![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Wave |
A vibrating disturbance by which energy is transmitted. |
|
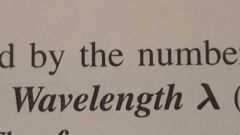
Wavelength |
Distance between identical points on the successive waves. |
|

Frequency |
The number of waves that pass through a particular point in 1 second. |
|
|
Amplitude |
The vertical distance from the middle of a wave to the peak or trough. |
|
|
Speed of a wave |
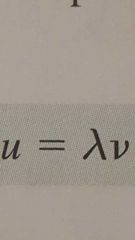
|
|
|
Electromagnetic wave |
Has an electric field component and a magnetic field component. |
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation |
The emission and trasmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. |
|
|
Quantum |
The smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted in the from of electromagnetic radiation. |
|
|
Photoelectric effect |
Electeons are ejected from the surface of certain metals exposed to light of at least a certain minimum frequency called the Threshold frequency. |
|
|
Photons |
Particles of light. |
|
|
Emission spectra |
Either continuous or line spectra of radiation emitted by substances. |
|
|
Line spectra |
Light emissions only at specific wavelengths. |
|
|
Ground state (Ground level) |
The lowest energy state of a system. |
|
|
Exicted state (Excited level) |
Higher energy then the ground state. |
|
|
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle |
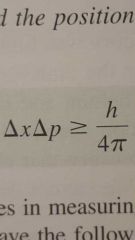
It is impossible to know simultaneously both the momentum (p, mass times velocity) and the position of a particle qith certainty. |
|
|
Electron density |
Gives the probability that an electron will be found in a particular region of an atom. |
|
|
Atomic orbital |
The wave function of an electron in an atom. |
|
|
Quantum numbers |
Describe the distribution of elwctrons in hydrogen and other atoms. |

