (jagged edges), transverse fx - indicates possibility of underlying pathology, overriding aka imbrication aka foreshortening aka telescoping of the 2 segments, radial and palmar displacement of the distal segment, posterior dislocation of the radial head, if angulation is greater than 10 degrees immediate referral to an orthopedic surgeon, complications: radial n. palsy from anterior displacement of radial head
|
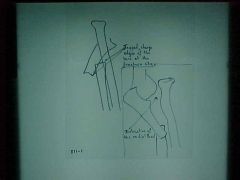
ID
|
|
|
812-1,2, Galleazzi fx, Complete transverse fx of the FOREARM - DISTAL 1/3 of the RADIUS, non-comminuted, healing (callus formation = fuzzy border) solid periosteal rxn at 10-14 days, anterior and radial angulation of the distal segment (displacement -reference proximal bone, refer to an orthopedic surgeon, complications:non-union, ulnar dislocation also seen
|
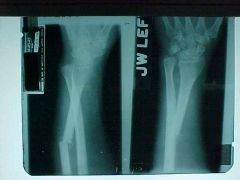
Identify
|
|
|
812-1,2(2), Galleazzi fx, Complete transverse fx of the FOREARM - DISTAL 1/3 of the RADIUS, non-comminuted, healing (callus formation = fuzzy border) solid periosteal rxn at 10-14 days, anterior and radial angulation of the distal segment (displacement -reference proximal bone, refer to an orthopedic surgeon, complications:non-union, ulnar dislocation also seen
|
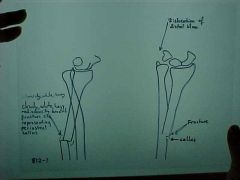
ID
|
|
|
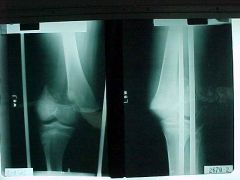
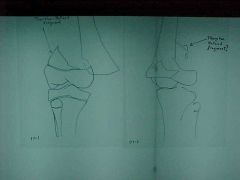
813-1,2, Salter-Harris Type II fx through growth plate and obliquely through the metaphysis, AP and lateral views, metaphyseal fragment is called Thurston-Holland fragment (corner sign), 75% of epipheseal injuries, favorable prognosis
|
Identify
|
|
|
813-1,2(2), Salter-Harris Type II fx through growth plate and obliquely through the metaphysis, AP and lateral views, metaphyseal fragment is called Thurston-Holland fragment (corner sign), 75% of epipheseal injuries, favorable prognosis
|
ID
|
|
|
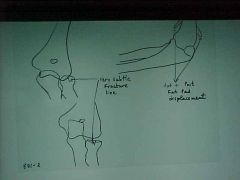
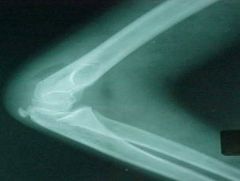
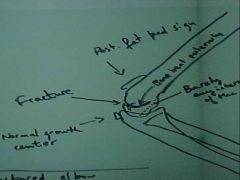
815-1a, Supracondylar fx, Right fractured elbow, Positive posterior fat pad sign (abnormal sign of fx), draw a line on the lateral elbow along the anterior surface of the humerus, it should intersect the humeral condyles 1/2 way or close, if most of the condyles are behind the line it is a fx, MOI: fall on outstretched arm, or child runs into something, elbow hyperextends and condyles twist and bend backward, UNSTABLE but treatment is conservative with bracing (all elbow fx's potentially unstable), M/C fx of the elbow in CHILDREN
|
Identify
|
|
|
815-1a(2), Supracondylar fx, Right fractured elbow, Positive posterior fat pad sign (abnormal sign of fx), draw a line on the lateral elbow along the anterior surface of the humerus, it should intersect the humeral condyles 1/2 way or close, if most of the condyles are behind the line it is a fx, MOI: fall on outstretched arm, or child runs into something, elbow hyperextends and condyles twist and bend backward, UNSTABLE but treatment is conservative with bracing (all elbow fx's potentially unstable), M/C fx of the elbow in CHILDREN
|
ID
|
|
|
815-2, Supracondylar fx, Left Normal film, NO posterior fat pad, Anterior humeral line bisects condyle
|
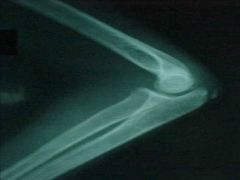
ID
|
|
|
815-1b(2), Supracondylar fx, Left Normal film, NO posterior fat pad, Anterior humeral line bisects condyle
|

ID
|
|
|
816-1, Femoral neck fx, Zone of impaction (sharp acute angle) in the subcapital portion of the femoral neck along the inferior border, that goes to the middle of the femoral neck and continues as a radioluscent line, Displacement of the fat planes (gluteal, psoas), needs to be pinned (intracapsular fx's always surgical), well defined homogenous calcification (renal stone) also seen (bladder stones can be cancerous b/c transitional cells of bladder have high turnover rate, indications of stone too big to get out by gender, females - up/down at toilet, males - move hips)
|
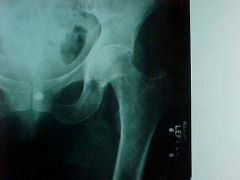
Identify
|
|
|
816-1(2), Femoral neck fx, Zone of impaction (sharp acute angle) in the subcapital portion of the femoral neck along the inferior border, that goes to the middle of the femoral neck and continues as a radioluscent line, Displacement of the fat planes (gluteal, psoas), needs to be pinned (intracapsular fx's always surgical), well defined homogenous calcification (renal stone) also seen (bladder stones can be cancerous b/c transitional cells of bladder have high turnover rate, indications of stone too big to get out by gender, females - up/down at toilet, males - move hips)
|
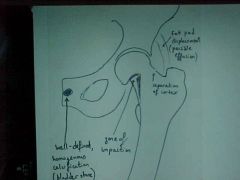
ID
|
|
|
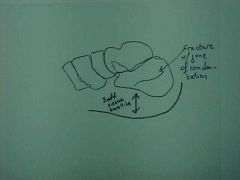
817-1, Calcaneal compression fx, Zone of condensation, soft tissue swelling (tells us injury is recent), dec in Boehler's angle (often times the only finding), MOI: fall from a height which force of body weight gets transmitted through the tibia and talus into calcaneous, x-ray T-L junction because of high incidence with vertebral compression fx (10-15%), no regrow height, can have multiple fx's in this area because all the ligaments and tendons keep it stable
|
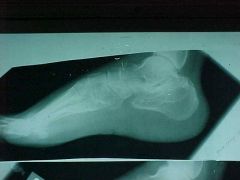
Identify
|
|
|
817-1(2), Calcaneal compression fx, Zone of condensation, soft tissue swelling (tells us injury is recent), dec in Boehler's angle (often times the only finding), MOI: fall from a height which force of body weight gets transmitted through the tibia and talus into calcaneous, x-ray T-L junction because of high incidence with vertebral compression fx (10-15%), no regrow height, can have multiple fx's in this area because all the ligaments and tendons keep it stable
|
ID
|
|
|
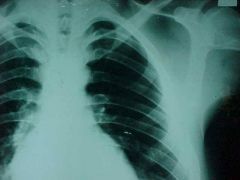
818-1,2, Rib and sternum fx's, PA and lateral chest film (rib fx's require 4 or 5 oblique films), a non-comminuted fx at the distal 2/3 of the body of the sternum with anterior displacement of the distal fragment, MOI: direct blow to chest, may or may not have cardiac findings, usually stable and left to heal in this position, another fx through the anterior margin of the 4th left rib, may be initially occult so follow up in 8-10 days and retake films (#1 place to get occult)
|
Identify
|
|
|
818-1,2(2), Rib and sternum fx's, PA and lateral chest film (rib fx's require 4 or 5 oblique films), a non-comminuted fx at the distal 2/3 of the body of the sternum with anterior displacement of the distal fragment, MOI: direct blow to chest, may or may not have cardiac findings, usually stable and left to heal in this position, another fx through the anterior margin of the 4th left rib, may be initially occult so follow up in 8-10 days and retake films (#1 place to get occult)
|
ID
|
|
|
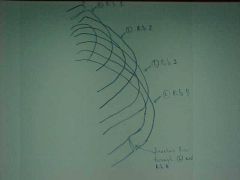
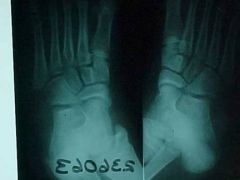
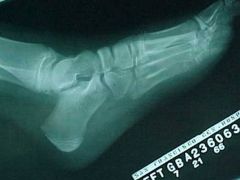
820-1, Jones fx, aka Dancer's fx, Transverse fx line at the base of the 5th metatarsal, M/C fx in the FOOT, MOI: inversion with plantarflexion where the tendon of the peroneous brevis or the lateral portion of the plantar aponeurosis tractions a piece of bone causing avulson fx (at the base of the 5th metatarsal), not to confuse with the longitudinally oriented normal apophysis (growth center), the further away the fx is from the base, the longer it take to heal (adult - boot, child - cast)
|
Identify
|
|
|
820-1(2), Jones fx, aka Dancer's fx, Transverse fx line at the base of the 5th metatarsal, M/C fx in the FOOT, MOI: inversion with plantarflexion where the tendon of the peroneous brevis or the lateral portion of the plantar aponeurosis tractions a piece of bone causing avulson fx (at the base of the 5th metatarsal), not to confuse with the longitudinally oriented normal apophysis (growth center), the further away the fx is from the base, the longer it take to heal (adult - boot, child - cast)
|
ID
|
|
|
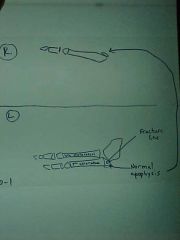
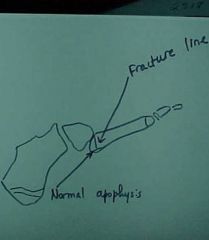
820-3, Jones fx, aka Dancer's fx, Transverse fx line at the base of the 5th metatarsal, not to confuse with the normal apophysis
820-4 Oblique view of ankle |
ID
|
|
|
820-3(2), Jones fx, aka Dancer's fx, Transverse fx line at the base of the 5th metatarsal, not to confuse with the normal apophysis
820-4 Oblique view of ankle |
ID
|
|
|
821-1,2, Stable compression fx, loss of body height, step defect at L2, no zone of condensation (impaction), no evidence of retropulsion, MOI: hyperflexio with or without axial load, STABLE injury, but may collapse further
|
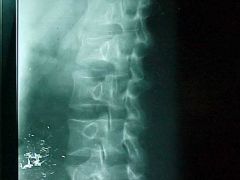
Identify
|
|
|
821-1,2(2), Stable compression fx, loss of body height, step defect at L2, no zone of condensation (impaction), no evidence of retropulsion, MOI: hyperflexio with or without axial load, STABLE injury, but may collapse further
|
ID
|
|
|
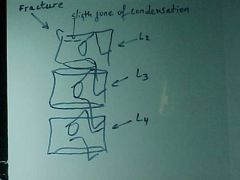
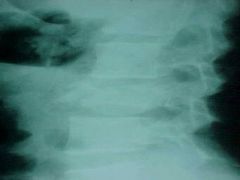
822-1, Burst fx, Comminuted fx at the body of L3, spreading of the pedicales (inc in the interpedicular distance) and fx of the posterior elements and retropulsion, very UNSTABLE, immediate referral
|
Identify
|
|
|
822-1(2), Burst fx, Comminuted fx at the body of L3, spreading of the pedicales (inc in the interpedicular distance) and fx of the posterior elements and retropulsion, very UNSTABLE, immediate referral
|
ID
|
|
|
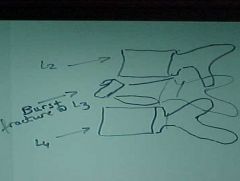
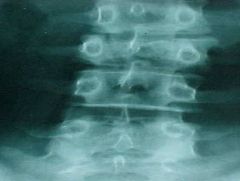
822-2, Burst fx, Comminuted fx at the body of L3, spreading of the pedicales (inc in the interpedicular distance)
|
ID
|
|
|
822-2(2), Burst fx, Comminuted fx at the body of L3, spreading of the pedicales (inc in the interpedicular distance)
|

ID
|
|
|
930-2a, Metatarsal fx, hair thin radioluscent horizontal line at the distal 1/3 of the 2nd metatarsal, probably missed initially, a few months later there evidence of callus around the fx, not an initially occult fx
|
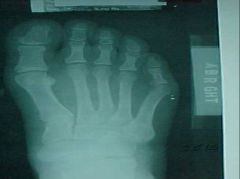
Identify
|
|
|
930-2a(2), Metatarsal fx, hair thin radioluscent horizontal line at the distal 1/3 of the 2nd metatarsal, probably missed initially, a few months later there evidence of callus around the fx, not an initially occult fx
|
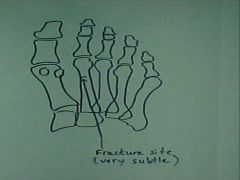
ID
|
|
|
930-2b, Metatarsal fx, fx site with periosteal callus, healing, not healed or acute
|
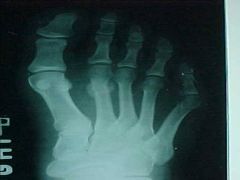
ID
|
|
|
930-2b(2), Metatarsal fx, fx site with periosteal callus, healing, not healed or acute
|
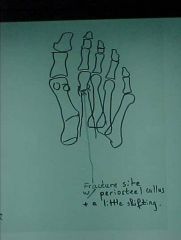
ID
|
|
|
834-2, Chance, aka Lap-belt fx, Lateral film, Radioluscent fx zone extending into the lamina and anterior margin of L2 causing separation of the posterior arch, UNSTABLE injury, MOI: hyperflexion with fulcrum further away from the spine, ex. running over a fence to catch a ball, lap belt with no shoulder component, STABLE compression fx at L3, step defect present at L2 & L3, Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP): 3% iodine in cubital fossa, x-ray pt at different time intervals, scout film, nephrogram (outline parenchyma), pyelogram (calyces and renal pelvis)
|
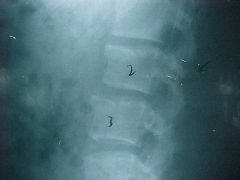
Identify
|
|
|
834-1(2), Chance, aka Lap-belt fx, Lateral film, Radioluscent fx zone extending into the lamina and anterior margin of L2 causing separation of the posterior arch, UNSTABLE injury, MOI: hyperflexion with fulcrum further away from the spine, ex. running over a fence to catch a ball, lap belt with no shoulder component, STABLE compression fx at L3, step defect present at L2 & L3, Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP): 3% iodine in cubital fossa, x-ray pt at different time intervals, scout film, nephrogram (outline parenchyma), pyelogram (calyces and renal pelvis)
|
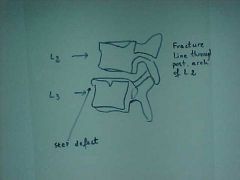
ID
|
|
|
834-4, Chance, aka Lap-belt fx, Lateral Tomogram, radioluscent fx zone extending into the lamina and anterior margin of L2 causing separation of the posterior arch, UNSTABLE injury, STABLE compression fx at L3, step defect and zone of condensation present at L2 & L3
|
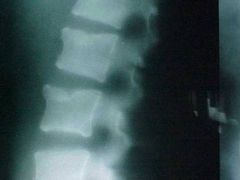
ID
|
|
|
834-2(2), Chance, aka Lap-belt fx, Lateral Tomogram, radioluscent fx zone extending into the lamina and anterior margin of L2 causing separation of the posterior arch, UNSTABLE injury, STABLE compression fx at L3, step defect and zone of condensation present at L2 & L3
|
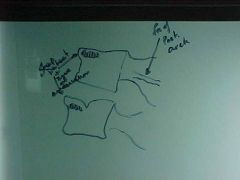
ID
|
|
|
834-3, Chance, aka Lap-belt fx, AP Tomogram, Radioluscent fx zone extending through lamina/pedicle of L2 causing separation of the posterior arch, UNSTABLE injury, STABLE compression fx at L3
|
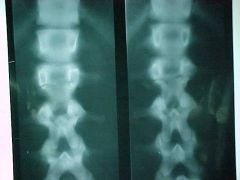
ID
|
|
|
834-3,4(2), Chance, aka Lap-belt fx, AP Tomogram, Radioluscent fx zone extending through lamina/pedicle of L2 causing separation of the posterior arch, UNSTABLE injury, STABLE compression fx at L3
|
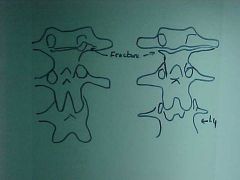
ID
|
|
|
835-1, Hangman's fx, Radioluscent fx zone at the body-pedicle junction of C2 with anterolisthesis, break in the spinolaminar junction line at C1, MOI: hyperextension with the chin being jerked back, refer pt to an orthopedic surgeon for fusion (use spine board for transportation, because of fx instability), MRI for soft tissue evaluation, possible occipitalization - need flex/ext films to be sure
|
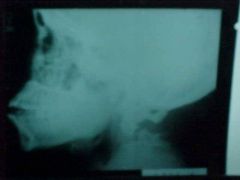
Identify
|
|
|
835-1(2), Hangman's fx, Radioluscent fx zone at the body-pedicle junction of C2 with anterolisthesis, break in the spinolaminar junction line at C1, MOI: hyperextension with the chin being jerked back, refer pt to an orthopedic surgeon for fusion (use spine board for transportation, because of fx instability), MRI for soft tissue evaluation, possible occipitalization - need flex/ext films to be sure
|
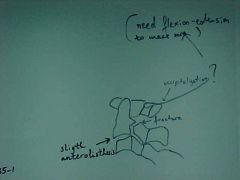
ID
|
|
|
836-2, Jefferson's fx, aka Burst fx C1, Tomogram (allows for detailed examination of an area), CT scan in current times, displacement of the lateral masses of C1 over the facets of C2 (overhanging of the lateral masses), MOI: hyperflexion with axial load (usually) or axial load only, fx may or may not be stable, but we always consider it as UNSTABLE, spine board transportation to ER
|
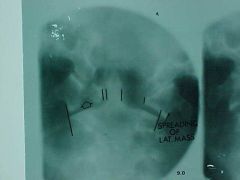
Identify
|
|
|
836-2(2), Jefferson's fx, aka Burst fx C1, Tomogram (allows for detailed examination of an area), CT scan in current times, displacement of the lateral masses of C1 over the facets of C2 (overhanging of the lateral masses), MOI: hyperflexion with axial load (usually) or axial load only, fx may or may not be stable, but we always consider it as UNSTABLE, spine board transportation to ER
|
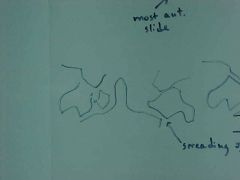
ID
|
|
|
902-1,2, Salter-Harris Type I & III, soft tissue swelling at the left ankle, wider GP at the distal fibula than at the adjacent tibia is Salter-Harris type I, radiographs may appear normal, however pt experiences pain over GP and has soft tissue swelling, fx partially through GP and portion of the epiphysis is Salter-Harris type III is intraarticular fx, may require surgical repair
|
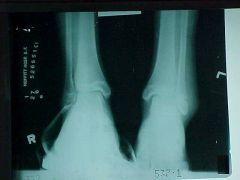
Identify
|
|
|
902-1,2(2), Salter-Harris Type I & III, soft tissue swelling at the left ankle, wider GP at the distal fibula than at the adjacent tibia is Salter-Harris type I, radiographs may appear normal, however pt experiences pain over GP and has soft tissue swelling, fx partially through GP and portion of the epiphysis is Salter-Harris type III is intraarticular fx, may require surgical repair
|
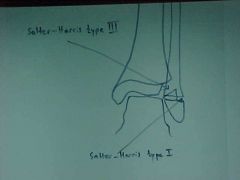
ID
|
|
|
908-1,2, Comminuted fx of the tibia, Butterfly segment, fx at the tibial eminences, cross table lateral x-ray (pt seated with knee fully extended for 30-45 sec before x-ray taken), taken when suspicion of intraarticular fx to check for fatty marrow leakage into the joint, FBI sign (Fat-Blood Interface) at the suprapatellar bursa, refer to an orthopedic surgeon
|
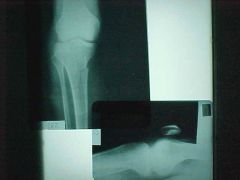
Identify
|
|
|
908-1,2(2), Comminuted fx of the tibia, Butterfly segment, fx at the tibial eminences, cross table lateral x-ray (pt seated with knee fully extended for 30-45 sec before x-ray taken), taken when suspicion of intraarticular fx to check for fatty marrow leakage into the joint, FBI sign (Fat-Blood Interface) at the suprapatellar bursa, refer to an orthopedic surgeon
|
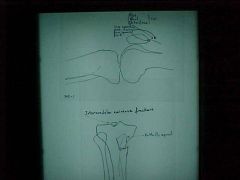
ID
|
|
|
954-1,2, Compression fx, dec in body height, step defect, zone of condensation, L2&L3 are STABLE, break in George's line at L4, L4 is UNSTABLE because of retropulsion into the spinal canal = burst fx, L5-S1 tropism (incidental findings), MOI for multiple compression fx's with skips in btwn - skier rolling downhill, multiple myeloma
|
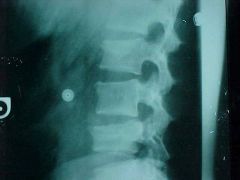
Identify
|
|
|
954-2(2), Compression fx, dec in body height, step defect, zone of condensation, L2&L3 are STABLE, break in George's line at L4, L4 is UNSTABLE because of retropulsion into the spinal canal = burst fx, L5-S1 tropism (incidental findings), MOI for multiple compression fx's with skips in btwn - skier rolling downhill, multiple myeloma
|

ID
|
|
|
810-1,2, AI dislocation of the shoulder at the Glenohumeral joint, M/C site of dislocation in the body, AI M/C, aka Subcoracoid dislocation, MOI: abduction, extension, external rotation, causes an Impaction fx (hatchet, hill sachs deformity) - v-shaped indentation as seen in Axillary view
|
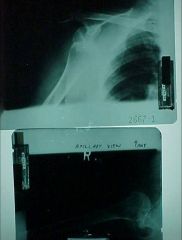
Identify
|
|
|
810-1,2(2), AI dislocation of the shoulder at the Glenohumeral joint, M/C site of dislocation in the body, AI M/C, aka Subcoracoid dislocation, MOI: abduction, extension, external rotation, causes an Impaction fx (hatchet, hill sachs deformity) - v-shaped indentation as seen in Axillary view
|
ID
|
|
|
808-7
|
Stress/Fatigue fx, sport's groin strain (sport's hernia), avulsion fx of pubic symphysis due to adductor mm., common in athletes and osteoporotics
|

