![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomically programmed technique (anatomically programmed radiography) |
Pre-program set of exposure factors that are displayed and selected for use |
|
|
|
Caliper |
Device used to measure part thickness -part measured at CR location or thickest portion of area to be radiographed -can be measured using cm. or in. |

|
|
|
Fixed kvp |
-Kvp remains constant -mAs varies with part thickness +4-5 cm increase -> double mAs -4-5 cm decrease -> half mAs |
|
|
|
Variable kVp |
-mAs remains constant -kvp varies with part thickness -Most effective with pediatric patients or small extremities +1 cm increase -> +2 kVp -1 cm decrease -> -2 kVp |
|
|
|
Additive pathology |
Diseases or conditions that increase absorption characteristics Generally requires an increase in technique |
|
|
|
Destructive pathology |
Diseases or conditions that can decrease absorption characteristics Generally requires a decrease in technique |
|
|
|
Pediatric considerations |
Require lower technique when compared to adults Requires fast exposure time to prevent motion Manual techniques recommended |
|
|
|
Geriatric considerations |
May require lower techniques due to decreased bone density, decreased thickness May require fast exposure time to prevent motion |
|
|
|
Bariatric considerations |
Requires an increase in exposure factors May need to be image and quadrants due to size limitations |
|
|
|
Contrast media considerations |
Positive contrast- requires an increase in exposure factors, increases attenuation Negative contrast- requires a decrease or no change in exposure factors, decreases attenuation |
|
|
|
Automatic exposure control |
Purpose is to control density and receptor exposure. mAs is always determined after exposure Consist of photocell/chamber/detector/cells Terminate exposure automatically when films/image reaches set density/receptor exposure |
|
|
|
Advantages of AEC |
Measurement of part is not required System will utilize shortest possible exposure time and appropriate receptor exposure / density |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of AEC |
Not suitable for breathing techniques Anatomy of interest must be properly centered over detector/cell Appropriate Bucky must be activated Appropriate cell / Chambers must be activated |
|
|
|
Minimum response time |
Required time for the AEC system to operate |
|
|
|
Backup time |
Safety mechanism for patient radiation dose Overrides the AEC if a component fails to terminate exposure -prevents excessive patient exposure and x-ray tube damage |
|
|
|
Photomultiplier system |
Generally an exit type AEC system Located behind or under IR require special cassette without lead backing. |
|
|
|
Ionization chamber |
Generally an entrance type AEC system Located between the IR and patient, increases object to image receptor distance (OID) Chambers is filled with air / gas atoms that are ionized by exit radiation coming from the patient Contains two electrodes: thin metal sheets and fine wire grid |
|
|
|
Thyratron |
electronic switch that sends signal to relay when predetermined |
|
|
|
Relay |
opens the exposure circuit and terminates the exposure |
|
|
|
Photomultiplier tube |
convert light to electrical signal |
|
|
|
Capacitor |
stores electrical energy |
|
|
|
Relay |
opens the exposure circuit and terminate exposure |
|
|
|
Light paddles |
-absorbs radiation and converts it to light PMT SYSTEM |
|
|
|
Minimum response time |
required time for AEC to operate |
|
|
|
Backup time |
Safety mechanism for patient radiation dose; overrides AEC if component fails to terminate exposure |
|
|
|
Technicals factors with AEC |
Appropriate Bucky activated Appropriate cells activated Part must be properly centered over cells |
|
|
|
Type of technique chart that has a constant kvp variable mAs according to part thickness |
Fixed kVp, Variable mAs |
|
|
|
Type of technique chart that has a variable kvp fixed mAs according to part thickness |
Variable kVp fixed mAs |
|
|
|
Plaster cast may require a(n) ____________ in technique |
Increase |
|
|
|
|
Variable kVp chart |
|
|
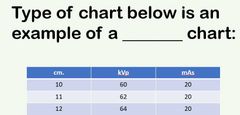
|
Variable kVp chart |
|

