![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
169 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Redox reactions involves ______________.
|
transfer of electrons
|
|
|
Oxidation is the _____ of electrons.
|
loss
|
|
|
Reduction is the _____ of electrons.
|
gain
|
|
|
What is the formula for electric charge? what is the unit?
|
q= n x F
n=# of e- F= Faraday constant 9.649E4 C/mole of e- the unit is C or coulombs |
|
|
Electric current is the _______ of ________ flowing each second through any cross section of a circuit. What is its unit?
|
amount, charge
unit=A or amperes |
|
|
Electric current is the amount of charge flowing each ______ through any _________ of a circuit. unit?
|
second, cross-section
A or amperes |
|
|
__________ is the difference in electric potential between two points. units?
|
Voltage
Volts or V |
|
|
Voltage is the difference in electric __________ between two points. units?
|
potential
V |
|
|
Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two _______. units?
|
points
V |
|
|
_____________ ____________ is the amount of charge flowing each second through any cross-section of a circuit.
|
Electric current
|
|
|
Formula for free energy change.
|
dltaG = -nFE
E = volts |
|
|
Ohm's Law?
|
E = IR
|
|
|
Power is work per ___________. units?
|
unit time
Watts |
|
|
_________ is work per unit time. units?
|
Power
Watts |
|
|
Formula for Power.
|
P = work/time = E x q / t = EI
|
|
|
Batteries use a spontaneous chemical reaction to generate electricity. This is called a __________ ________.
|
voltaic cell
|
|
|
_____________ use a spontaneous chemical reaction to generate electricity. This is called a voltaic cell.
|
Batteries
|
|
|
Batteries use a _____________ chemical reaction to generate electricity. This is called a voltaic cell.
|
spontaneous
|
|
|
Batteries use a spontaneous chemical reaction to generate _____________. This is called a voltaic cell.
|
electricity
|
|
|
The cathode is where __________ occurs.
|
reduction
|
|
|
The _________ is where reduction occurs.
|
Cathode
|
|
|
The anode is where __________ occurs.
|
oxidation
|
|
|
The _________ is where oxidation occurs.
|
Anode
|
|
|
If E' is positive the reaction is?
|
spontaneous
|
|
|
If E' is _____ the reaction is spontaneous.
|
positive
|
|
|
If dltaG is negative the reaction is _____________.
|
spontaneous
|
|
|
If dltaG is _________ the reaction is spontaneous.
|
negative
|
|
|
What is the voltage of a cell when the chemical reaction reaches equilibrium?
|
zero
|
|
|
E(cell)= E(?) - E(?)
|
cathode, anode
|
|
|
E(?) = E(?) - E(?)
|
cell, cathode, anode
|
|
|
Potentiometry is the use of electrodes to measure voltages that provide ____________ ____________.
|
chemical information
|
|
|
______________ is the use of electrodes to measure voltages that provide chemical information.
|
potentiometry
|
|
|
Potentiometry is the use of _________ to measure voltages that provide chemical information.
|
electrodes
|
|
|
Potentiometry is the use of electrodes to measure ________ that provide chemical information.
|
voltages
|
|
|
What is an electroactive species?
|
a reagent that can donate or accept electrons at an electrode
|
|
|
What is a reagent that can donate or accept electrons at an electrode.
|
electractive species
|
|
|
In measuring cell potential an _________ electrode responds to analyte concentrations.
|
indicator electrode
|
|
|
In measuring a cell potential an indicator electrode responds to _________ __________.
|
analyte concentrations
|
|
|
In measuring cell potential a _________ _______ maintains a fixed potential at one end of the circuit.
|
reference electrode
|
|
|
In measuring cell potential a reference electrode maintains a _________ _________ at one end of the circuit.
|
fixed potential
|
|
|
What are the two kinds of reference electrodes discussed?
|
Ag/AgCl electrode
Calomel which uses Hg and KCl |
|
|
The E(cell) vs _______ = E+ - 0.197V
|
Ag/AgCl
|
|
|
The E(cell) vs Ag/AgCl = E+ - _______V.
|
0.197
|
|
|
How would you convert the E(cell) vs Ag/AgCl to the Voltage vs. SHE
|
E(cell) + .197V
|
|
|
The E(cell) vs calomel = E+ - _____V.
|
0.241
|
|
|
The E(cell) vs ________ = E+ - 0.241V.
|
calomel
|
|
|
How would you convert the E(cell) vs calomel to the Voltage vs. SHE
|
E(measured) + 0.241 = E(cell) vs SHE
|
|
|
Metal electrodes develop an electric potential that is dependent on the analyte _____________.
|
concentration
|
|
|
Metal electrodes develop an electric _________ that is dependent on the analyte concentration.
|
potential
|
|
|
Metal __________ develop an electric potential that is dependent on the analyte concentration.
|
electrodes
|
|
|
Metal electrodes develop an electric potential that is ___________ on the analyte concentration.
|
dependent
|
|
|
What is the x-intercept on a Gran Plot?
|
the V(eq)
|
|
|
What is the Y axis on a gran plot?
|
V x 10 ^(-nE/0.05916)
|
|
|
What is a redox indicator?
|
it is a compound that changes color when it goes from its oxidized to reduced state
|
|
|
A redox indicator is a compound that changes color when it goes for its _________ to __________ state.
|
oxidized, reduced
|
|
|
The potential range over which the indicator color will change can be predicted using the _____________.
|
Nernst equation
|
|
|
The ________ ________ over which the indicator color will change can be predicted using the Nernst equation.
|
potential range
|
|
|
The potential range over which the ___________ ________ will change can be predicted using the Nernst equation.
|
indicator color
|
|
|
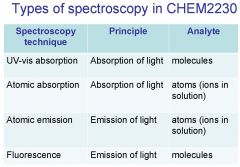
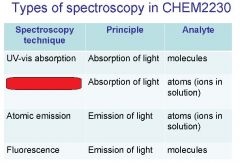
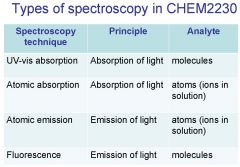
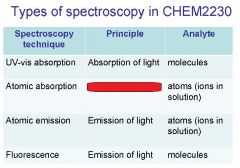
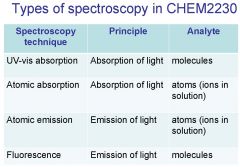
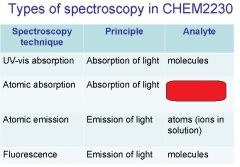
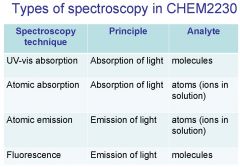
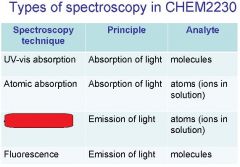
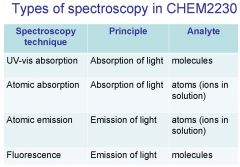
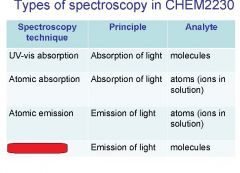
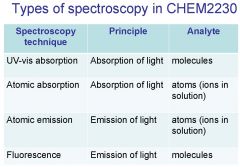
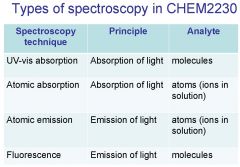
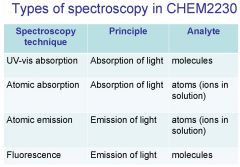
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of light with matter specifically, ___________ energy and matter.
|
radiated
|
|
|
____________ is the study of the interaction of light with matter specifically, radiated energy and matter.
|
Spectroscopy
|
|
|
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of ___________ with ____________ specifically, radiated energy and matter.
|
light, matter
|
|
|
Spectrophotometry is any technique that uses light to measure ___________ ____________.
|
chemical concentration
|
|
|
_______________ is any technique that uses light to measure chemical concentration.
|
Spectrophotometry
|
|
|
Spectrophotometry is any technique that uses _________ to measure chemical concentration.
|
light
|
|
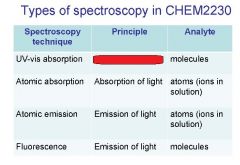
x
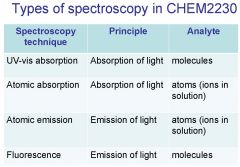
|
x
|
|

|
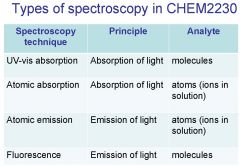
|
|
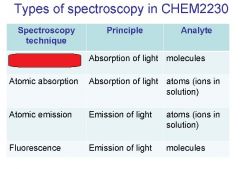
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
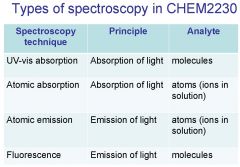
|
|
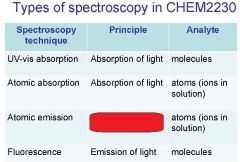
|
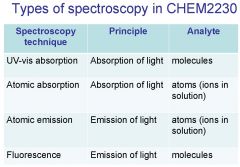
|
|
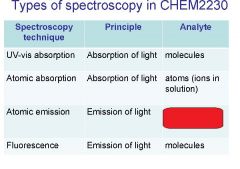
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
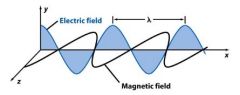
Light consists of ____________, oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
|
pependicular
|
|
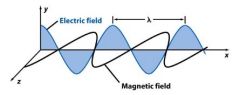
__________ consists of perpendicular, oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
|
light
|
|
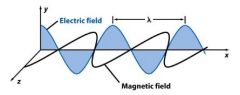
Light consists of perpendicular, ___________ electric and magnetic fields.
|
oscillating
|
|
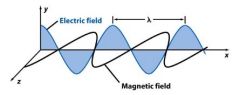
Light consists of perpendicular, oscillating ___________ and _____________ fields.
|
Light consists of perpendicular, oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
|
|
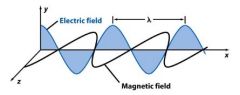
Wavelength (λ) is the crest to crest distance between ________.
|
waves
|
|
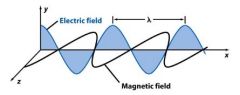
Wavelength (λ) is the ______________ distance between waves.
|
crest to crest
|
|
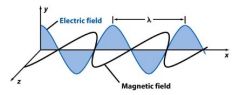
________________ (λ) is the crest to crest distance between waves.
|
wavelength
|
|
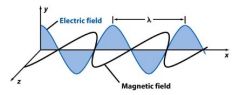
Wavelength (_) is the crest to crest distance between waves.
|
lambda λ
|
|
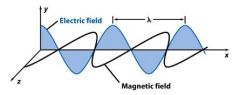
Frequency (ν) is the number of oscillations the wave makes each second. Its unit is _________.
|
Hertz Hz
|
|
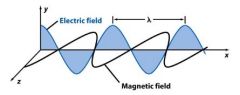
Frequency (ν) is the __________________ the wave makes each second. Its unit is Hertz (Hz).
|
the number oscillations
|
|
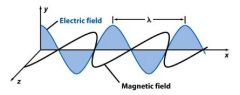
Frequency (_) is the number of oscillations the wave makes each second. Its unit is Hertz (Hz).
|
v
|
|
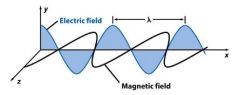
______________ (ν) is the number of oscillations the wave makes each second. Its unit is Hertz (Hz).
|
Frequency
|
|
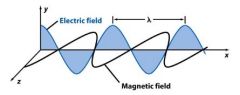
Frequency (ν) is the number of oscillations the _______ makes each second. Its unit is Hertz (Hz).
|
wave
|
|
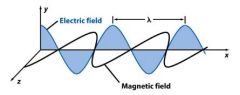
Frequency (ν) is the number of oscillations the wave makes each ____________. Its unit is Hertz (Hz).
|
second
|
|
|
The symbol for wavelength is?
|
λ
|
|
|
The symbol for frequency is?
|
v
|
|
|
In a vacuum __ x ___ = c = speed of light = ___________.
|
λ,v 2.998E8m/s
|
|
|
In a vacuum λ x v = __ = ______.
|
c speed of light
|
|
|
In a medium other than a vacuum the speed of light = v (frequency) = c/n (n is the ___________ __________)
|
refractive index
|
|
|
In a medium other than a __________ the speed of light = v (frequency) = c/n (n is the refractive index)
|
vacuum
|
|
|
In a medium other than a vacuum the speed of light = _____________ = c/n (n is the refractive index)
|
v (frequency)
|
|
|
In a medium other than a vacuum the speed of light = v (frequency) = __/n (n is the refractive index)
|
c
|
|
|
In a medium other than a vacuum the speed of light = v (frequency) = c/__ (__ is the refractive index)
|
n
|
|
|
When a ___________ ________ travels from one medium to another its frequency remains unchanged but its wavelength changes.
|
light wave
|
|
|
When a light wave travels from one __________ to another its frequency remains unchanged but its wavelength changes.
|
medium
|
|
|
When a light wave travels from one medium to another its ____________ remains unchanged but its wavelength changes.
|
frequency (v)
|
|
|
When a light wave travels from one medium to another its frequency remains unchanged but its ___________ changes.
|
wavelength λ
|
|
|
When a light wave travels from one medium to another its ___________ remains unchanged but its _____________ changes.
|
frequency (v) , wavelength (λ)
|
|
|
When the speed of light decreases the __________ remains the same, but the _____________ decreases.
|
frequency(v), wavelength(λ)
|
|
|
Light can also be thought of as particles called _________.
|
photons
|
|
|
The energy of a photon is E=hv. What is h?
|
Planck's constant 6.626E-34 J x sec
|
|
|
The energy of a photon is ___ = ____ x_____
|
E=hv
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
____________ is the energy carried by a light beam per second per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
Irradiance
|
|
|
Irradiance is the ________ carried by a light beam per second per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
energy
|
|
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a ________ ________ per second per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
light beam
|
|
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a light beam per _______ per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
second
|
|
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a light beam per second per ________ _______. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
unit area
|
|
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a light beam per second per unit area. Its unit is ___________ or W/ m^2.
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a light beam per second per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
|
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a light beam per second per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or ___________.
|
Irradiance is the energy carried by a light beam per second per unit area. Its unit is J/ s x m^2 or W/ m^2.
|
|
|
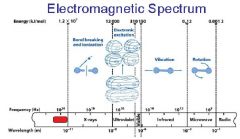
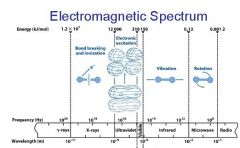
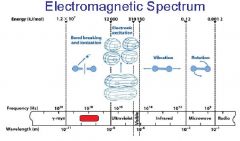
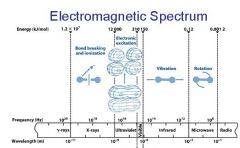
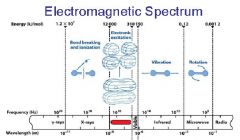
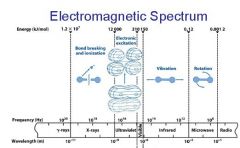
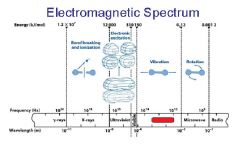
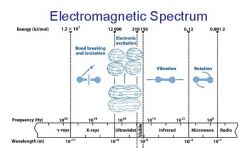
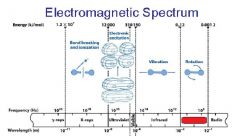
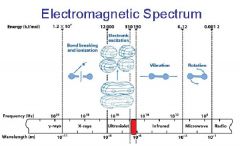
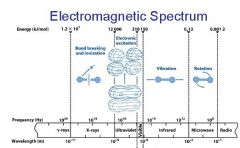
What is the range of the visible spectrum?
|
400-700nm
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
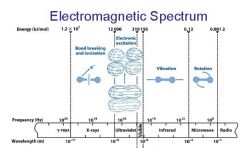
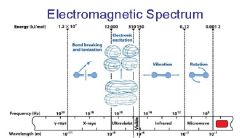
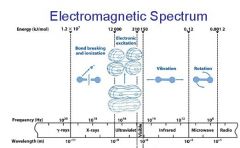
________ light has the longest wavelength. _________ light has the shortest wavelength.
|
Red, blue
|
|
|
The shorter the wavelength the ________ the energy.
|
higher
|
|
|
The _________ the wavelength the higher the energy.
|
shorter
|
|
|
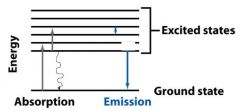
__________________________
When a molecule absorbs a photon, its energy increases from the ground state to the excited state. |
ABSORPTION OF LIGHT
|
|
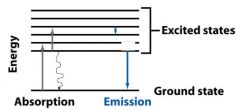
ABSORPTION OF LIGHT
When a molecule absorbs a ________, its energy increases from the ground state to the excited state. |
photon
|
|
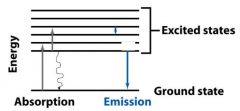
ABSORPTION OF LIGHT
When a molecule absorbs a photon, its energy __________ from the ground state to the excited state. |
increases
|
|
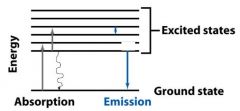
ABSORPTION OF LIGHT
When a molecule absorbs a photon, its energy increases from the __________ state to the __________ state. |
ground, excited
|
|
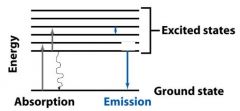
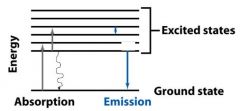
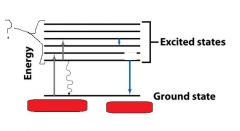
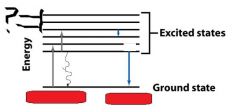
The molecules returning to the ground state do this by emitting __________, a __________ transition. They can also do this by emitting a ________.
|
heat, radiationless, photon
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
singlet
|
|
|
vibrational levels
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
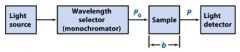
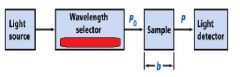
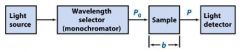
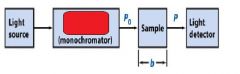
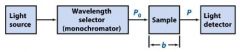
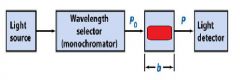
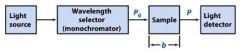
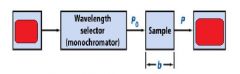
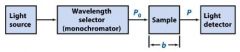
The monochromator allows light of a __________ wavelength to pass through and makes it monochromatic.
|
single
|
|
|
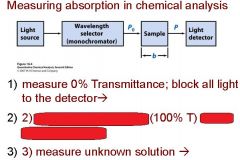
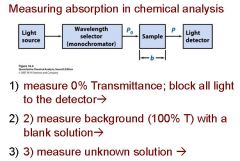
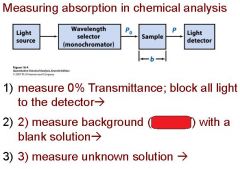
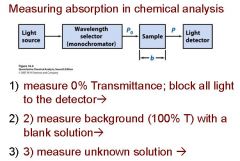
Transmittance = ?
|
P/Po
|
|
|
In T=P/Po, what is P? what is Po?
|
Po is the blank light, P is the sample light
these are detected by the light detector |
|
|
Absorbance = log (?/?) = -log T = - log(?/?)
|
Po/P , P/Po
|
|
|
Absorbance = log (Po/P) = - log ?
|
? = T
|
|
|
What is Beer's law?
|
A = EbC
|
|
|
In Beers law A = E b C , what do the letters stand for?
|
A = absorbance
E = molar extinction coefficient b = path length C = concentration in Molarity |
|
|
What are the units of molar absorptivity or molar extinction coefficient?
|
M^-1, cm^-1
|
|
|
A chromophore is the part of the molecule that _______ ________.
|
absorbs light
|
|
|
Molar absorptivity is a function of?
|
the wavelength of light
|
|
|
__________ __________ is a function of the wavelength of light.
|
molar absorptivity
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
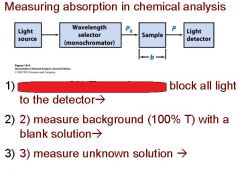
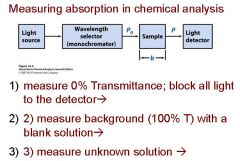
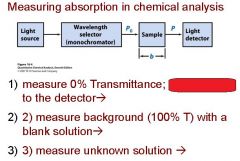
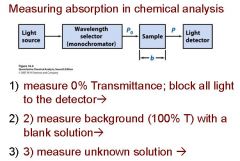
What are the four stipulations of Beer's law?
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
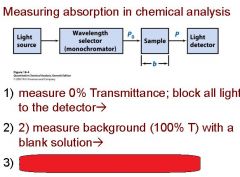
|
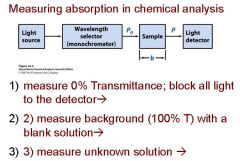
|
|
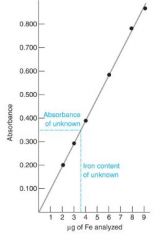
what is the slope on an absorbance calibration curve?
|
slope = molar absorptivity x b (path length)
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
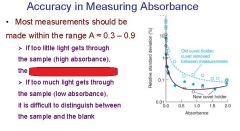
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

