![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Classical conditioning |
Association of automatic responses with a new neutral stimulus |
|
|
|
Unconditoned stimulus (UCS) |
Stimulus that elicits automatic response |
|
|
|
Unconditioned response (UCR) |
Automatic Response to UCS |
|
|
|
Neutral stimulus (NS) |
Stimulus that elicits no response |
|
|
|
Conditioned stimulus (CS) |
Stimulus elicits response after conditioning |
|
|
|
Conditioned response (Cr) |
Learn response to previously NS |
|
|
|
Operant conditioning |
Form of learning in which consequences of behaviors produce changes in the probability of the behaviors being repeated |
|
|
|
Operant conditioning #2 |
Learning in which voluntary behavior is strengthened or weakened by consequences |
A desirable or aversive consequence is added or subtracted leading to an increase or decrease in the behavior |
|
|
Reinforcement |
Process in which consequence strengths behavior |
Increases the probability that the behavior will be repeated |
|
|
Positive reinforcement |
Presentation of a desirable stimulus following a behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will be repeated |
|
|
|
Negative reinforcement |
Removeal of an aversive stimulus following a behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will be repeated |
|
|
|
Punishment |
Process in which consequences weakens behavior - decreases the probability that the behavior will be repeated |
|
|
|
Positive punishment |
Presentation of an aversive stimulus following a behavior that increases the probability that the behavior will be repeated |
|
|
|
Negative punishment (penalty) |
Remove all of a desirable stimulus following a behavior that decreases the probability you will be repeated |
|
|
|
Observational learning |
Learning by observing the behavior of other people |
|
|
|
Vicarious learning |
Likelihood of a behavior changes depends upon whether another is reinforced or punished for the behavior |
|
|
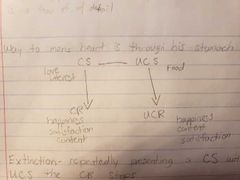
|
Extinction- Repeatedly presenting CS without UCS CR stops |
|
|
|
Generalization |
Generalized response to familiar items (bell or food) |
|
|
|
Phobias |
Irrational fear |
|
|
|
Systematic desensitization |
Technique used to overcome a phobia |
|
|
|
Spontaneous recovery of CS |
Food aversion- contamination in food which makes you sick.....avoids that food in future |
|
|
|
Primary reinforcers |
Automatically rewarding or reinforcing |
|
|
|
Secondary Reinforcers |
A stimulus that gains it's reinforcing powers through its association with the primary reinforcer aka conditioned reinforcer |
|
|
|
Continuous reinforcement schedule |
Reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs |
|
|
|
Intermittent reinforcement schedule |
Reinforcing response only part of the time; Results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction then does continuous reinforcement |
|
|
|
Memory |
The persistence of learning over time thru the encoding, storage and retrieval of info |
|
|
|
Recall |
Measure of memory in which a person must retrieve info learned earlier |
|
|
|
Recognition |
A measure of memory in which the person must identifies items previously learned |
|
|
|
Encoding |
The processing of info into the memory system |
|
|
|
Parallel processing |
The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously |
|
|
|
Sensory memory |
The immediate very brief recording of sensory info in memory system |
|
|
|
Explicit memory |
Memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare" |
|
|
|
Implicit memory |
Retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection aka nondeclarative memory |
|
|
|
Iconic memory |
A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli, a photographic or picturre-image memory lasting a few tenths of a second |
|
|
|
Echoic memory |
A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli |
|
|
|
Semantic memory |
Explicit memory of facts and general knowledge |
|
|
|
Episodic memory |
Explicit memory of personally experience events |
|
|
|
Procedural memory |
Memory of how to do things like ride a bike |
|

