![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
160 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Use of oxygen therapy in COPD |
◆ resting arterial oxygen tension- PaO2 <55 ◆ Pulse oxygen saturation SaO2 <88 OR ◆ pt with cor pulmonale PaO2 < 59 SaO2 < 89 OR Hematocrit > 55% |
|
|
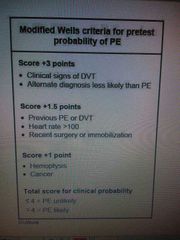
Pulmonary embolism |
Sudden onset pleuritic chest pain , cough , dyspnea , hemoptysis ◆ chest CT = wedge shaped infraction = pathognomic |
|
|
Pulmonary embolism |
|
|
|
Alveolar hypoventilation |
◆Reduced inspired oxygen tension ◆Respiratory acidosis , normal A-a , ◆COPD ,Sleep apnea , scoliosis ◆MG , GBS , ◆Anesthetic , narcotic , sedation ◆Brian stem lesion ,infection |
|
|
Intrapulmonary shunt |
Position change , ⬇ventilation in alveolar consolidation |
|
|
⬇airflow rate during inspiration and expiration |
Fixed upper airway obstruction = laryngeal edema |
|
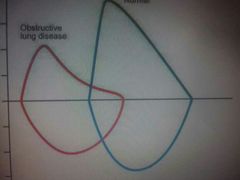
Asthma |
Scooped-out pattern |
|
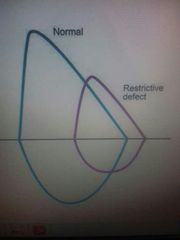
Restrictive pattern |
Pneumothorax , pulmonary edema |
|
|
Alpha-1 antitrpysin deficiency |
=COPD + Liver disease ◆Destruction of lobes = lucency |
|
|
A.spondylitis |
=restrictive lung disease ⬇ chest wall &spinal mobility |
|
|
|
|
|
Acute bronchitis |
( Cough + blood tinged sputum ) Wheezing and crackle clear after coughing |
|
|
Asbestosis |
Pneumoconiosis = progressive dyspnea , clubbing , end-inspiratory crackles ◆Restrictive lung disease = ⬇lung volume , ⬇diffusion lung capacity , normal FEV1/FVC ◆Pleural plaques = hallmark of asbestosis ◆Blue asbestosis most dangerous form Mesothelioma Malignant disease of pleura , very poor prognosis |
|
|
Beta-2-agonist side effect |
Hypokalemia = muscle weakness , arrhythmias , ECG abnormalities ◆ tremor , palpitation , headache |
|
|
Primary pulmonary HTN |
= exertional breathlessness CX-ray = enlarge pulmonary artery + enlarge Rt ventricle |
|
|
Exercise induced bronchoconstriction |
SABA befor 10-20 before exercise ◆+ Ipratropium inhaler |
|
|
Aspirin exacerbated RD = pseudoallergic |
Risk factor = athma , rhinosinusitis , ◆Non-IgE mediated reaction |
|
|
Acute asthma exacerbation |
= respiratory alkalosis = ⬇paCO2 = hyperventilation |
|
|
Bronchiectasis |
Bronchial thickening and dilitatiob due to recurrent infection and inflammation ◆Cough with large volume sputum , dyspnea , hemoptysis ◆High-resolution CT scan of the chest |
|
|
Upper airway cough syndrome Postnasal drip |
Confirmed by elimination of nasal discharge and cough with use of H1 histamin receptor antogonist |
|
|
Chronic cough |
>90% of chronic cough ◆ asthma ◆GERD ◆post nasal drip - upper airway cough syndrome |
|
|
Lung consoludation |
Dullness to percussuion , ⬆intensity breath sound , ⬆tactile fremitus |
|
|
V/Q mismatch |
Emphysema , interstitial lung disease , pulmonary embolism |
|
|
Pneumonia Due to = V/Q mismatch Rt-to-Lt intrapulmonary shunting |
FiO2 improve hypoxemia in pneumonia de to V/Q mismatch |
|
|
PE |
◆⬆A-a |
|
|
COPD exacerbation |
⬆ dyspnea ⬆ cough ⬆ sputum production Chest X-ray = hyperinflation ◆Bronchodilators ◆Systemic glucocorticoud ◆ antibiotics |
|
|
Theophylline toxicity |
= cytochrome oxidase system Some drug eg.antibiotics = reduced clearance ◆Headache , insomnia , seizures ◆Nausea , vomiting ◆ arrhythmia |
|
|
COPD |
⬇ expiratory follow rate ⬆ lung compliance ⬆ lungvolume Ⓜ anti-muscarinic agent = ipratropium |
|
|
Cor pulmonale Diagnosis by = Rt heart catheterization |
Rt-sided HF from pulmonary HTN - jagular venous distention , Rt ventriculat heave , hepatomegaly , ascites edema |
|
|
Pleural effusion |
40% of pneumonia ◆Complicated parapneumonic effusion , empyema Empyema = frank pus on paracentesis or bacteria on pleural space = exudative , ⬆ protein , ⬆LDH , ⬇ pH ⬇gulocose |
|
|
Nonseminomatous germ cell tumors |
. |
|
|
Goodpasture's disease |
◆Lung = cough , dyspnea , , hemoptysis ◆Kidney = proteinuria , ARF , dysmorphic red cell , ◆Renal biopsy = linear IgG antibodies along glomerul basment membrane = alpha-3 chain of type 4 collagen
|
|
|
Granulomatosis with polyangitis Wegener granulomatosis = chronic rhinosinusitis |
◆Systemic vasculitis Upper and lower respiratory tract granulomatous inflammation & glomerulonephritis 🚫 chest X-ray =multiple bilateral nodules with cavitation , tracheal narrowing and ulceration ◆ANCA& biopsy |
|
|
Bird fancier's lung Form of hypersensitivity pneumonitis |
hypersensitivity pneumonitis = repeated inhalation of an inciting antigen |
|
|
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy |
Sudden onset joint arthropathy in chronic smoker = lung malignany |
|
|
Interstitial lung disease |
. |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of the lung |
Common in smoker & nonsmoker = primary lung cancer in nonsmoker = peripherally and solitary nodule |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma sCa++mous |
History of smoking = hypercalcemia and hilar mass |
|
|
Pancoast tumor Superior pulmonary sulcus Squamous & adenocarcinoma |
Located thoracic inlet Sholder pain Horner syndrome Supraclavicular LN enlargment ⬇ Wt Damage brachial plexus - ulner nerve Hoarseness , SVC syndrome Squamous cell lung cancer & adenocarcinoma ◆Smoking strongest risk factor |
|
|
Solitary pulmonary nodule SPN |
◆ rounded opacity ◆ < 3 cm ◆ surrounded by pulmonary parenchyma ◆ no lymph node enlargment |
|
|
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome |
◆BMI > 30 mg ◆Daytime hypercapnia paCO2 >45 ◆alveolar hypoventilation ◆Hypoxemia ◆Respiratory acidosis |
|
|
S |
H |
|
|
Primary ciliary dyskinesia |
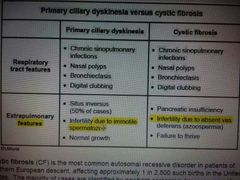
|
|
|
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax |
Patient with underlying lung disease = rupture of alveolar blebs |
|
|
I want to play |
. |
|
|
Bronchogenic carcinoma |
⬆Risk with asbestosis =6-fold Smoking + asbestosis = 59 fold |
|
|
Invasive aspergillosis |
◆Effect immunocompromised patient ◆Fever , pleuritic chest pain , hemoptysis ◆ CT = pulmonary nodules with surrounding ground-glass opacities = halo sign Ⓜvoricazole + echinocandin |
|
|
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis |
◆ >3 Month of symptoms = fever , wt loss , fatigue , cough , hemoptysis dypnea ◆ Cavitary lesion ◆ positive Aspergillus IgG serology |
|
|
Aspiration pneumonia |
◆ altered conciousness ◆Neurologic decificit ◆GERD ◆Mechanical disruption |
|
|
Aspiration pneumonitis *aspiration pneumonia |
Acute lung injury secondary to chemical burn from aspirated sterilr gastric content *aspiration pneumonia = infectious disease = aspiration of infected oropharyngeal secretion |
|
|
ACE inhibitor side effect |

Nonproductive cough = metabolism of kinins and substance P |
|
|
Chronic bronchitis |
◆ common couse of hemoltysis ◆ Chronic productive cough for > 3 mounth in 2 successive years , smoking leadind couse |
|
|
Massive pulmonary embolism Syncope , shock , hemodynamic instability |
Postoprative patient with hypotention , jagular venous distention , new onset Rt bundle branch block |
|
|
Scheduled |
Found |
|
|
Post-ictal state |
◆Prolonged and foreful skeletal muscle activity = lactic acidosis = metabolic acidosis ◆Hypoventilation = respiratory acidosis |
|
|
Complication of posative pressure ventilation |
Alveolar damage , pneumothorax , hypotention |
|
|
pneumothorax |
Sudden onset of shortness of breath , hypotention , tachycardia , tracheal deviation , unilatral absence of breath sound |
|
|
Small cell lung cancer |
= SIADH = Initial treatment = fluid restriction |
|
|
SIADH |
Hypotonic hyponatremia , euvolenic |
|
|
Nonallergic rhinitis = vasomotor rhinitis |
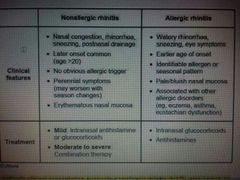
Predominant nasal congestion , stuffness , postnasal drip - dry cough , no spesific triggers |
|
|
Amniotic fluid embolism syndrome |
Rapin onset respiratory failure , severe hypotension , DIC , during labour or immediate postpartum period , Manegment supporutive |
|
|
Anaphylaxis |
Severe allergic reaction = sudden collapse , symptoms involved > 1 organ after exposure to offending antigen Intravascular epinephrine = B2 agonist 👉 bronchodilation & ⬇systemic release of inflammatory mediators , ◆ a1 agonist 👉 vasoconstriction ⬆ BP , ⬇upper airway edema |
|
|
Apgar score |
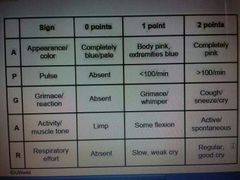
|
|
|
Kartagener syndrome |
◆ situs inversus ◆ recurrent sinusitis ◆ bronchiectasis |
|
|
Respiratory distress syndrome |
Criteria :- ◆Acute onset ◆Bilateral infltration ◆Non-cardiogenic ◆PO2/FiO2 < 200 mmHg Risk factor = Premature infant & maternal DM , male sex , perinatal asphyxia , c,section= grunting , flaring , retraction immediately after birth Chest X-ray = fine reticular granularity of the lung |
|
|
Bronchiolitis |
Caused by RSV , ◆ complication apnea , respirotart failure |
|
|
Mucus plugging |
= large volume atelectasis , lung collapse due to airway obstruction X-ray = opacification , M shifting to side of atelectasis |
|
|
Atelectasis
|
Common postoprative , pulmonary complication , after abdominal and thoracoabdominal surgery ◆⬆work of breathing ◆A-a mismatch |
|
|
Bronchospasm |
Postoprative COPD & asthma ◆ wheezing , dyspnea + hypoxia |
|
|
Tension Pneumothorax , |
Life-threatening condition ◆Rapid onset dysnea , tachycardia , tachypnea , hypotension , distended neck vein |
|
|
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax /omer |
◆Repture of subpleueal blebs ◆If rim <2 cm no SOB discharge patient ◆Otherwise aspiration |
|
|
Anemia |
1- ⬇ RBCs production 2- ⬆ RBCs destruction 3- Blood loss Anemia of lymphoprolifrative disorders due to bone morrow infiltration with cancerous cell |
|
|
Epiglottitis |
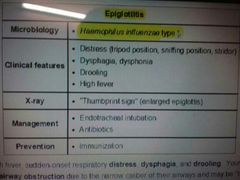
|
|
|
Massive pulmonary embolism |
◆ postoprative pt with hypotension ◆Jugular venous distension ◆New onset Rt bundle branch block |
|
|
Crest syndrome related pulmonary arterial HtN |
◆Raynaud phenomenon , eosaphagial dysmotility , ◆pulmonary arterial HtN ◆Ex = Rt ventricular heave |
|
|
pulmonary arterial HtN with ss |
Hyperplasia of the intimal smooth muscle layer of artery |
|
|
Emperic treatment of CAP |
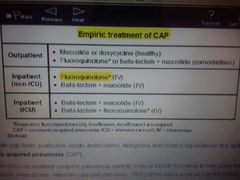
|
|
|
Peak airway pressure pulmonary comliance |
◆Sum of airway resistance and plateau pressure ◆◆plateau pressure is sum of elastic pressure and PEEP |
|
|
Low glucose concentration empyema |
Due to high metabolic activity of leukocyte |
|
|
Theophylline toxicity ⬆With AB , ingection |
Cns atimulation ◆Headache insomnia , seizures , nausae , vomiting , palpitation |
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
◆Hospital acquired ◆CF Adult |
|
|
Long thoracic nerve injury |
◆During axillary lymphadenectomy ◆serratus anterior palsy = winged scapula |
|
|
Pulmonary contusion |

|
|
|
Middle mediastinum mass |
Bronchogenic cyst Tracheal tumor Pericardisl cyst Lymphoma Ourtic aneyursm |
|
|
Anterior mediastinum mass |
Thymoma |
|
|
Posterior mediastinum mass |
Neurogenic tumor Meningicele Enteric cyst Esophageal tumor Aortic aneurysm |
|
|
Transient tachypnea of the newborn |
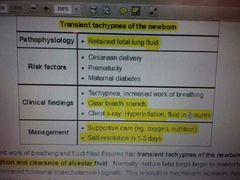
|
|
|
Alpha-1 antitrysin deficiency |
◆Panacinar emphysema = lower lobe ◆Centrocenar emphysema = upper lobe by smoking ◆◆COPD in young age ◆Non smoking ◆Liver disease |
|
|
Postnasal drip |
Treated by frist-generation antihistamin eg.clorpheniramine |
|
|
Use of AB in COPD exacerbation |
Moderate severe case Use of mechanical ventilation |
|
|
Primary pulnonary htn |
Autosomal-dominant ◆Elevated JVP ◆Rt ventricular Left parasternal heave ◆Periphral edema ◆Load P2 ◆Rt sided S4 ◆Normal TLC , FEV1/FVC ◆⬇⬇DLCO |
|
|
In COPD increase work of breating |
⬇Alveolar elasticity in copd ◆⬆Total lung capacity + functional residual capacity + residul valume ◆Diaphragmetic flattenin |
|
|
Cause of hypoxia |
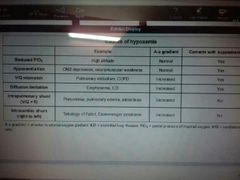
|
|
|
Respiratory acidosis = hypoventilation |
Normal A-a gradient |
|
|
Acute broncitis |
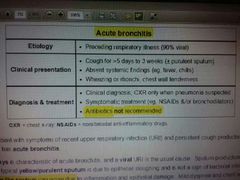
|
|
|
Antimuscarinic agent |
Ipratropium uses in COPD |
|
|
Transfer factor |
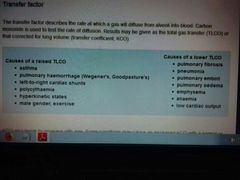
Rate at which a gas will diffuse from alveoli into blood |
|
|
Extrinsic allargic alveolitis |
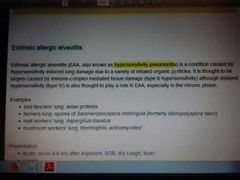
Chest X-ray = upper zone fibrosis No eosniphilia |
|
|
Saccharropolyspora |
. |
|
|
Curb-65 criteria of severe pneumonia |
◆Confusion ◆Urea > 7mmol/L ◆Respiratory rate >30 ◆BP <90/60 ◆Age > 65 yrs + Albumin <35 , leucocytosis >20 , leukopenia < 2 , hypoxia |
|
|
Surgery contraindication in lung cancer |
◆SVC obstruction ◆FEV < 1.5 ◆Malignant pleural effusion ◆Vocal cord paralysis |
|
|
Klebsialla pneumonia |
In alcoholic patient |
|
|
Flow volume loop = |
Investigation for upper airway compression |
|
|
Fibrosis effect upper lobe |
◆extrinsic allergic alveolitis ◆Coal worker pneumoconiosis ◆Silicosis ◆Saecoidosis ◆Ankylosing apondylitis ◆ histocytosis ◆TB |
|
|
Fibrosis effect lower lobe |
◆Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis ◆Drug-induced ◆Asbestosis |
|
|
Sarcoidosis |
Multisystem disorder , not casuated granuloma ◆ constitional symptoms , erythema nodosum , lymphoedenopathy ◆stages 1 - BHL 2 BHL + intersitial filtration 3 intersitial filtration without BHL ◆Investigation X-ray , transbronchial biopsy , transbronchial biopsy , serum ACE leve , seram Ca , PFT = restrictive lung disease ◆Erythema nodosum indication to good prognosis
Indication for steroid: Hypercalcemia Worsening lung function Eye , heart on neuro involvment |
|
|
Non invasive ventilation |
◆COPD respiratory acidosis7.25-7.35 ◆Type2 respirstory failure ◆Cardiogenic pulmonary odema ◆weaning from tracheal intubation |
|
|
Acute respitatory distress syndrome |
Damage to alveolar epithilium & capillary endotheliun = alveolar space flooded with edema , |
|
|
PE |
◆CTPA frist line for diagnosis S1Q3T3 ecg change |
|
|
Oxygen saturtion |
◆Acutly ill patient 94-98% ◆COPD 88-98% prior to blood gases |
|
|
Bilateral hilar lyphadenopathy |
Mainly TB & sarcoidosis ◆ lymphoma , pneumoconiosis - berylliosis , histoplasmosis , coccidoidomycosis |
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
Atypical pneumonia , precede flu like symptoms ◆Cold agglutin HA ◆Erythema multiforme ◆Acute glumolunephritis ◆GBS Diagnosis = mycoplasma serology |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma lung |
Cavitation |
|
|
Cavitating lung lesion |
◆TB ◆SCEll lung cancer ◆Abscess ◆Weneres granulomatosis small vessell vasculitis ◆PE ◆RA ◆Aspergillosis |
|
|
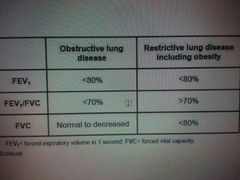
PFT obstrucrive lung disease |
◆FEV1 - significant reduced ◆FVC- reduced or normal ◆FEV1% - reduced ◆Asthma , bronchiectasis , bronchilotis |
|
|
PFT , restrictve lung disease |
◆ FEV1 -reduced ◆FVC -significant Reduced ◆FEV1/FVC - normal or inceased ◆pulnonary fibrosis , asbestosis , sarcoidosis , ARDS , kyphoscolisis , neuromuscular disorder |
|
|
Lofgren's syndrome |
◆Parasite such as Ascaris lumbricoides Acute form sarcoidosis BHL + erythema nodosum + polyarthralgia |
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Assosiated with cold sores , herpes simplex virus |
|
|
Insertion of chest tube in pleural effusion |
◆Fluid is purulent or turbid/ cloudy ◆pH is less than 7.2
|
|
|
Paraneoplastic features of lung cancer |
Squmous cell : ◆parathyroid hormone-related protein , ◆clubbing , ◆hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy HPOA ◆hyperthyroidism due to ectopic TSH Small cell : ◆ADH ◆ACTH ◆Lambert-Eaton syndrome Adenocarcinoma ◆Gynaeco mastia |
|
|
Life-threatening Asthma |
◆PEF < 33% ◆O saturation ◆Cyonosis ◆Hypotention ◆ confusion ◆Normal pa CO2 ◆poor respiratory effort ◆Exhaustion ◆Bradycardia
Treatment Magnesium sulphate IV aminophylline IV salbutamol |
|
|
Respiratory acisosis secondry to hypoventilation |
◆COPD ◆Life thereatening asthma , ◆Sedative drug , opiate overdose |
|
|
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency |
Inherited autosomal recessive Investigation = A1AT |
|
|
Pneumocystis carinii - jiroveci pneumonia |
Opportunistic infection in AIDS CD4< 200 Features : dysnoea , dry cough , fever , very few chest sign |
|
|
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
|
|
|
Pulmonary hypertension du to LV systolic dysfunction ↪pulmonart HTN |
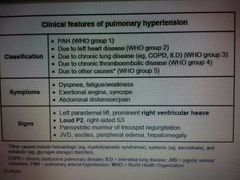
Loop diuretics , ACEI |
|
|
Scleroderma renal crisis |
Acute renal failure - without previous kidney disease - and malignant htn , ◆Pripheral blood smear = schistocytes - hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Target cell |
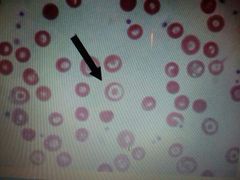
Bull's eye apperance = thalassemia |
|
|
Spur cell - acanthocyte |
RBCs irregular size , in liver disease |
|
|
Burr cells |
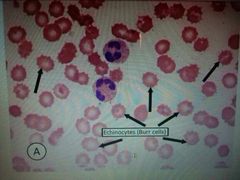
|
|
|
Lung adenocarcinoma |
Non-smokers Periphral lesion not seen by broncoscopy |
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
Most common causative organism exacerbation of COPD |
|
|
Bronchiectasis |
Perminant dilatiation of the airway secondry to chronic infection or inflammation ◆Post-infective ◆CF ◆bronchial obstruction ◆Immune deficiency ◆Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis ◆Ciliary dyskinetics syndrome ◆Yellow nail syndrome Manegment = inspiratory muscle training + postural drainage Most common organism isolated = haemophilus influenzae |
|
|
Silicosis |
Risk factor for developing TB ( silica toxic to macrophages ◆Fibrosing lung disease ◆ egg-shell calcification of the hilar lymph nodes |
|
|
Eosunophilia |

|
|
|
Hyperoesinophilic syndrome |
. |
|
|
Pneumonia |
Amoxicilline + calvunic acid |
|
|
Chronic bronchitis |
⬆ oxygen = coarse flapping tremor |
|
|
Peak expiratory flow rate PEFR |
◆Measurement of small airway obstruction ◆It is more related to high than age , ◆Effort -independent |
|
|
Type I respiratory failure |
Hypoxemia without hypercapnia |
|
|
Type II respiratory failure |
Hypoxemia with hypercapnia |
|
|
Clubbing |
Bulbous enlargment & broadening of the fingertips due to connective tissue proliferation |
|
|
DLCO |
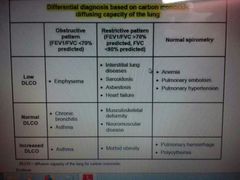
◆Diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide ◆ |
|
|
Emphysema |
Destruction of the interalveolar wall ◆⬇DLCO ◆Chest X-ray = decreased vascular marking & hyperinflated lung |
|
|
Obstructive sleep apnea OSA |
snoring & daytime sleepiness ◆Nocturnal polysomnography = record abnormal ventilation during sleep |
|
|
Pulmonary contusion |
◆Complication of blunt thoracic trauma with ot without rib fracture ◆Tachycardia , tachypnea , hypoxia, develop within 24 hrs ◆Chest X-ray = patchy alveolar infltrate |
|
|
,parapneumonic effusion |
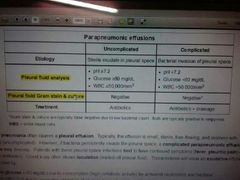
|
|
|
Rhinitis |
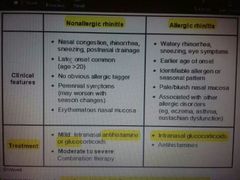
|
|
|
Granulomatosis with polyangitis |

Systemic vasculitis ◆U, L RT granulomatous inflamation ◆G.Nephritis ◆CXR = multiple lung nodules with cavitation , ◆Anemia for chronic disease ◆Diagnosis made ; qualitative serum antibody = ANCA And tissue biopsy |
|
|
Systemic glucocorticoid S.E |
Leukocytosis ◆By mechanism 1- mobilazation of narginated neutrophil 2- inhibition of neutrophil apoptosis 3- stimulate release immature neutrophil from bone barrow |
|
|
Restrictive pattern |
⬆Alveolar -arterial gradient |
|
|
Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
Low tid volume ventilation to ⬇⬇ overdistending alveoli |
|
|
Chylothorax |
Exudative effusion due to disruption of lymphatic flow within thoracic duct ◆Pleural fluid = milky white fluid with elevated triglyceride |
|
|
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure PCWP |
Indicate Lt atreal pressure ◆Cardiac origin of symptoms |
|
|
Kartagener syndrome |

◆Situs inversus , recurrent sinusitis , bronchiectasis ◆ |
|
|
Respiratory alkalosis = V/Q mismatch |
⬆A-a gradient PE , Atelectasis , pleural effusion |
|
|
High dose of beta agonist |
Hypokalamia |
|
|
Palivizumab |
Antibody aganist RSV used as profl.baby >2 yrs |
|
|
Risk factor of RDS |
Premature , perinatal asphyxia , maternal Dm , C/S |
|
|
Invasive aspergillosis |

|

