![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

a |
optic nerve - comprised of axons from retinal ganglion cells |
|

b |
optic chiasm - decussation of the optic nerve axons |
|

c |
optic tract |
|
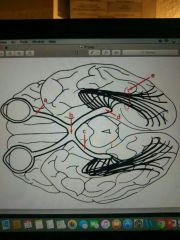
d |
lateral geniculate nucleus/body (LGN)
-termination of axons in the optic tract -thalamic nucleus for vison |
|

e |
optic (visual) radiation fibers - projections from LGN --> primary visual cortex through the posterior limb of the internal capsule |
|
|
The superior colliculus receives fibers for _______ |
visual reflexes |
|
|
Brachium of the superior colliculus contains ________ fibers passing to the __________ area and _____________ |
Optic tract fibers |
|

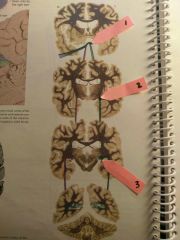
a |
calcarine fissure/sulcus |
|

b |
cuneus gyrus |
|

c |
lingual gyrus |
|

purple |
Primary visual cortex - the calcarine cortex |
|

1 |
optic chiasm |
|

2 |
optic tract |
|
3 |
lateral geniculate nucleus/body (LGN) -major thalamic nucleus that relays visual stimuli to cortex |
|
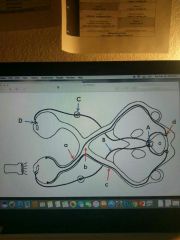
a-d (red) pathway |
Visuomotor (pupillary light) reflex pathway |
|

a (red) |
optic nerve |
|

b (red) |
optic chiasm |
|

c (red) |
optic tract |
|

d (red) |
pretectal nucleus of midbrain - (lateral to PAG) -Synaptic center relaying info about light reflexes |
|

A-D (blue) |
efferent pathway |
|

A (blue) |
Edinger-Westphal nucleus - preganglionic parasym cell bodies |
|
|
Edinger-Westphal nucleus : receives fibers from _______ and ________ and sends axons via CN ___________ for _______ constriction and lens ________ |
-pretectal area and superior colliculus |
|

B (blue) |
oculomotor nerve (efferent limb) |
|
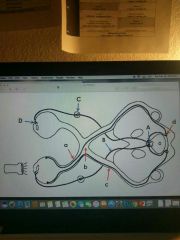
C (blue) |
ciliary ganglion |
|
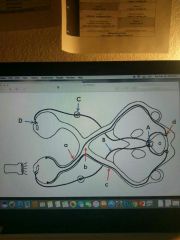
D (blue) |
axons to constrictor pupillae |
|
|
Oculomotor nerve fibers: axons from the ___________ to the ___________ |
Edinger-Westphal nucleus to the Ciliary ganglion |
|
|
Visual acuity tests for |
near versus distance vision |
|
|
Visual fields test plots |
visual field maps for each eye |
|
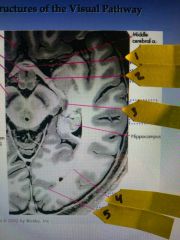
1 (ppt picture) |
optic chiasm |
|

2 |
optic tract |
|

3 |
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) |
|

4 |
Optic radiation |
|

5 |
Striate cortex |
|

Blue arrow |
Lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus |
|

Red arrow |
Superior colliculus |
|
|
Scotoma |
loss of part of a visual field of an eyeball |
|
|
Hemianopia/hemianopsia |
loss of half the visual field |
|
|
Quadranopia |
loss of a quarter of the visual field |
|
|
Homonymous |
loss of the same part of visual field in both eyes |
|
|
Heteronymous |
loss in different part of visual field for two eyes |
|

A (visual field deficits) |

Soctoma: Blindness in one eye |
|

B |

Bi-Temporal hemianopia: |
|

C |

Homonymous Hemianopia: |
|

D |

Quadrantanopsia: |
|
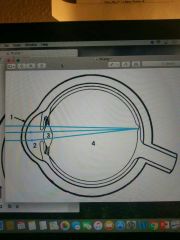
1-4 (Horizontal section through eye) |
Refraction Media of the Eye |
|
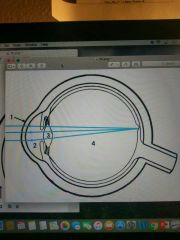
1 |
Cornea |
|

2 |
Aqueous humor |
|

3 |
Lens |
|

4 |
Vitreous body |
|

a is what layer of the eye |
sclera (pigmented [tapetum lucidum] in cows not humans) |
|

b is what layer of the eye |
choroid |
|

c is what layer of the eye |
retina |
|

d is what layer of the eye |
ciliary body w/muscle |
|

e is what layer of the eye |
iris - divides space b/w aq humor into anterior and posterior chambers |
|
|
External or fibrous tunic/layer: consisting of the ______ and _______ |
cornea and sclera |
|
|
Middle or vascular tunic/layer: consisting of the _____, _______, and _______ |
iris, ciliary body, and choroid |
|
|
Internal tunic/layer: consisting of the _______ |
retina |
|
|
Lens is held in position by the ____________ |
suspensory ligaments |
|

1 (bovine eyeball) |
cornea |
|
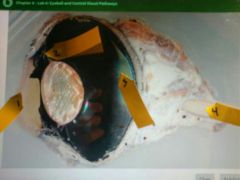
2 |
suspensory ligaments |
|

3 |
tapetum lucidum (TL): provides a surface that reflects light within the vitreous chamber and back onto the retina to enhance sensitivity as an adaption to functioning in low-light conditions. (cat glow) |
|

4 |
optic nerve |
|
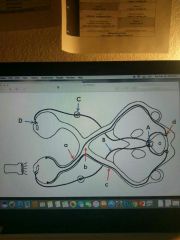
Damage to which nervous structure (A-D) would lead to an absence of the efferent limb of the pupillary reflex , select all that apply. |
A (Edinger-Westphal nucleus) and D (axons to constrictor pupillae) |
|

1 |
Edinger-Westphal nucleus |
|

2 |
Oculomotor nucleus (3) |
|

3 |
Oculomotor nerve fibers |
|
|
Glaucoma results from abnormal drainage of _________ characterized by an increase in _________. If untreated can lead to damage of ________ and blindness. |
aqueous humor |
|
|
Contraction of the ciliary muscle (increase/decrease) the tension on the ligaments of the _____ to round (aka: _________) |
Decrease |
|
|
The inner layer, the ______, contains the light-detecting cells of the eye and is closely associated with the choroid. |
retina |

