![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|

|

E! |
|

|

|
|
|
Where do most emboli come from? What is this called? Two other places? What are components of non-blood clot emboli? |

Prostate cancer, cerival cancer, uterine cancer Upper extremity from central line catheterization |
|
|
What are predisposing risk factors for clot formation? (Virchow's triad)? |

|
|
|
What are some risk factors related to stasis? |

|
|
|
What are some congenital associations related to hypercoagulability? |

|
|
|
What are some acquired hypercoagulability conditions? |

Look over HIT Most common cause of DIC in ICU = Sepsis! another cause = cancer. |
|
|
What are some causes of endothelial injury? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
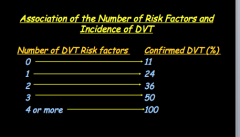
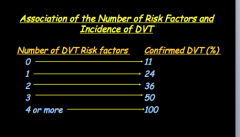
What factors carry the highest relative risk for VTE? |
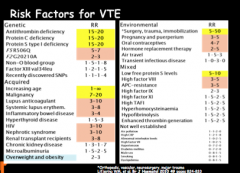
No need to memorize |
|
|
What determines the physiologic consequence of PE? |

|
|
|
What are some causes of increased pulmonary vascular resistance?
Does vascular obstruction increase or deacrease alveolar dead space? What does it do to V/Q ratio? How is DLCO affected? What type of shunt is established? |

Almost never check DLCO in PE patient. |
|
|
Why do you get alveolar hyperventilation? What happens to airway resistance? Why? Result? Increased or decreased pulmonary compliance? Why? |

|
|
|
Does the uninvolved vascular dilate or constrict? Why? What does this improve overall? |

|
|
|
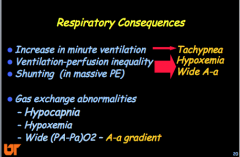
Respiratory consequences: What is increased? What about A-a?
What are the three gas change abnormalities? |
|
|
|
What are the circulatory consequences? |

|
|
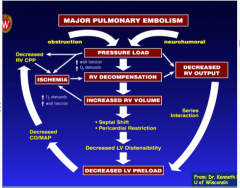
|
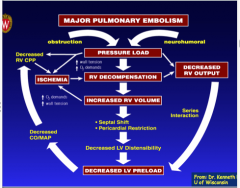
|
|
|
What is the most favorable natural outcome? What are some compensation mechanisms? |

|
|
|
What are some diagnostic measures for PE? |
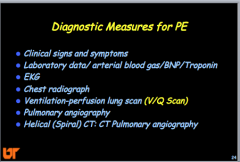
|
|
|
What are the major symptoms and signs in PE? HR, RR, CO2, O2? |
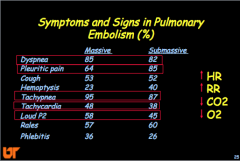
|
|
|
What are some important lab data? PaO2, PaCO2, A-a gradient, WBC, D-dimer, LDH and bilirubin |

|
|
|
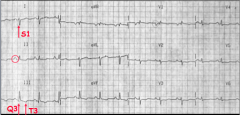
What are some EKG findings in PE? |

|
|
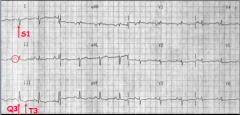
What is shown here? |
|
|
|
What is typically seen in CXR? What are some other possible signs? What about when the emboli are small? |

|
|
|
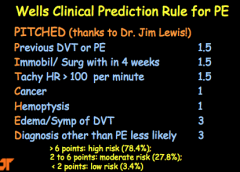
What is the Wells Clinical Prediction Rule for PE? (PITCHED). Ranges of risk. |
|
|
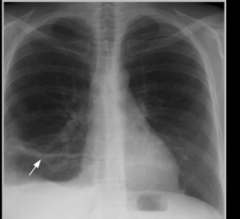
What is shown here? |
Discoid atelectasis |
|
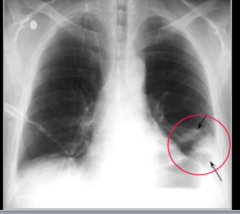
What is this sign? |
Hampton's hump --> PE |
|
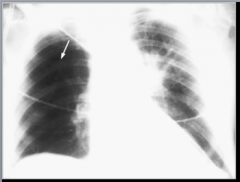
What sign is this? |
Westermark's sign |
|
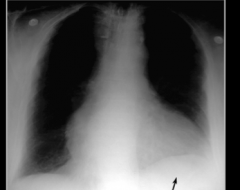
What sign is shown here? |
Elevated left hemi diaphragm |
|

|

|
|
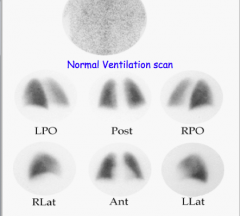
|
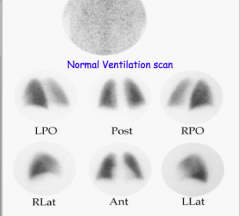
|
|
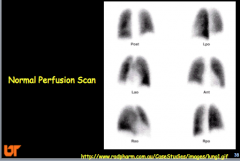
|
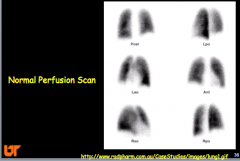
|
|
|
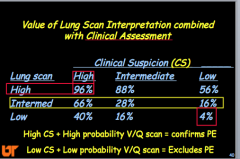
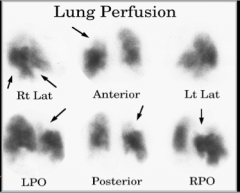
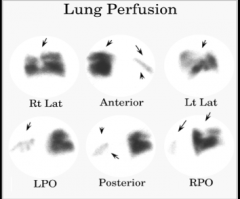
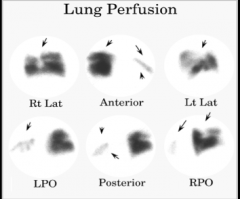
Lung scan high, intermediate, and low --> sensitivity and specificity (high or low)? |
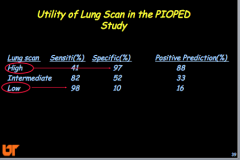
|
|
|
How does it change when combined with CLINICAL ASSESSMENT? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
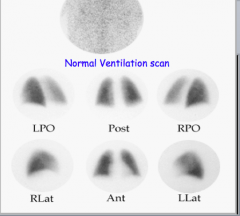
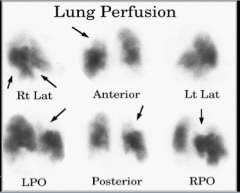
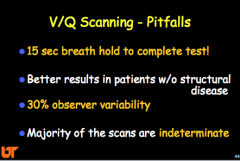
What are some V/Q scanning pitfalls? |
|
|
|
What is the GOLD STANDARD? How is PE seen? |

|
|
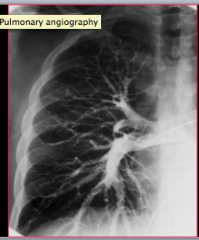
What is this? |
Pulmonary angiography |
|
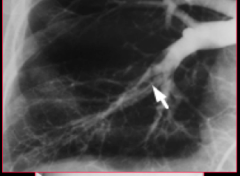
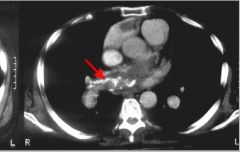
What does the arrow indicate? |
PE? |
|
|
What are some newer techniques? |

|
|
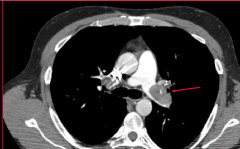
What is indicated on the CT? |
HRCT showing L. main pulmonary artery filling defect. |
|
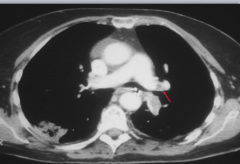
|
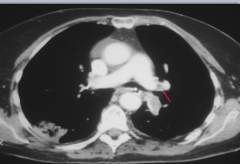
HRCT showing R. main pulmonary artery filling defect. |
|
|
|
|
|
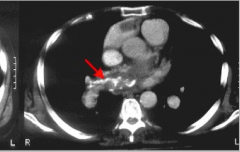
|
|
|
What two things reliably establishes PE? |

|
|
|
What can exclude PE? Other studies? What if patient has non-high probability scan and negative noninvasive studies for DVT? |

|
|
|
What has become the primary diagnostic modality of choice for PE? What does it provide if PE excluded? |

|
|
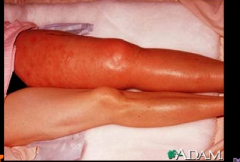
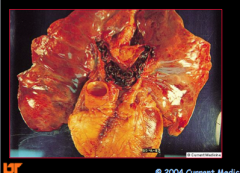
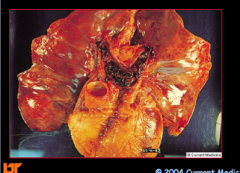
What would you suspect if you saw this? |
DVT |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of DVT? |

|
|
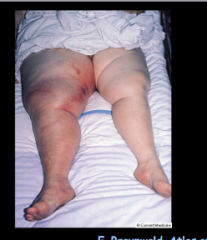
|
DVT |
|
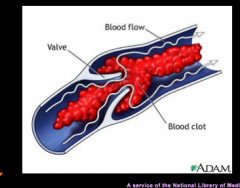
|
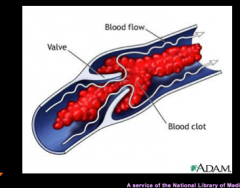
|
|
|
What are some diagnostic measures for DVT? |
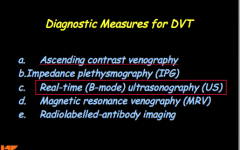
|
|
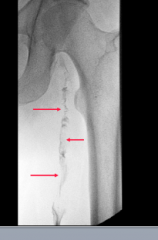
|
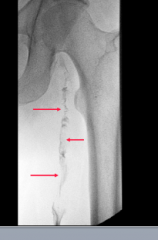
|
|
|
How do you prevent DVT (prophylaxis)? Drug? |

|
|
|
What is the treatment for PE and DVT? |

|
|
|
What are the two newer anticoagulants available? |

|
|
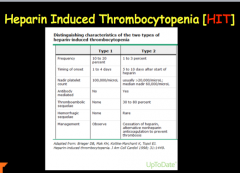
Don't forget HIT! |
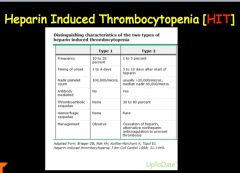
|
|
|
What are the three interventions? |
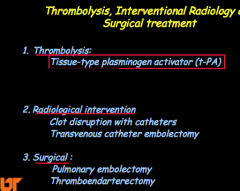
|
|
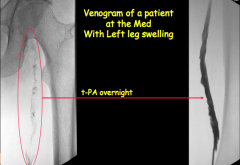
|
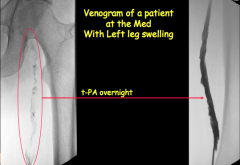
|
|
|
Is death common? When to hemodynamic levels return to normal? Do most patients develop pulmonary hypertension? |

|
|
|
What do non-blood clot pulmonary emboli contain? Disease? |
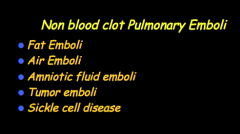
|
|
|
When are fat embolisms common? What is the clinical triad? |
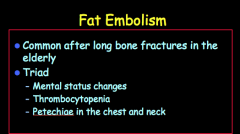
|
|
|
Most common complaint from a patient with acute PE is what? |
Shortness of breath |
|
|
Strong suspicion for PE, no contraindications to anticoagulation therapy, awaiting helical CT, what do you do next? |
Proceed with starting anticoagulation since your suspicion for pulmonary embolism is very high in this patient. |
|
|
What will the chest X-ray likely show? |
Atelectasis or decrease in lung volume (most common if there is an abnormality...most likely will be normal)
Any enlargement will be on the right side of the heart
Pleural effusions will be very small. |

