![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
40yo pt. w/SOB cough, leg ulcers, purulent nasall d/c. Dx? |
Granulomatosis w/polyangiitis |
|
|
What Tx decreases mortality in COPD pt.? |
Long term supplemental O2 Tx
|
|
|
When are Factor Xa-i contraindicated in Tx of PE? |
Pt. estimated GFR <30 ml/min/1.63m^2 |
|
|
Pt. w/likely asbestosis exposure, pleural plaques and worsening dyspnea, weight loss. Dx? |
Bronchogenic carcinoma (much more likely than mesothelioma) |
|
|
Pt. on ventilaor w/alkalosis and a low pCO2 What vent. setting needs to be changed? |
Decrease the RR |
|
|
Chlorpheniramine drug class |
H-1 receptor antagonist |
|
|
Three factors that contribute to ARDS |
Impaired gas X∆, decreased lung compliance, increased pulmonary arterial pressure. |
|
|
Wells criteria are >4, in a pt. with distress. Next step? |
IV Heparin infusion |
|
|
Causes of digital clubbing? |
Lung malignancy, CF, R-L pulm. shunt. (NOT Hypoxia) |
|
|
Mechanism of digital clubbing. |
Megakaryocytes bipass lung and don't break down, trap in extremities and rease PDGF/VEGF |
|
|
BAL (bronchoscopy and lavage) is useful for... |
-Suspected malignancy -Suspected opportunistic pulmonary infx. |
|
|
What effect to gluccocorticoids have on WBCs? |
Glucocoticoid-induced neutrophilia: mobilize marginal neutrophil pool
|
|
|
Anatomical location of bronchogenic cyst. |
Middle mediastinum |
|
|
Anatomical location of thymoma. |
Ant. mediastinum |
|
|
Thymoma assoc. with what Dz? |
Myesthenia Gravis |
|
|
Anatomical location of neurogenic tumors in chest? |
Post. mediastinum |
|
|
Highest risk of TB in the US is in pt. who... |
Emigrated from endemic area w/in 5 years. |
|
|
Anatomic location of esophageal leiomyoma. |
Post. mediastinum |
|
|
Indication for abx. in COPD exacerbation |
- 2/3: dyspnea, cough, sputum - Moderate-Severe exacerbation - Req. mechanical ventilation |
|
|
OSA/OHS resp. acidosis or alkalosis? |
Acidosis (retained CO2) |
|
|
OSA/OHS met. acidosis or alkalosis? |
Alkalosis (compensation by retaining HCO3 and excreting Cl) |
|
|
Sputum w/broad based budding yeast yeast. Dx? |
Blastomycosis
|
|
|
Tx for blastomycosis |
Itraconazole or Amphotericin B |
|
|
Characterists x-ray of sarcoidosis |
B/L hilar lymphadenopathy, interstitial infiltrates |
|
|
Most common side effect of using inhaled corticosteroids |
oral condidiasis (thrush) |
|
|
Property of pleural fluid indicating that it likely must be drained. |
pH < 7.2 indicates empyema and therefore removal of fluid via thoracostomy |
|
|
Some causes of exudates |
- Infxn. - Malignancy - Connective Tissue Dz - Pulmonary Embolism |
|
|
Repeat PNA in same anatomical location. 1. suspect. 2. perform? |
1. local obstruction 2. CT-Scan |
|
|
Pt. w/sudden collapse, increaesd JVP, CP, Decreased O2 Sat and hypotension, and clear lungs |
Massive PE w/subsequent RV disfunction |
|
|
Empiric OP Tx for pt. with CAP |
- Healthy: doxycycline or macrolide (e.g. azythromycin) - Comorbid: fluoroquinolone (e.g. moxifloxacine) or macrolide + ß-lactam |
|
|
Empiric IP Tx for pt. with CAP |
- fluoroquinolone (e.g. moxifloxacine) or - macrolide (e.g. azythromycin) + ß-lactam |
|
|
Empiric IP Tx in the ICU for pt. with CAP |
- fluoroquinolone (e.g. moxifloxacine) + ß-lactam or - macrolide (e.g. azythromycin) + ß-lactam |
|
|
Body's response to decreased CO2 (rep. alk.) |
Excrete HCO3 (e.g. alk. urine, met. acid.) |
|
|
CURB-65 1. Define 2. Scores? |
1. Confusion, Uremia, Resp (>30), BP (<90/60), age > 65 2. ≥2 admit, ≥4 admit to ICU |
|
|
Post operative pt. w/hypotension, JVD, new onset RBBB |
Massive PE w/RV strain. |
|
|
Tx for UACS |
1st gen H1-blocker (e.g. chlorpheniramine) or combined anti-histamine decongestant (e.g. brompheniramine and pseudoephedrine) |
|
|
Tiotropium drug class. |
Long Acting Muscarinic Antagonist (LAMA) |
|
|
S/Sx of theophylline tox? Common cause? |
1. HA, insomnia, seizure, N/V, arrythmia 2. CYP450-i (e.g. new antbx.) |
|
|
Chronic cough (>8wk), worse at night in pt. on PPI unresponsive to H1-i Next step? Likely Dx? |
PFT Asthma |
|
|
Elevation of left main bronchus in dyspneic pt. |
LA enlargement 2/2 mitral stenosis |
|
|
New onset yellow blood tinged sputum in pt. w/ acute bronchitis (mild fever) 1. Dx? 2. Tx? |
1. Still viral URI! 2. Tx is supportive |
|
|
Common asymptomatic pulm. infx in Mississippi and Ohio river valley (and Central America). |
Histoplasmosis |
|
|
Reversible (>12% increase in FEV1) airway obstruction at any age. Dx? |
Asthma! |
|
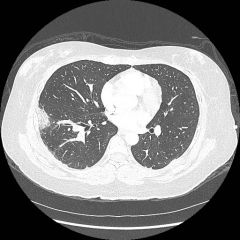
Dx? |
PE (big one) |
|
|
Glomeruloniphritis w/respiratory tract dz. Dx? Dx via? |
Granulomatosis w/polyangiitis dx via positive c-ANCA on serology |
|
|
test to confirm clx suspicion for primary pulm. HTN |
Echo |
|
|
Best Tx for ARDS |
PEEP |
|
|
SIADH assoc. w/which malignancy |
Small Cell Lung Cancer |
|
|
Best way to definitively confirm sarcoidosis dx? |
Bronchoschopy and transbornchial lung Bx |
|
|
Tx for anaerobic lun abscess (e.g. in alcoholic or demented pt.) |
4-6wk of clindamycin |
|
|
Bosetan Rx class and primary use |
endothelin-1 receptor antagonist (constricts pulmonary blood vessels in order to tx pulmonary HTN) |
|
|
3 Tx for primary pulm. HTN |
Bosentan, PDE-5-i (-nafil and dipyridamole), prostanoids |
|
|
Abx for UTI causing hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
Nitrofurantoin |
|
|
Pt. who used fenfluramine-type appetite suppression is at risk for what lung dz? |
Primary pulm. HTN |
|
|
Occupational exposure, egg-shell calcifications in lung Dx? |
Silicosis |
|
|
Characteristc that tips pleural effusion is 2/2 boerhaver syn? |
dramatically decreases pH b/c of gastric acid |

