![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three layers of the meninges? |
1. Dura mater: thick, most fibrous, tough outer layer
2. Arachnoid: middle, thinner layer
3.Pia mater: inner, most delicate layer which carries blood vessels to the brain |
|
|
Where does cerebrospinal fluid belong? |
In the subarachnoid space (this is located between the layers of the arachnoid and pia mater. cerebrospinal fluid surrounds the brain and fills the ventricles within. |
|
|
What is the difference between gray matter and white matter? |
Gray matter has 3 functions transmitted by 3 parts: The posterior horn transmits sensory impulses.The anterior horn transmits motor impulses. The posterior columns transmits the sensations of proprioception, pressure, and vibration.
White matter contains ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) fiber pathways. Each pathway carries a specific type of impulse, such as touch, to and from a specific area. |
|
|
Name the different parts of a vertebrae: |
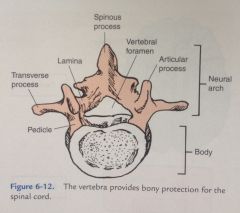
-Spinous process -Vertebral foramen -Articular process -Pedicle -Transverse process -Lamina -Body of vertebrae -Neural arch
|
|
|
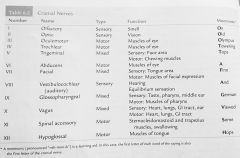
NAME the cranial nerves:
**BONUS = functions of cranial nerves** (pages 61 & 62) |
I. Olfactory: (sensory) smell II. Optic: (sensory) vision III. Oculomotor: (motor) muscles of the eye IV. Trochlear: (motor) muscles of the eye V. Trigeminal: (mixed) sensory: face area; motor: chewing muscles VI. Abducens:(motor) muscles of eye
|
|
|
Cranial nerves continued: |
VII. Facial: (mixed) sensory: tongue area; motor: muscles of facial expression VIII. Vestibulocochlear: (sensory) hearing and equilibrium sensation IX. Glossopharyngeal: (mixed) sensory: taste, pharynx, middle ear; motor: muscles of pharynx X. Vagus: (mixed) sensory: heart, lungs, GI tract, ear; motor: heart, lungs, GI tract XI. Spinal accessory: (motor) SCM and trap muscles, swallowing XII. Hypoglossal: (motor) muscles of tongue |
|
|
Where do the first seven cervical nerves (C1-C7) exit the vertebral column?
(Pg 60 under spinal nerves paragraph) |
ABOVE the corresponding vertebrae. For example, the C3 nerve exits above the C3 vertebrae. |
|
|
Where does the C8 nerve exit? |
UNDER C7 and OVER T1, since there is one more cervical nerve than there are vertebrae. |
|
|
Where do the 12 thoracic nerves exit? |
UNDER the corresponding vertebrae. |
|
|
Where do the 5 lumbar nerves exit? |
UNDER the corresponding vertebrae. |
|
|
How many sacral nerves are there? |
5 |
|
|
True or False:
The coccygeal nerve exits below the coccyx. |
TRUE |
|
|
What are the names of the 3 plexuses? |
1. Cervical plexus
2. Brachial plexus
3. Lumbosacral plexus |
|
|
Where do the elbow flexors receive innervation? |
C5 and C6 nerves
pg. 63, second paragraph |
|
|
True or False:
A person with an injury at or above C3 would NOT ahve the function of the diaphragm and would be unable to breathe without assistance. |
TRUE; the C3 also innervated the trapezius
pg. 63, third paragraph |
|
|
Deltoid and biceps: |
C5 |
|
|
Wrist extensors: |
C6 |
|
|
Triceps: |
C7 |
|
|
Hand intrinsics: |
C8 and T1 |
|
|
Intercostals: |
T2 - T6 |
|
|
Abdominals: |
T6 - T12 |
|
|
The hip flexors and knee extensors are innervated between: |
L2 and L4
Pg 63, last paragraph |
|
|
Hip adductors are innervated at: |
L2 - L3 |
|
|
Hip abductors: |
L4 - L5 |
|
|
Hip extensors and knee flexors: |
L5 - S2 |
|
|
Ankle : |
L4 - S2 |
|
|
Bowel and bladder control: |
S4 - S5 |
|
|
Leg muscles in general: |
L2 - S2 |
|
|
Foot muscles: |
L4 - S2 |
|
|
Table 6.1 on page 61 |
:D |
|
|
Dermatome map: |
:D |
|
|
Names of peripheral nerves: |
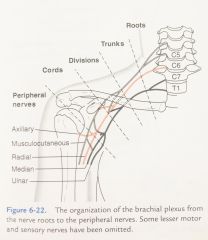
1. Musculocutaneous nerve 2. Axillary nerve 3. Radial nerve 4. Median nerve 5. Ulnar nerve
|
|
|
In a first class lever, the axis is located: |
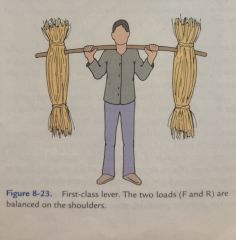
Between the force and the resistance
|
|
|
In this type of lever, the resistance is located in the middle with the axis at one end and the force at the other end. |
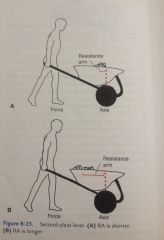
Second class lever
|
|
|
A third class lever: |
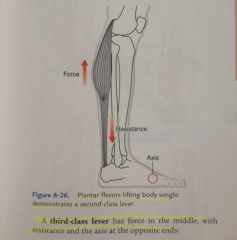
Has force in the middle with resistance and the axis at the opposite ends.
|
|
|
General innervation levels of major muscles. Figure 6-20 on page 62 |
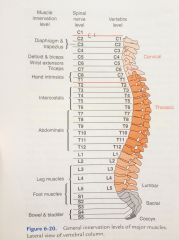
|
|
|
Spinal nerves and plexus Figure 6-21 page 64 |
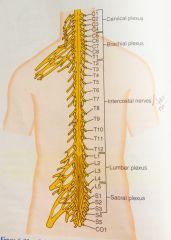
|
|
|
Dermatomes Figure 6-19 page 63 |
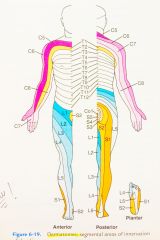
|
|
|
Cranial nerves Table 6-2 page 62 |
|

