![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four characteristics of all plant cells? |
Eukaryotic (internal membrane-bound organelles), autotrophic (producers), cellulose cell walls, and multicellular |
|
|
How are some plants adapted to life on land? |
1. They have cellulose cell walls, which provide support for the plant outside of water. 2. They have root-like structures to provide for water absorption from soil. 3. They have root-like structures to provide for anchoring and support on land |
|
|
What differentiates bryophytes from tracheophytes? Name some examples. |
Bryophytes- lack vascular tissue for water transport. They do not have "true" roots, stems, or leaves. They transport water by diffusion from cell to cell. Tend to be smaller in size. Do not produce seeds. Reproduce with spores or vegetative propagation. They are pioneer species. Some examples include hair-capped moss, liverworts, and hornworts. |
|
|
What are the characteristics of tracheophytes? Name some examples. |
1) Have xylem to transport water from roots to leaves 2) have phloem to transport sugars throughout the plant 3) have "true" roots, stems, and leaves. 4) can transport water and nutrients more quickly than bryophytes. 5) grow taller Some examples include ferns, club mosses, and horsetails. |
|
|
What advantages do seed plants have over seedless plants? |
Seeds have protective covering to prevent water loss. They already contain a small, partially developed plant, called an embryo. They contain their own food supply. Seeds can survive many years in a dormant state. |
|
|
How does a Monocot differ from a Dicot? Name some examples of each. |
Monocots and dicots are both forms of angiosperms. MONOCOTS- 1) 1 cotyledon 2) root xylem and phloem in a ring 3) vascular bundles scattered in stem 4) leaf veins form a parallel pattern 5) flower parts in threes and multiples of three DICOTS- 1) 2 cotyledons 2) root phloem between arms of xylem 3) vascular bundles in a distinct ring 4) leaf veins form a net pattern 5) flower parts in fours or fives and their multiples |
|
|
Compare/contrast angiosperms and gymnosperms. Name examples of each. |
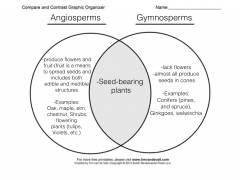
|
|
|
What are the different layers of a woody tree trunk? (be able to label a diagram of the trunk. Be sure to understand the function of each layer. |
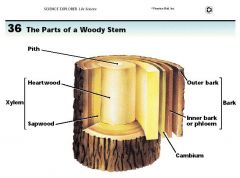
|
|
|
Plant Dichotomous Key |
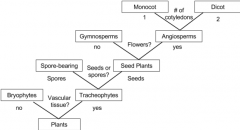
|
|
|
What is photosynthesis? What are the reactants? What are the products? How is photosynthesis related to respiration? |
Photosynthesis is the process in which plants store energy from the sun in food. The reactants are H20, CO2, and light energy. The products are O2 and glucose. Photosynthesis is the opposite of respiration (it undoes respiration) |
|
|
Auxin |
1. stem elongation (promotion of vascular tissue growth) 2. suppression of lateral buds 3. controls production of other hormones 4. causes plants/leaves to have a positive response to light |
|
|
Cytokinins |
1. Stimulation of cell division 2. Rapid plant growth 3. keeps veggies fresh |
|
|
Gibberellins |
1. cause growth of plant cells and germination of seeds |
|
|
Ethylene |
1. ripens fruit 2. forms a cell layer between leaf and stem-- causes leaf to fall off (Fall/Autumn) |
|
|
Abscisic Acid
|
1. keeps seed from sprouting and buds from developing during winter 2. causes stomata to close and plants to respond to water loss on hot days |

