![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a patch of myocytes in the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava
|
Sinoatrial (SA) node
|
|
|
a patch of cells at the lower end of the interatrial septum near the right AV (tricuspid) valve
|
Atrioventricular (AV) node
|
|
|
connects the AV node to the conduction branches that travel down the interventricular septum and allow for ventricular depolarization
|
Bundle of His (atrioventricular bundle)
|
|
|
these collectively travel the septum and provide independent depolarization waves for each of the ventricles
|
right and left bundle branches
|
|
|
conduct an electrical stimulus or impulse that enables the heart to contract in a coordinated fashion
|
purkinje fibers
|
|
|
the dissociation of atrial and ventricular excitation
|
heart block
|
|
|
the signal from the atria to the ventricles is completely blocked
|
total heart block
|
|
|
anarchy in the heart chambers where contraction is random and unorganized
|
fibrillation
|
|
|
signal originates at the heart (doesn't need stimulus from the CNS)
|
myogenic
|
|
|
cardiac rest; period when ventricles are filling with blood
|
diastole
|
|
|
ventricular contraction; blood is being ejected
|
systole
|
|
|
wave produced when the atria depolarize
the first wave (ECG) |
P-wave
|
|
|
first negative ventricular deflection
|
Q-wave
|
|
|
first positive ventricular deflection
|
R-wave
|
|
|
first negative deflection after the R-wave
|
S-wave
|
|
|
if there is no positive R-wave, the negative deflection is called the _-_ wave
|
Q-S wave
|
|
|
this wave marks the change in voltage created by ventricular repolarization
|
T-wave
|
|
|
the _-_ segment corresponds to the time when calcium has entered the cardiac myocytes
ventricles are contracting |
S-T segment
|
|
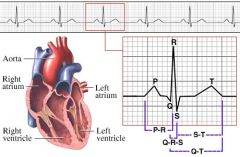
Describe what is happening at each of these points:
P Q R S T ST segment |
P: atria depolarize
Q: first negative ventricular deflection R: first positive deflections from the ventricle S: first negative deflection after the R-Wave T: the change in voltage ST: corresponds to the time when calcium has entered the cardiac myocytes and the ventricles are contracting |
|
|
Identify:
Nasal septum Nasal concha External Nares Hard palate Soft palate Trachea Cartilage rings |
Nasal septum
Nasal concha External Nares Hard palate Soft palate Trachea Cartilage rings |
|
|
Identify:
Nasal septum Nasal concha External Nares Hard palate Soft palate Trachea Cartilage rings |
Nasal septum
Nasal concha External Nares Hard palate Soft palate Trachea Cartilage rings |
|
|
Identify:
Nasal septum Nasal concha External Nares Hard palate Soft palate Nasal cavity Nasopharynx Oral cavity Uvula & palatine tonsils Oropharynx Tongue Thyrohyoid ligament Hyoid bone |
picture
|
|
|
Identify:
Hyoid bone Thyroid cartilage Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Diaphragm Right lung- [superior, middle, inferior lobes] Left lung- [superior, inferior lobes] Trachea Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi Sternum Ribs Intercostal muscles Esophagus Trachea Cartilage rings |
picture
|
|
|
internal cavity of the nose; internally divided into a right and left half by the nasal septum
|
nasal cavity
|
|
|
from the posterior naris to the oropharynx
|
nasopharynx
|
|
|
the space between the tongue and the heard and soft palate- extends posteriorly to the fauces where it continues with the oropharynx
|
oral cavity
|
|
|
"throat"- from uvula -> larynx
|
oropharynx
|
|
|
muscular organ on the floor of the oral cavity between sides of the mandible
|
tongue
|
|
|
a large cartilaginous pieced shaped like a shield
|
thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
this consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus
|
thyroid gland
|
|
|
a collection of small structure embedded on the lateral aspects of the thyroid gland
|
parathyroid gland
|
|
|
a sheet of skeletal muscle at the base of lungs that divides the thoracic and abdominal cavities
|
diaphragm
|
|
|
the "windpipe" - a rigid tube
|
trachea
|
|
|
two main divisions of the trachea which deliver air to the two lungs
|
primary bronchi
|
|
|
the primary bronchi separate into the __________ bronchi. The right pulmonary bronchus divides into three and the left primary bronchus divides into two
|
secondary bronchi
|
|
|
continuations of the airway that lack supportive cartilage
|
bronchioles
|
|
|
what do the sternum and ribs do as the thoracic cavity inhales?
|
move up due to expansion
|
|
|
intercostal muscles -- what do they do?
|
?
|
|
|
pink tubular organ that emerges from behind the trachea and passes through an opening in the diaphragm into the abdominal cavity
|
esophagus
|
|
|
the ______ bone is joined to the superior part of the larynx by a strong ligament called the ___________ _________
|
hyoid bone
thyrohyoid ligament |
|
|
describe the trachea and the cartilate rings
|
just do it
|
|
|
the larynx consists of:
thyroid cartilage cricoid cartilage two arytenoid cartilages epiglottis cuneiform corniculate cartilaginous pieces |
review these
|
|
|
the largest cartilage (shied like)
|
thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
inferior to the thyroid cartilage is the
|
cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
the flexible ________ is attached to the anterior, superior edge of the thyroid cartilage. The paired _______ ________ are attached to the superior surface of the cricoid cartilage by synovial joints
|
epiglottis
arytenoid cartilages |
|
|
"leather flaps"
|
true vocal cords
|
|
|
the space between right and left true vocal cords
|
glottis
|
|
|
This is the change in volume caused by a known pressure in change
|
compliance
|

