![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
201 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is a spine sign?
|
summation sign on the spine
|
|
|
What is the presentation of CMV pneumonitis?
|
fever, hypoxia, cough, bilateral interstitial infiltrates
|
|
|
How is CMV pneumonitis treated?
|
Ganciclovir, cidofovir, foscarnet
|
|
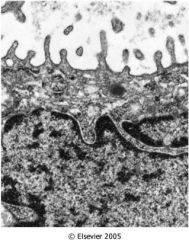
What is seen here?
|
Adenocarcinoma.
|
|
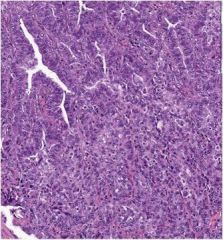
What is seen here?
|
Adenocarcinoma, acinar & solid
|
|
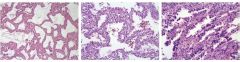
What is this showing the development of?
|
Adenocarcinoma
|
|
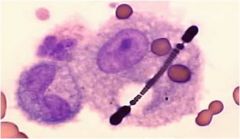
What is this?
|
Asbestos body
|
|
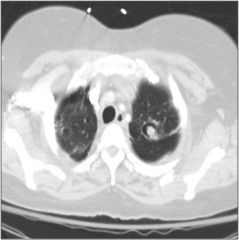
What is this?
|
Aspergilloma
|
|
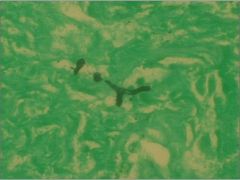
What could this be?
|
Aspergillus
|
|
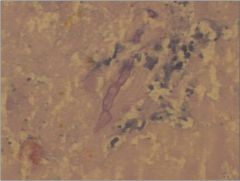
What could this be?
|
Aspergillus
|
|
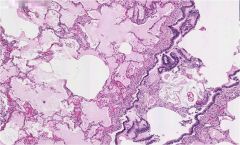
What disease is this causing?
|
Aspiration pneumonia
Dominated by oral anaerobes. |
|
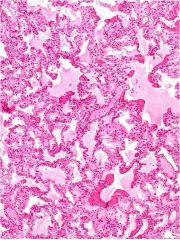
What is this?
|
Atypical pneumonia
|
|
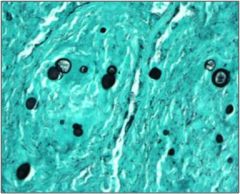
What is this organism?
|
Blastomycosis
|
|
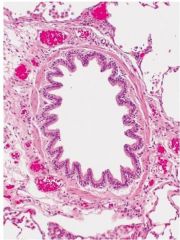
What part of the airway is shown here?
|
Bronchiole
|
|
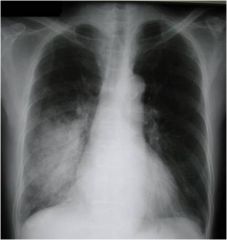
What does this indicate is a possiblity?
|
Bronchopneumonia
|
|
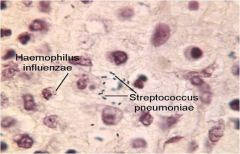
|
Bronchopneumonia causes
|
|
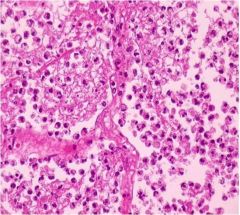
What is seen here and what is it associated with?
|
Bronchopneumonia inflammation
|
|
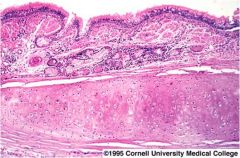
What part of the airway does this show?
|
Bronchus
|
|
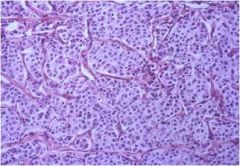
What do you see here?
|
Carcinoid
|
|
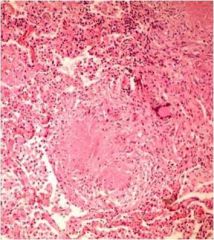
What is this?
|
Caseating granuloma
|
|
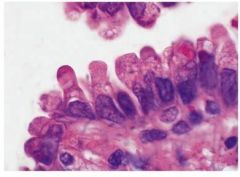
What cells are these?
|
Clara cells
|
|
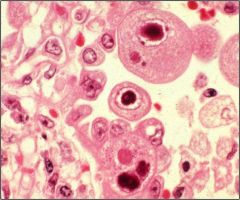
What does this indicate?
|
CMV
|
|
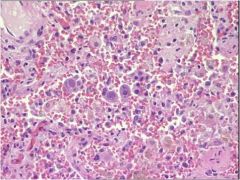
What does this show?
|
CMV pneumonia
|
|
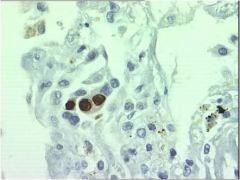
What does this show?
|
CMV pneumonia
|
|
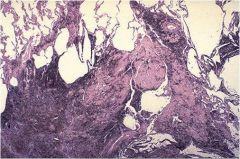
What disease does this show?
|
Coal Workers' Pneumonitis
|
|
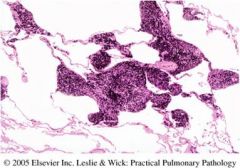
What disease does this show?
|
Simple CWP
|
|
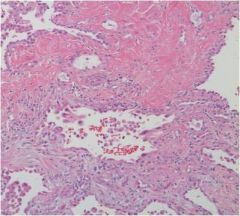
What disease might this be associated with?
|
IPF (UIP)
dense fibrosis |
|
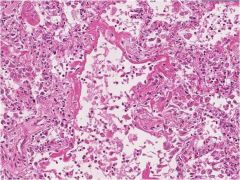
What disease might this be associated with?
|
Influenza
Diffuse alveolar damage |
|
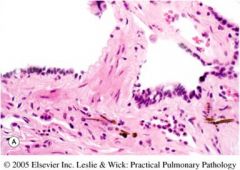
What disease might this be associated with?
|
Asbestosis
Diffuse interstitial fibrosis |
|
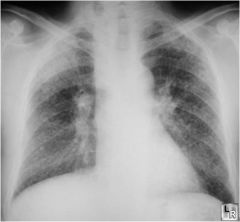
What disease might this be associated with?
|
Silicosis
Diffuse micronodular disease |
|
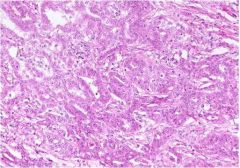
What disease might this be?
|
Epithelial mesothelioma
|
|
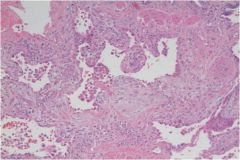
What is seen here?
|
Fibroblastic foci indicative of UIP
|
|
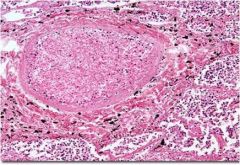
What is this?
|
Pulmonary abscess w/fibrin wall
|
|
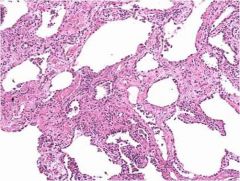
What is this?
|
Fibrotic NSIP
|
|
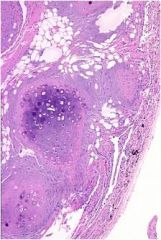
what is this?
|
hamartoma
|
|
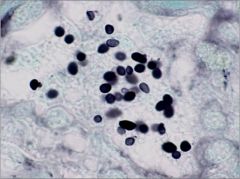
what is this?
|
histoplasma
|
|
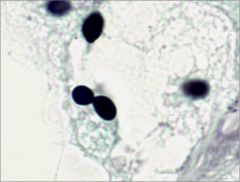
what is this?
|
histo
|
|
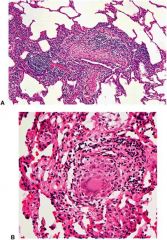
what is this?
|
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
|
|
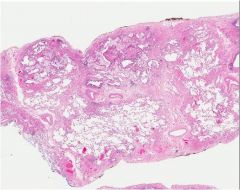
what is this?
|
UIP
|
|
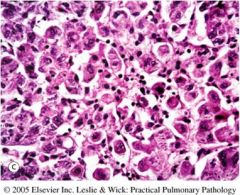
What is this?
|
Large cell carcinoma
|
|
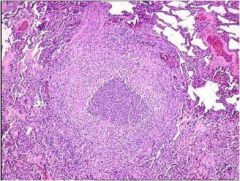
What process is seen here?
|
Liquefactive necrosis
|
|
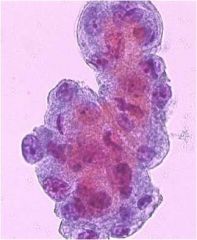
What is seen in this pleural effusion?
|
Malignant cells
|
|
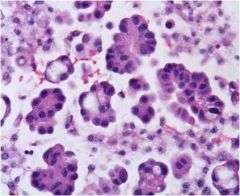
What is seen in this pleural effusion?
|
adenocarcinoma
|
|
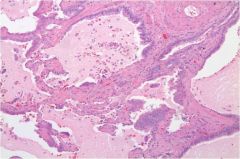
What is this?
|
mesothelioma
|
|
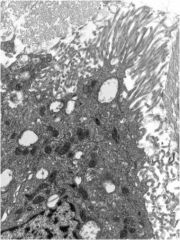
What is this and what is it related to?
|
Microcysts related to pulmonary fibrosis
|
|
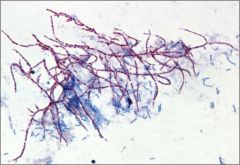
What is this?
|
Nocardia
|
|
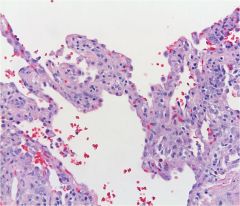
What is this?
|
NSIP
See alveolar wall expansion |
|
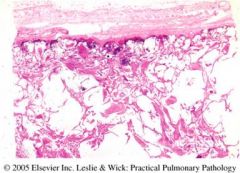
what is this?
|
organizing pneumonia
|
|
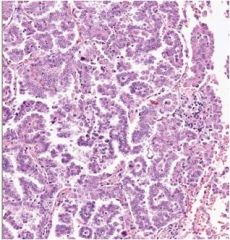
What malignancy is seen here?
|
Papillary adenocarcinoma
|
|
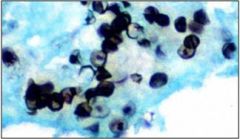
What is this?
|
PCP
|
|
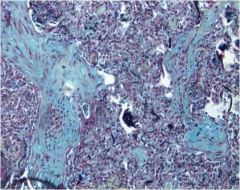
what is seen here & what is it related to?
|
Pleural fibrosis-->asbestosis
|
|
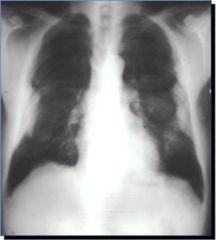
What is this?
|
Pleural plaque
|
|
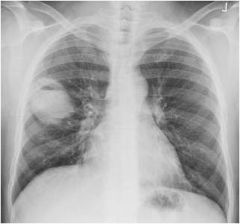
What is seen here?
|
pulmonary abscess
|
|
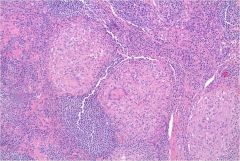
What does this indicate?
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
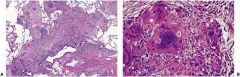
What is this and when is it found?
|
Noncaseating granuloma-->sarcoidosis
|
|
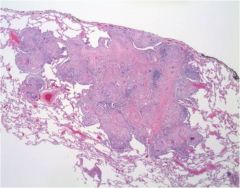
What is this?
|
Noncaseating granuloma-->sarcoidosis
|
|
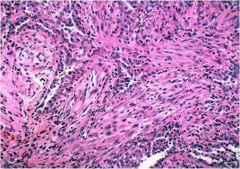
What is this?
|
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma
|
|
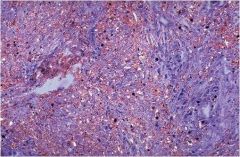
What disease is shown?
|
Silicosis
|
|
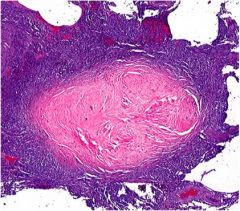
What is this?
|
Silicotic nodule
|
|
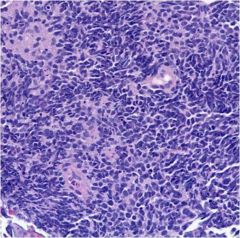
What is this?
|
Small cell carcinoma
|
|
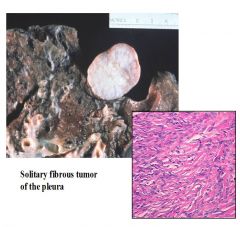
What is this?
|
Solitary fibrous tumor
|
|
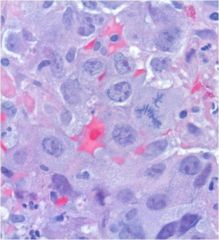
What is this malignancy?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
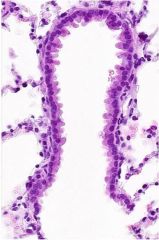
What part of the respiratory tract is this?
|
Terminal bronchiole
|
|
|
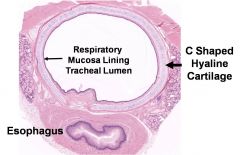
What part of the respiratory tract is this?
|
trachea
|
|
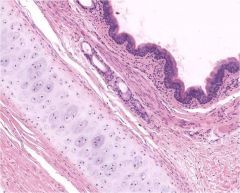
What part of the respiratory tract is this?
|
trachea
|
|
What part of the respiratory tract is this?
|
trachea
|
|
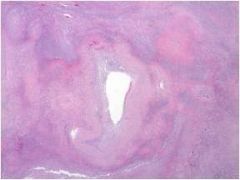
What disease is this?
|
Wegener's granulomatosis
|
|
|
What is normal pCO2?
|
40mmHg
|
|
|
What is the cutoff for pulmonary hypertension?
|
mPAP>25mmHg at rest
mPAP>30mmHg exercise |
|
|
What is normal HCO3?
|
24
|
|
|
What is normal A-a gradient?
|
4+(age/4)
|
|
|
What is normal anion gap?
|
12+/-2
|
|
|
What is respiratory acidosis?
|
pH<7.4
pCO2>40 |
|
|
What is respiratory alkalosis?
|
pH>7.4
pCO2<40 |
|
|
What is metabolic acidosis?
|
pH<7.4
HCO3 decreased |
|
|
What is metabolic alkalosis?
|
pH>7.4
HCO3 increased |
|
|
What are some causes of respiratory acidosis?
|
Hypoventilation
CNS depression Thoracic cage abnormality Obstructive lung disease Obesity Hypothyroidism |
|
|
What are some causes of respiratory alkalosis?
|
Hyperventilation
Anxiety Pain Chronic liver disease Pregnancy PE Hyperthyroidism CNS stimulation Aspirin |
|
|
What are some causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis?
|
Ketoacidosis
Lactic acidosis Uremia MeOH or ethylene glycol poisoning Aspirin OD |
|
|
What are some causes of non-anion gap metabolic acidosis?
|
Diarrhea
Renal tubular acidosis TPN Ureteral diversion Pancreas transplant |
|
|
What are some causes of chloride responsive metabolic alkalosis?
|
Vomitinig
Nasogastric suctioning Diuretics |
|
|
What are some causes of chloride unresponsive metabolic alkalosis?
|
Corticosteroids
Cushings Hyperaldosteronism |
|
|
What is the prototypical perfusion limited gas?
|
NO
|
|
|
What is the prototypical diffusion limited gas?
|
CO
|
|
|
How do you calculate DLCO?
|
DLCO=Vco/PACO
Vco=minute ventilation PACO=alveolar pressure of CO |
|
|
What is normal DLCO?
|
25ml/min/mmHg
|
|
|
where do bronchial arteries arise from?
|
Aorta & intercostal arteries
|
|
|
what is the TMG?
|
Transmural pressure gradient
TMG=Pinside-Poutside |
|
|
What are the effects of inhalation on the size of the extra- and intra-alveolar vessels?
|
Extra-alveolar: lung distension increases TMG-->vessel distension
Intra-alveolar: lung distension decreases TMG-->increased vascular resistance |
|
|
What happens to the PVR & mPAP during exercise?
|
mPAP increases
PVR decreases |
|
|
What are the target chemicals for treating patients with pulmonary hypertension?
|
Vasodilators: NO & PGI2
Vasoconstrictors: Endothelin-1, 5HT |
|
|
What does PAOP represent?
|
Left atrial pressure (LAP) measured from the tip of the Schwan-Ganz catheter
|
|
|
How do you calculate PVR?
|
(mPAP-PAOP)/CO=PVR
|
|
|
What is the Starling equation?
|
Jv=Kfc[(Pc-Pt)-σ(∏p - ∏t)]
|
|
|
What happens with ACE in the pulmonary circulation?
|
Angiotensin I-->Angiotensin II by ACE
|
|
|
What happens to bradykinin in the pulmonary circulation?
|
80% degraded by ACE
|
|
|
What happens to serotonin in the pulmonary circulation?
|
Nearly completely removed.
|
|
|
What is normal A-a gradient?
|
<20mmHg in young people
|
|
|
What is anatomic shunt?
|
Systemic blood enters the left ventricle w/o passing through pulmonary vasculature
|
|
|
What are physiological causes of anatomic shunt?
|
From bronchial & pleural veins
|
|
|
What are some pathologic causes of anatomic shunt?
|
Congenital heart disease
|
|
|
What is an absolute intrapulmonary shunt?
|
True shunt arising from completely collapsed alveoli which remain perfused causing blood to pass through w/o participating in gas exchange
|
|
|
What is a shunt-like condition?
|
Lung unit with relatively low amount of ventilation relative to perfusion-V/Q inequality
|
|
|
What is V/Q?
|
Ventilation-perfusion ratio
V=alveolar ventilation in L/min Q=cardiac output in L/min |
|
|
What does a V/Q of 0 represent?
|
0/x
No ventilation-->intrapulmonary shunt |
|
|
What does a V/Q of infinity represent?
|
x/0
No blood flow-->dead space ventilation |
|
|
What is the main compensatory mechanism for V/Q mismatch?
|
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
|
|
|
What is a normal PAOP?
|
<12
Higher indicates type II PH (left heart) |
|
|
What is defined as PAH?
|
Pulmonary hypertension due to problems with the pulmonary arteries.
|
|
|
What are some diseases associated w/PAH (APAH)?
|
CT diseases (SLE, RA, scleroderma), congenital shunts (patent foramen ovale), portal hypertension, drugs (anorexigens), HIV infection
|
|
|
What is group 2 PH?
|
Associated with left heart disease
|
|
|
What is group 3 PH?
|
PH due to lung disease and/or hypoxemia
|
|
|
What is group 4 PH?
|
PH related to chronic thrombotic and/or embolic disease
|
|
|
What is group 5 PH?
|
PH related to a variety of causes...
Sarcoidosis, LAM, Eosinophilic granuloma (Histiocytosis X), pulmonary vessel compression |
|
|
What are the mechanisms of vascular injury in PH?
|
Endothelial dysfunction
decreased NO synthase decreased PGI2 production increased ET-1 production increased thromboxane production Vascular smooth muscle dysfunction |
|
|
What are the changes seen in PH when it is still reversible?
|
Early intimal proliferation
Smooth muscle hypertrophy |
|
|
What vascular changes are seen in irreversible PH?
|
In situ thrombosis
Adventitial & intimal proliferation Smooth muscle hypertrophy Plexiform lesion |
|
|
What is sildenafil?
|
Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor
Used in PH inhibits cGMP breakdown-->perpetuates action of NO Pill form |
|
|
What are the endothelin-1 receptor antagonists (ETRA)?
|
Bosentan
Ambrisentan/Sitaxsentan |
|
|
What does bosentan do?
|
Blocks ETA and ETB
"Dual ETRA" PH medication |
|
|
What does ambrisentan do?
|
ETRA selective for ETA
PH medication |
|
|
What are the prostanoids?
|
Epoprostenol
Treprostinil Iloprost |
|
|
How do the prostanoids work?
|
Analogs of PGI2
Stimulate adenylate cyclase to produce cAMP |
|
|
What is the problem with epoprostenol?
|
IV infusion that must be given continuously
Side effect=fatal rebound hypertension |
|
|
How is iloprost administered?
|
inhalation
|
|
|
How is treprostinil administered?
|
IV or SC
|
|
|
What are the calcium channel blockers?
|
Nifedipine, amlopidine, diltiazem
|
|
|
What do the calcium channel blockers do?
|
Vasodilators
Only 10% of patients will have good sustained response Used for PH |
|
|
What are symptoms of PH?
|
Dyspnea
Chest pain Syncope Edema (usually of legs) |
|
|
What is LaPlace's law for alveoli?
|
P=4T/r
P=pressure T=surface tension of liquid r=radius |
|
|
What LaPlace's law for soap bubble?
|
P=2T/r
P=pressure T=surface tension of liquid r=radius |
|
|
What determines the type of airflow?
|
Re=2rvd/n
r=radius v=velocity d=density of gas n=viscosity |
|
|
What has turbulent flow?
|
Trachea
|
|
|
What kind of airflow do the smallest airways have?
|
laminar
|
|
|
What is the resistance of laminar flow?
|
R=8nl/(pi)r^4
|
|
|
Where does most of the resistance in the airways come from?
|
Middle-sized airways out to division 7
|
|
|
What is the equal pressure point?
|
The point in the airway during forced expiration when IPP is greater than the airway pressure and the airway collapses
|
|
|
What problems make the equal pressure point happen sooner?
|
Low lung volumes (IPF)
High resistance (obstructive diseases) Poor airway traction surfaces (emphysema) |
|
|
What is respiratory failure?
|
Failure to maintain adequate oxygen and carbon dioxide homeostasis
|
|
|
What is hypoxemia respiratory failure?
|
Respiratory failure due to too little oxygen
Caused by decreased partial pressure of oxygen, shunt, hypoventilation, V/Q mismatch, impaired diffusion |
|
|
What is hypercapnia?
|
too much carbon dioxide in the blood
|
|
|
What is a clinical situation of low V/Q?
|
Alveoli filled with fluid (pus, blood, etc.)
|
|
|
When is the A-a gradient high?
|
V/Q mismatch
Impaired diffusion Shunt |
|
|
What is a Venturi mask?
|
Mask that delivers high controlled ventilation to patient at high oxygen levels using Bernoulli's principle
|
|
|
What is the result of hypoventilation?
|
Hypoxemia that is ALWAYS associated with hypercapnia
|
|
|
What happens in hypercapnic respiratory failure?
|
Minute ventilation cannot keep up with PCO2 production
|
|
|
What are some causes of hypercapnic respiratory failure?
|
Depressed respiratory drive
Inadequate neuromuscular competence Excessive respiratory muscle load |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of respiratory failure?
|
Signs & symptoms of hypoxemia and/or hypercapnia:
somnolence dyspnea tachypnea use of accessory muscles |
|
|
What is the course of respiratory failure management?
|
Correct underlying problem
Airway Correct hypoxemia Manage acid/base status |
|
|
What is Virchow's triad?
|
Major risk factors for DVT/PE
Hypercoagulability Venous stasis Endothelial injury |
|
|
What are some causes of endothelial injury?
|
Surgery, invasive procedures
Vasculitis (Behcets or anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome) |
|
|
What clotting factors are related to hypercoagulability?
|
V, VIII, X
|
|
|
What are inherited causes of hypercoagulability?
|
Factor V Leiden
Protein C or S deficiency Prothrombin gene mutation 20210 |
|
|
What is Homan's sign?
|
Palpable cord felt in DVT
|
|
|
What is the gold standard of DVT diagnosis?
|
Duplex compression ultrasonography
|
|
|
What are methods of detecting DVT?
|
Duplex compression ultrasonography
Helical CT of leg Impedance plethysmography Contrast venography |
|
|
What are the limitations of duplex compression ultrasonography?
|
Cannot detect DVT below the knee
Must use serial exams to rule out below the knee DVT |
|
|
If a D-dimer is normal and clinical suspicision of PE is low, what should you do?
|
Nothing.
|
|
|
What would you do if you have a high suspicion of PE?
|
either start treatment or chest radiography
|
|
|
What should you do if chest radiography is abnormal in the evaluation of a possible PE?
|
Chest CT arteriography
|
|
|
How do you treat a massive PE?
|
Thrombolytics: tPA
|
|
|
What is used in treating PE or DVT if the patient has a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
|
Argatroban
|
|
|
What should tPA be used?
|
Massive PE requiring mechanical ventilation & vasopressors
Shock present |
|
|
How long does anticoagulant therapy need to be continued following a PE?
|
3 months with INR at 2-2.5
6 months if idiopathic Indefinitely if recurrent |
|
|
What is used as VTE prophylaxis?
|
UFH 5000 units BID or TID
LMWH 30mg BID or 40mg QD Compression boots |
|
|
Where is the medullary respiratory center?
|
Floor of 4th ventricle
|
|
|
What is the medullary respiratory center responsible for?
|
Inspiratory ramp of periodic firing
Independent of afferent stimuli |
|
|
Where is the apneustic center?
|
Lower pons
Stimulates/prolongs inspiratory ramp |
|
|
Where is the pneumotaxic center?
|
Upper pons
|
|
|
What does the pneumotaxic center do?
|
Inhibits/attenuates inspiration
May fine tune respiration |
|
|
Where are the central chemoreceptors?
|
Ventral medulla near exit of CNIX and X
|
|
|
What do the central chemoreceptors respond to?
|
pH changes in the CSF due to increased/decreased bicarbonate content of CSF
Acidosis-->stimulates respiration Alkalosis-->inhibits respiration |
|
|
Where are the peripheral chemoreceptors?
|
Carotid bodies & aortic arch
|
|
|
What do the peripheral chemoreceptors respond to?
|
decreases in arterial pO2 and pH, and, to a lesser degree, changes in PCO2
|
|
|
What is the nature of the response of the peripheral chemoreceptors to changes in PO2?
|
PO2<100mmg-->non-linear response that increases rapidly
|
|
|
When do the lung stretch receptors respond?
|
Lung distension-->decrease respiratory rate
Act mostly during exercise at high lung volumes |
|
|
Where are the irritant receptors?
|
Between epithelial cells in the respiratory tract
Result in airway restrction & reduced RR |
|
|
Where are the J receptors?
|
In the alveolar walls close to the capillaries
|
|
|
What is caused by stimulation of the J receptors?
|
Rapid shallow breathing usually associated with pulmonary vessel distension
|
|
|
What are the bronchial C fibers?
|
Fulfill same role as J receptors
Supplied by bronchial aa. |
|
|
What is the gamma system?
|
Intramuscular receptors controlling the strength of contraction of the muscles of inspiration
|
|
|
What is the nature of the response of the respiratory system to rise in CO2?
|
Non-linear increase in ventilation
|
|
|
When does the hypoxic ventilatory response become important?
|
When arterial pO2 drops below 50mmHg
Examples: high altitude, chornic lung disease |
|
|
What are the phases of sepsis treatment?
|
Recognition
Resuscitation Initial management Maintenance Recovery |
|
|
What is SIRS?
|
Clinical response arising from a nonspecific insult resulting in at least 2 of the following:
Temp. >38C or <36C HR>9BPM WBC>12000 OR <4000 OR >10% immature neutrophils |
|
|
What is sepsis?
|
SIRS with a presumed or confirmed infectious process
|
|
|
What is severe sepsis?
|
Sepsis with signs of at least 1 major organ failure
|
|
|
What is the most consistent feature of sepsis?
|
Neurologic changes
|
|
|
What are the most common organisms found in sepsis today?
|
Gram + bactera
Gram - bacteria Fungi |
|
|
What are the most common sites of infection in severe sepsis?
|
Respiratory
|
|
|
What are some risk factors for sepsis?
|
Male gender
African American Cancer (esp. hematologic) HIV Venous access devices |
|
|
What is involved in the resuscitation phase of sepsis management?
|
Keep patient alive for 24 hours.
A=airway-->intubation B=breathing-->mechanical ventilation C=circulation-->vasopressors, IV access, IV volume, goal-directed therapy |
|
|
How is fluid management done in sepsis treatment?
|
Administer fluid challenge and see changes
|
|
|
What are the common vasopressors used in sepsis?
|
Dopamine
Norepinephrine Norepinephrine increases heart contractility, heart rate and causes vasoconstriction Dopamine does the same at high doses. |
|
|
What is goal-directed therapy?
|
Additional goal for 1st 6 hours: get central venous oxygenation>70%
Give RBCs if HgB<10 Give dobutamine if HgB>10 |
|
|
What are the risks of drotecogin alfa?
|
Bleeding
Need risk of dying>risk of bleeding |
|
|
What is seen in an xray of ARDS or ALI?
|
Fluffy white bilateral infiltrate
|
|
|
What is the definition of ALI & ARDS?
|
PaO2/FiO2<300=>ALI
PaO2/FiO2<200=>ARDS |
|
|
What are common causes of direct lung injury?
|
Pneumonia
Aspiration |
|
|
What are common causes of indirect lung injury?
|
Sepsis
Massive trauma Multiple transfusions |
|
|
What is essential in treatment of ALI/ARDS?
|
Low tidal volume ventilation
Fluid balance: perfused kidney vs. dry lung? |

