![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
166 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Psychology |
involves the study of mental activity and behavior |
|
|
Everyone |
Who does psychology? (intensely trying to understand, predict, and control others around us.) |
|
|
Psychological science |
involves the study, through quality research, of mind, brain, and behavior. |
|
|
Noncritical Thinking |

can lead to erroneous conclusions. –Ignoringevidence (confirmation bias) –Failingto accurately judge source credibility –Misunderstandingor not using statistics –Seeingrelationships that do not exist –Usingrelative comparisons |
|
|
ProfessionalPsychology |
InstitutionalAffiliation/PrivatePractice
|
|
|
ScientificPsychology |
Research |
|
|
Nature/Nurture |
–Example: Language Development•Skinner– Language development is guided by behavior operating on the environment(nurture)•Chomsky– Language development is guided by an innate language-acquisition device(nature) |
|
|
BOTH nature and nurture |
–Now,psychologists recognize that most phenomena involve___ |
|
|
Mind / Body Problem |
–Aremind and body separate and distinct, or is the mind simply the subjectiveexperience of brain activity? |
|
|
Dualism |
Psychologistsnow reject___, and believe that mind is produced by brain activity. |
|
|
Characteristicsof valid scientific research |
Verifiable results, Public disclosure, Cumulative effects |
|
|
Verifiable results |
Researchis evaluated and the research findings are determined to be reliable and theresulting interpretations are valid (peer review). |
|
|
Public disclosure |
Peerreviewed findings are published in scientific journals so scientists areinformed and can evaluate and build on them. |
|
|
Cumulative effects |
Scienceis moved forward by building on past researchragment |
|
|
Research Methods in Psychology |
Descriptive Studies, Developmental Studies, Experiemental Studies |
|
|
Descriptive Method |
•Naturalistic and participant observation •Surveys •Case studies •Many case studies by Oliver Sacks •Luria’s “S” •Milner’s “H.M.” •Phinneas Gage •Correlational studies |
|
|
Naturalistic Observation |
JaneGoodall, DianFossey |
|
|
Participant Observation |
•adescriptiveresearchmethod in which the researcher not only observes the research participants, butalso actively engages in the activities of the research participants. •Thisrequires the researcher to become integrated into the participants' environmentwhile also taking objective notes about what is going on. •Qualitativeresearch rather than quantitative research |
|
|
Surveys |
•Opinionpolls•Politicalpolls•Marketingsurveys•AtTech (Office of Assessment):•CIOS•Student Exit Survey•Student Experience Survey•Graduatealumni survey•Etc. |
|
|
Case Study |
Oliver Sacks - Man who mistook his wife for a hat Alexander R. Luria - “S” – Solomon Shereshevsky BrendaMilner - HM - Henry Molaison Phineas Gage |
|
|
Correlations |
To what extent do two or more variables co-vary? ex) New study discussed January 13,2016 in GamesPolitic showed that playing videogames wasrelated to “Acquired Capability for Suicide” (Mitchell et al., 2015) |
|
|
causation |
A correlation does show a relationship but itdoes not imply___ |
|
|
-1 and +1 |
Correlationcoefficient goes between |
|
|
Developmental Method |
Longitudinal Design and Cross-sectional Design |
|
|
Longitudinal Design |
Within subject |
|
|
Cross-sectional Design |
Between subject subjectscannot be randomly assigned to groups "quasi-experimentaldesigns" |
|
|
Hypothetical Constructs |
Psychologistsuse____ Manypsychological constructs cannot be directly measured, but only inferred frombehavior, e.g., Love,learning, personality, intelligence, boredom, memory,emotion, and hunger |
|
|
Importanceof random sampling |
Socialdesirability bias Volunteerbias |
|
|
Validity |
•Measuresshould reflect what they are supposed to reflect. (face, construct, andecological validity) |
|
|
Reliability |
Measuresneed to be consistent |
|
|
Ethics |
Institutional Review Board (IRB) and Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) |
|
|
IRB Concerns |
a. Informed consent b. Deception c. Inducementsto participate d. Debriefing e. Confidentiality f. NoHarm |
|
|
Manipulate |
In Experimental Method, We control allvariables except the one that we ______ to try to determine what causes what. |
|
|
independent variable dependent variable |
We manipulatethe ___ and measure the ___ |
|
|
Causation |
DV = f (IV) :_____ |
|
|
Experimental Method |
The best way todetermine causation is by using the________ |
|
|
Experimental method |
randomly assign participants to groups |
|
|
Quasi-experimental method |
cannot randomly assign participants to groups (e.g., young andold adults; frontal patients andcontrols) |
|
|
Experimental Method |
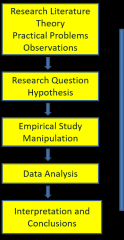
|
|
|
falsifiable |
A theory must be ___ |
|
|
testable
|
A hypothesis must be ___ |
|
|
manipulation |
A ___ must be controlled |
|
|
Analysis |
___ determinessignificance; is it due to chance? |
|
|
Theory |
An explanation using anintegrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviorsor events. |
|
|
Hypothesis |
A single, testableprediction, often implied by a theory |
|
|
Null Hypotesis |
•No difference betweenconditions (cannot be proven) |
|
|
Operational Definition |
•A statement of theprocedures used to define the research variables. |
|
|
Independent Variable |
variable wemanipulate, change, control; typically astimulus variable |
|
|
Dependent Variable |
variable wemeasure; typically a response variable (behavior) |
|
|
Confounding Variable |
variablevarying with independent variable because of lack of control (third variableproblem) |
|
|
Confounding Variable |
•In 1949, Dr.Benjamin Sandler noticed a correlation between the incidence of polio and icecream consumption, and concluded sugar made children more susceptible to thedisease.•Public Healthofficials issued warnings about sugar consumption in children.•BUT, it was warm weather that increased thedisease and increase in ice cream consumption. •Viruses become moreactive in the summer. |
|
|
Hypothetical Construct |
We can only infer many of the major constructs in Psychology byhow we manipulate and measure constructs |
|
|
Operational Definition |

Explains exactly how the variable will be manipulated and/ormeasured |
|
|
Hypothesis |
“Taking tests in hot rooms reduces test scores” |
|
|
Variance |
Variance is very important indetermining____ |
|
|
Measuresof central tendency |
Mean, Median, Mode |
|
|
Measures of Variability |
Range, Variance, Standard Deviation |
|
|
Mode |
Most common score |
|
|
Median |
Middle of all ranked scores |
|
|
Mean |
Average of all scores |
|
|
Range |
lowest to the highest |
|
|
Variance |
V= (SUM)(score - mean)2/n(number of scores) –“average of squareddeviations |
|
|
Standard Deviation |
sqrt(variance) |
|
|
Standard Score |
We can take any normal distribution of scores and convert it toa distribution with a mean of 0 and a SD of 1. This allows us to compare scores across distributions. Z=(score-mean of scores)/SD |
|
|
Scientific findings |
____ are verifiable (Findings are determinedto be reliable and valid through peer review). |
|
|
Public |
•Scientific findingsare ___ (They must be published and judged by other scientists). |
|
|
cumulative |
•Scientific findingsare ____ (Scientists build on past research). |
|
|
Experimental Method |
1.Feedingbehavior in the ordinary house fly– Vincent Dethier (Princeton)
2.Altruism(helping behavior) in social settings – Bibb Latanéand John Darley (Princeton) 3.Memory and aging– Andy Smith (Georgia Tech)
|
|
|
Bystander Apathy |
Catherine Genovese was stabbed and killed but nobody helped because of ____ ______ |
|
|
Responsibility |
Bystander Apathy is caused by diffusion of ___ |
|
|
Biopsychology |
Feeding behavior (starting and stopping eating) – Vincent Dethier |
|
|
Social Psychology |
Bystander apathy in social situations - Bibb Latané andJohn Darley |
|
|
Cognitive Psychology |
Memory and aging – Andy Smithnd stopping eating) – vincent dethier |
|
|
adult aging |
Researchhas shown that retrieval processes for episodic memories are affected by ____ |
|
|
Episodic Memory |
Rememberingevents from our past. (“When did you last see your parents? What were the words we presented to you five minutes ago?”) |
|
|
cues |
Theretrieval process can be improved if good ____ are available that help encodeduring learning and retrieve at the time of recall. |
|
|
Neurons |
basic unit of a nervous system |
|
|
central nervous system |
brain and the spinal cord |
|
|
peripheral nervous system |
consists of all the nerve cells other than brain and spinal cord |
|
|
sensory neurons |
____ detect information from the physical world and pass that information along to the brain, usually through the spinal cord |
|
|
Motor neurons |
direct muscles to contract or relax, producing movement |
|
|
Interneurons |
communicate within local or short-distance circuits |
|
|
dendrites |
short, branchlike appendages that detect chemical signals from neighboring neurons. |
|
|
Cell Body |
The site in the neuron where information from thousands of other neurons is collected and integrated |
|
|
axon |
a long narrow outgrowth of a neuron by which information is transmitted to other neurons |
|
|
Central nervous system
|
Brain and Spinal Cord form ___? |
|
|
Peripheral nervous system
|
Somatic nervous system and Autonomic nervous system
|
|
|
Sensory Neurons |
Skin, muscles, and joints send signals to the spinal cord and brain |
|
|
Motor Neurons |
Brain and spinal cord send signals to the muscles, joints, and skin |
|
|
Sympathetic nervous system |
Prepares body for action "fight or flight" |
|
|
Parasympathetic nervous system |
Returns body to normal state "rest or digest" |
|
|
Spinal Reflex
|
Sensory receptors in skin - sensory neurons - interneuron - motor neuron - muscle contraction raises forearm
|
|
|
dendrites, cell body, and axon
|
All neurons contain ____
|
|
|
neurons and glial cells
|
Nervous system contains two types of cells, ___ and ____
|
|
|
information
|
____ processing in the neuron is electrical and electro-chemical
|
|
|
Neuron
|
|
|
|
terminal buttons
|
Dendrites collect all the input from _____ of all presynaptic cells, the cell body gathers and interprets this information, and if it reaches a threshold, the cell fires (action potential generated)
|
|
|
Cell Body
|
Synapse - Dendrites - _____ - Axon - Synapse
|
|
|
action potential
|
The ____ is all-or-none and it does not diminish along the entire axon
|
|
|
strength
|
Number of cells firing and frequency of firing determine the ____ of input
|
|
|
excite inhibit
|
Some neurotransmitters ____ post-synaptic cell and others ___ (less likely to have action potential)
|
|
|
Agonist
|
increase neurotransmitter action
|
|
|
Antagonist
|
decrease neurotransmitter action |
|
|
Alcohol
|
___ is an agonist for GABA, serotonin, dopamine, and the endorphins - it increases their activity
|
|
|
antagonist
|
Alcohol is also an ____ for glutamate (reduces learning and memory) - it reduces glutamate activity (glutamate receptors - primary receptors increasing action potentials)
|
|
|
prosopagnosia
|
Face blindness
|
|
|
Wernicke's Aphasia
|
Language comprehension - can't speak in coherent sentences and understanding speech - don't know that they are not making sense |
|
|
Biopsychology research methods
|
Case Studies, Lesion Studies, EEG, PET,MRI, fMRI, DTI, TMS
|
|
|
Genotype
|
Our genetic composition determined at conception
|
|
|
Phenotype
|
Observable characteristics determined by dominant genes and environment |
|
|
genetics
|
For most behaviors, both ___ and the environment are important - Caspi Study
|
|
|
heuristics
|
mental shortcuts / simple rules people follow
|
|
|
Psychological Science |
the study, through research, of mind, brain, and behavior |
|
|
intuitive |
Most of us function as ____ psychologists, but many of our intuitions and beliefs are wrong |
|
|
Critical Thinking |
Systematically questioning and evaluating information using well-supported evidence |
|
|
Culture |
The beliefs, values, rules, and customs that exist within a group of people who share a common language and environment |
|
|
Nature/Nurture Debate |
The arguments concerning whether psychological characteristics are biologically innate or acquired through education, experience, and culture |
|
|
Biology
|
___ is increasingly emphasized in explaining psychological phenomena.
|
|
|
evolutionary psychology
|
Psychological science has been influenced heavily by _______, which argues that the brain has evolved in response to our ancestors' problems of survival
|
|
|
Culture
|
____ provides adaptive solutions. Contemporary psychology is characterized by an increasing interest in cultural norms and their influence on thought processes and behavior
|
|
|
mind, brain, and behavior
|
Psychologists share the goal of understanding ________
|
|
|
Peer-Reviewed Journals
|
the most trust-worthy source for scientific evidence
|
|
|
research
|
a scientific process that involves the careful collection of data |
|
|
scientific method |
a systematic and dynamic procedure of observing and measuring phenomena |
|
|
theory
|
a model of interconnected ideas or concepts that explains what is observed and makes predictions about future events |
|
|
hypothesis |
a specific, testable prediction, narrower than the theory it is based on. |
|
|
replication
|
repetition of a research study to confirm the results |
|
|
Case Study
|
A descriptive research method that involves the intensive examination of an unusual person or organization |
|
|
naturalistic observation
|
A type of descriptive study in which the researcher is a passive observer, separated from the situation and making no attempt to change or alter ongoing behavior |
|
|
reactivity |
The phenomena that occurs when knowledge that one is being observed alters the behavior being observed |
|
|
Observer Bias |
Systematic errors in observation that occur because of an observer's expectations |
|
|
Experimenter expectancy effect |
Actual change in the behavior of the people or nonhuman animals being observed that is due to the expectations of the observer |
|
|
Positive Correlation
|
A relationship between two variables in which both variables either increase or decrease together |
|
|
Negative Correlation
|
A relationship between two variables in which one variable increases when the other decreases |
|
|
zero correlation |
A relationship between two variables in which one variable is not predictably related to the other. |
|
|
experiment
|
a research method that tests causal hypotheses by manipulating and measuring variables |
|
|
experimental group
|
the participants in an experiment who receive the treatment |
|
|
control group |
the participants in an experiment who receive no intervention or who receive an intervention that is unrelated to the independent variable being investigated |
|
|
confound |
anything that affects a dependent variable and that may unintentionally vary between the experimental conditions of a study |
|
|
population |
Everyone in the group the experimenter is interested in |
|
|
sample |
a subset of a population |
|
|
random assignment |
placing research participants into the conditions of an experiment in such a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any level of the independent variable |
|
|
selection bias |
in an experiment, unintended differences between the participants in different groups; it could be caused by nonrandom assignment to groups |
|
|
descriptive, correlational, and experimental
|
three main types of studies are used in psychological research |
|
|
causality
|
Descriptive and correlational designs are useful for describing and predicting behavior, but they do not assess ____
|
|
|
experiments
|
Only ____ allow researchers to determine causality
|
|
|
IRB
|
groups of people responsible for reviewing proposed research to ensure that it is ethical |
|
|
research animals
|
Strict rules govern research with both human participants and ___
|
|
|
IRB
|
Each research study with human participants is evaluated for scientific and ethical validity by an ___
|
|
|
privacy, relative risks, informed consent, and access to data
|
Four key issues addressed in the IRB approval process are ___
|
|
|
Construct Validity
|
The extent to which variables measure what they are supposed to measure |
|
|
External Validity |
The degree to which the findings of a study can be generalized to other people, settings, or situations
|
|
|
internal validity
|
The degree to which the effects observed in an experiment are due to the independent variable and not confounds |
|
|
reliability
|
the degree to which a measure is stable and consistent over time |
|
|
accuracy |
the degree to which an experimental measure is free from error |
|
|
descriptive statistics |
statistics that summarize the data collected in a study |
|
|
central tendency |
A measure that represents the typical response or the behavior of a group as a whole |
|
|
mean |
a measure of central tendency that is the arithmetic average of a set of numbers |
|
|
Variability
|
how widely dispersed the values are from each other and from the mean |
|
|
Standard Deviation
|
A statistical measure of how far away each value is, on average, from the mean. |
|
|
Scatterplot
|
A graphical relationship of the relationship between two variables |
|
|
Correlation Coefficient
|
A descriptive statistic that indicates the strength of the relationship between two variables |
|
|
Inferential Statistics
|
A set of assumption and procedures used to evaluate the likelihood that an observed effect is present in the population from which the sample was drawn |
|
|
meta-analysis |
A "study of studies" that combines the findings of multiple studies to arrive at a conclusion |
|
|
construct validity, external validity, and internal validity
|
Data should have ___ |
|
|
|
|

