![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Devices that moves fluids(liquids or gases) or sometimes slurpies, by mechanical action. Machines used to add energy to a liquid in order to transfer it from one point to another point of higher energy level |
PUMPS |
|
|
2 classification of pumps |
Positive displacement ang rotodynamic pumps |
|
|
Types of positive displacement pumps |
Reciprocating and rotary |
|
|
Type of reciprocating pumps |
Piston or plunger and diaphragm |
|
|
Types of rotodynamic pumps |
Centrifugal and special effect pumps |
|
|
Types of centrifugal pump |
Axial flow Mixedflow, radial flow Peripheralt |
|
|
Examples of special effect pumps |
Jet (eductor) Gas lift Hydraulic ram Electro magnetic Reversible centrifugal |
|
|
Makes a fluid move by trapping fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe At some cases use an expanding cavity on suction side and decreasing cavity on the discharge side. |
Positive displacement pumps |
|
|
Are type of velocity pump in which kinetic energy is added to the fluid by increasing the flow velocity. |
Rotodynamic pumps |
|
|
The increase in energy is converted to a gain in potential energy (pressure) when the velocity is reduced prior to or as the flow exits the pump into the discharge pipe. This conversion of kinetic energy to pressure is explained by the first law of thermodynamics, or more specifically |
Bernoulli's principle |
|
|
Traits of rotodynamic pumps |
Dynamic pumps can be further subdivided according to the means of velocity gain is achieved These types of pumps have a number of characteristics Continuous energy Conversion of added energy to increase in kinetic energy(increase in velocity) Conversion of increased velocity (kinetic energy) to an increase in pressure head |
|
|
Example of rotodynamic pump |
Centrifugal pump |
|
|
Examples of positive displacement pumps |
Single acting triplex pump Screw pump Turbine pump Jet pump |
|
|
Typical pump installation |
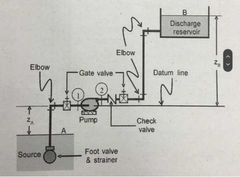
|
|
|
Reciprocating pumps |
Low discharge, high head, low speed, self priming |
|
|
Centrifugal pumps |
High discharge, low head, high speed, not self priming |
|
|
Rotary pumps |
Low discharge, low head, and for pumping viscous liquid |
|
|
Turbine pump |
For pumping water with high suction lift and for pumping condensate |
|
|
Jet pump (injector) |
Used for pumping boiler feed water and as an accessory for centrifugal pump |
|
|
Is a turbine pump for suction lift up to 22 ft |
Shallow well pump |
|
|
A centrifugal pump with a injector for suction lift up to 120 ft |
Jet deep well pump |
|
|
Is a deep well pump used for heads up to 1000ft and for capacities up to 7000gpm |
Turbine pump |
|
|
Is a deep well pump used for heads up to 8000 ft |
Submersible pump |
|
|
Is the speed in rpm at which geometrically similar pumos impeller operate to develop one foot of head when discharging 1 gallon per minute |
Specific speed |
|
|
All wheels with the same specific speed have the same efficiency excepts for variations due to |
Viscosity of fluids |
|
|
English unit for NS |
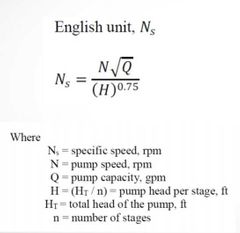
|
|
|
Si units for Ns |

|

