![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 4 drug/drug types that have been used for wt loss?
|
Amphetamins, adrenergic, fenfluramine, & orlistat
|
|
|
What are the SE of amphetamines?
|
Euphoria & addiction
|
|
|
SE of adrenergic agents?
|
HTN & arrhythmogenic
|
|
|
SE of fenfluramine & orlistat?
|
Valvular effects & steatorrhea
|
|
|
What will long term treatment of obesity likely to require?
|
Multiple drugs aimed at different targets
|
|
|
A 35 year old female presents to her primary care physician seeking treatment for weight loss. She has tried several “fad diets” which incorporate the intake of low carbohydrates and has failed at each attempt. She states that she does exercise” when she finds the time”.
BMI = 32; Waist Circumference = 38 inches, BP = 167/99 and HR = 82 Labs: TC 253 mg/dl LDL 154 mg/dl HDL 33 mg/dl TG 267 mg/dl ALT 23 IU/l HgA1c 6.8 % Gluc 109 mg/dl What is the most appropriate weight loss goal for this patient? a. 5-10% of body weight b. 15-20% of body weight c. 20-25% of body weight d. BMI < 25 |
The correct answer is a. By achieving 5-10% body weight loss, a significant change in comorbid conditions, such as her hypertension, may be accomplished. Although the other goals may be desirable, particularly to the patient, they may not be realistic and can set the patient up for what they consider failure and relapse. See objective 4.
|
|
|
The patient is amenable to another attempt at lifestyle modifications. Which diet would be the most appropriate for this particular patient?
a. Low Fat b. Low Carbohydrate c. Balanced low calorie diet d. A or C |
d. A or C
The correct answer is d. We know the patient has failed several attempts at a low carb diet. The one diet recommended for individuals is the one they will best adhere to. Therefore, either A or C may be a good choice for the patient. See objective 4. |
|
|
Once the diet has been implemented, is this patient also a candidate for weight loss medication?
a. Yes, she her BMI is greater than 27 and she has two comorbid conditions b. No, her BMI is greater than 27, but she does not have two comorbid conditions c. Yes, her BMI is greater than 30 d. No, her BMI is not greater than 35 |
c. Yes, her BMI is greater than 30
|
|
|
27. If Pharmacotherapy is deemed appropriate which medication below would be most correct to recommend?
a. Sibutramine b. Orlistat c. Phentermine d. A or C |
b. Orlistat
The correct answer is b. We would rule out both sibutramine and phentermine given the fact that the patient has uncontrolled hypertension. See objective 4. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. If a patient being treated for obesity does not lose 2 lbs within the first 4 weeks of drug therapy, it is unlikely that drug therapy will be successful b. Obesity-related risk factors include: coronary heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, hypertension and sleep apnea c. Ghrelin regulates food intake and energy expenditure by acting as a satiety signal to decrease appetite in the CNS d. Pharmacotherapy is indicated for patients who have a BMI > 30 or a BMI > 27 with concomitant obesity-related risk factors or diseases. |
c. Ghrelin regulates food intake and energy expenditure by acting as a satiety signal to decrease appetite in the CNS
Ghrelin is a neurotransmitter that stimulates food intake. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. Patients taking orlistat should be counseled to expect gastrointestinal side-effects such as oily spotting, abdominal pain, flatus with discharge; which should improve over time b. Sleep deprivation, viruses, and toxins are potential environmental factors that may contribute to obesity c. The goals of therapy for obesity include: prevent further weight gain, reduce body weight by 10% in the first 6 months, and maintain a lower body weight, long term d. Sibutramine is a safe drug therapy for treatment of obesity in patients with uncontrolled hypertension |
d. Sibutramine is a safe drug therapy for treatment of obesity in patients with uncontrolled hypertension
Answer d is correct. Sibutramine has the potential to raise blood pressure and therefore should be avoided in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. |
|
|
Ms. White is a 42 year-old white female with a medical history significant for hypertension and sleep apnea. Her current body weight is 190 lbs, BMI is 33 and waist circumference is 37 inches. Ms. White’s blood pressure today is 148/92 mmHg. Current medications include: lisinopril 20 mg qd, HCTZ 12.5 mg qd and Yasmin (an oral contraceptive pill containing ethinyl estradiol and drosperinone). Ms. White states that she has struggled with her weight and has been on and off diets all of her life. While she tries to eat healthy she admits that there are numerous high fat foods that she just “cannot give up”. She states that she power- walks during her lunch hour 5 days per week for 30 minutes. This has helped her keep her weight from going up. It is noted that Ms. White’s insurance does not cover prescriptions for weight loss. Dr. Albert has asked for your assistance in selecting a drug therapy.
Which pharmacological strategy is most appropriate for Ms. White? a. Alli (Orlistat) 60 mg three times daily with fat-containing meals only b. Phentermine 15 mg every morning c. Sibutramine 10 mg every morning d. Do not start drug therapy in this patient because she does not meet the National Institutes of Health obesity guideline criteria for pharmacotherapy. |
d. Do not start drug therapy in this patient because she does not meet the National Institutes of Health obesity guideline criteria for pharmacotherapy.
A, This patient does not have any contraindications to use orlistat; whereas, all other approved drug therapies for treatment of obesity may increase the risk to raise BP. B, Phentermine would not be a good choice because of its potential to raise blood pressure and this patient has uncontrolled HTN C, Sibutramine would not be a good choice because of its potential to raise blood pressure and this patient has uncontrolled HTN D, This patient meets the criteria for drug therapy in that he has failed diet and exercise and has a BMI > 30 or BMI > 27 with risk factors (sleep apnea, HTN) |
|
|
Which of the following statements is FALSE ?
a. If a patient being treated for obesity does not lose 2 lbs within the 1st 4 weeks of drug therapy, it is unlikely that drug therapy will be successful. b. Obesity related risk factors include: coronary heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, hypertension and sleep apnea. c. Leptin regulates food intake and energy expenditure by acting as a satiety signal to decrease appetite in the CNS. d. Pharmacotherapy is indicated for patients who have a BMI ≥ 25 or a BMI ≥ 27 with concomitant obesity related risk factors or diseases. |
d. Pharmacotherapy is indicated for patients who have a BMI ≥ 25 or a
BMI ≥ 27 with concomitant obesity related risk factors or diseases. d. Pharmacotherapy is indicated in patients who have a BMI ≥ 30 or a BMI ≥ 27 with concomitant obesity related risk factors or diseases. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. Patients taking orlistat (xenical) should be counseled to expect GI sideeffects such as oily spotting, abdominal pain, flatus with discharge; which should diminish over time. b. Sleep deprivation, viruses and toxins are potential environmental factors that may contribute to obesity. c. The goals of therapy for obesity include: prevent further weight gain, reduce body weight by 10% in the first 6 months and maintain a lower body weight, long term. d. Sibutramine (Meridia) is a safe drug of therapy for treatment of obesity in patients with uncontrolled hypertension |
d. Sibutramine (Meridia) is a safe drug of therapy for treatment of obesity in patients with uncontrolled hypertension
d. sibutramine has the potential to raise blood pressure and therefore should be avoided in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. |
|
|
Mr. Fulmore is a 52 year old white male with a past medical history of Type 2
diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. Current wt= 280 lbs, BMI = 38 and waist circumference = 46”. Blood pressure today is 166/92 mmHg. Current medications include: glucophage (Metformin) 850 mg tid, Glucotrol (glipizide) 10 mg qd and pioglitazone (Actos) 30 mg qd. Mr. Fulmore has tried “every diet under the sun (including the Dunkin Donuts only diet) ” over several years with little success. He walks for 45 minutes/ 5 days per week. This has helped him lose 40 lbs. Dr. Albert has asked for your assistance in choosing a drug therapy. Mr. Fulmore states that he has a terrific health insurance plan through the state of Tennessee. a. Orlistat (Xenical) 120 mg tid with high-fat meals only b. Phentermine (Adipex) 15 mg q am c. Sibutramine (Meridia) 10 mg q am d. Do not start drug therapy in this patient because he does not meet the NIH obesity guideline criteria for pharmacotherapy. |
a. Orlistat (Xenical) 120 mg tid with high-fat meals only
a. This patient does not have any contraindications to use orlistat; whereas, all other approved drug therapies for treatment of obesity may increase the risk to raise BP. b. Phentermine would not be a good choice because of it’s potential to raise blood pressure and this patient has uncontrolled HTN c. Sibutramine would not be a good choice because of it’s potential to raise blood pressure and this patient has uncontrolled HTN d. This patient meets the criteria for drug therapy in that he has failed diet and exercise and has a BMI > 30 or BMI > 27 with risk factors (HTN, Type 2 DM, sleep apnea) |
|
|
Mr. Fulmore is a 52 year-old white male with a past medical history of Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, sleep apnea and cholestasis. Current weight is 280 lbs, BMI is 38 kg/m2 and waist circumference is 46 inches. Blood pressure today is 166/92 mmHg. Current medications include: metformin 850 mg tid, glipizide 10 mg qd and pioglitazone 30 mg qd. Mr. Fulmore has tried “every diet under the sun (including the Dunkin’ Donuts only diet)” over several years with little success. He walks for 45 minutes for 5 days per week which has helped him lose 40 lbs. Dr. Albert has asked for your assistance in choosing a drug therapy for this patient. Mr. Fulmore states that he will pay cash for any medications needed to help him lose weight. What would be the most appropriate choice for this patient?
A. Orlistat 120 mg tid with high-fat meals only B. Diethylpropion CR 75 mg qam C. Sibutramine 10 mg qam D. Do not start drug therapy in this patient because he does not meet the NIH obesity guideline criteria for pharmacotherapy. |
Answer A is correct.
A. This patient does not have any contraindications to orlistat use; whereas, all other approved drug therapies for treatment of obesity of the risk to increase blood pressure. B. Diethylpropion would not be a good choice because of its potential to raise blood pressure and this patient has uncontrolled hypertension C. Sibutramine would not be a good choice because of it’s potential to raise blood pressure and this patient has uncontrolled hypertension D. This patient meets the criteria for drug therapy in that he has failed diet and exercise and has a BMI > 30 or BMI > 27 with risk factors (hypertension, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, sleep apnea) Note: this patient needs to be started on antihypertensive therapy. |
|
|
w/ current available pharmacologic therapies, what is the % of wt loss? Maximal effect occurs when?
|
4-6% w/ maximal effect occurring w/n the 1st yr
|
|
|
Do these meds work for everyone who takes them?
|
No significant portion experiencing no wt loss.
|
|
|
What is the criterion for the current available wt loss meds?
|
Criterion of a 4 lb loss in 4 wks
|
|
|
If this criterion is not met, what does it mean? What should be the next step?
|
Then this is good evidence that the meds are not working & therefore should be stopped
|
|
|
To consider the Rx medically effective, many MDs require what amount of wt loss?
|
A minimum of 4 lb a month for 3 months
|
|
|
Upon cessation of Tx, % who regain the wt?
|
>90% regain the wt
|
|
|
Wt loss meds are usually reserved for who?
|
For those who have failed diet & exercise combo
|
|
|
What are the meds that have been approved by the FDA specifically for wt loss?
|
Phentermine, sibutramine, & orlistat
|
|
|
What is the MOA of phentermine?
|
It’s an adrenergic reuptake inhibitor; it’s thought to promote wt loss by activation of the sympathetic nervous system
|
|
|
Phentermine has been approved by the FDA for what length of time to be used?
|
3 months
|
|
|
What is the brand name of phentermine?
|
Adipex-P, Oby-Cap, T-Diet, Zantryl
|
|
|
What are the SE of phentermine?
|
Since it’s an adrenergic agonist, it can be associated w/ tachycardia & HTN
|
|
|
What should be done w/ patients on phentermine therapy?
|
It is good practice to monitor the pulse and blood pressure of patients closely during the first few weeks of phentermine therapy.
|
|
|
w/c drug is the most prescribed wt loss therapy? Why?
|
Phentermine b/c it’s the least expensive since there are several generic formulations available
|
|
|
What are the 2 major forms of phentermine?
|
Phentermine resin (lonamin) & phentermine HCl
|
|
|
Therapeutic response of phentermine is considered how much wt loss?
|
4 lbs/4wks for at least the first 8-12 wks
|
|
|
Name the 5 drugs approved by the FDA for other indications but exhibit wt loss promoting effects? Know the generic & brand names?
|
Generic Name: bupropion (byoo PRO pee on)
Brand Names: Aplenzin, Budeprion, Wellbutrin, Zyban metformin (glucophage), Generic Name: exenatide (ex EN a tide) Brand Names: Byetta Prefilled Pen Generic Name: topiramate (toe PYRE a mate) Brand Names: Topamax, Topamax Sprinkle, Topiragen Generic Name: zonisamide (zoe NIS a mide) Brand Names: Zonegran |
|
|
w/c wt loss drugs or drugs that have wt loss effects should not be given to pts taking MAO inhibitors?
|
Generic Name: phentermine (FEN ter meen)
Brand names: Adipex-P, Oby-Cap, T-Diet, Zantryl Generic Name: sibutramine (si BUE tra meen) Brand Names: Meridia bupropion |
|
|
bupropion is CI in w/c pts?
|
Bipolar dz & those taking MAO inhibitors
|
|
|
MOA of sibutramine?
|
It’s MAO inhibitor, enhances adrenergic, serotonergic, & dopaminergic signaling in the brain
|
|
|
Brand name of sibutramine?
|
Meridia
|
|
|
What is the avg loss w/ sibutramine?
|
5-8%
|
|
|
What happens w/ sibutramine extension therapy for up to 2 yrs?
|
It’s associated w/ an avg regain of approximately ½ the wt lost initially
|
|
|
What is the normal dosing for sibutramine in adults?
|
10-15 mg/d taken once daily.
|
|
|
Sibutramine is currently approved by the FDA for up to ______ ________ of treatment (amount of time)?
|
Up to 1 yr
|
|
|
What are the SE of sibutramine?
|
Relate to its adrenergic properties such as HTN but <3% of pts stop the drug for uncontrolled HTN. Some may experience tachycardia so this med should be avoided in those pts who have uncontrolled tachycardia or won’t tolerate it
|
|
|
What is CI w/ sibutramine?
|
SSRI b/c it increases the risk of serotonin syndrome
|
|
|
What is serotonin syndrome?
|
Marked by combo of flushing, diarrhea, & hypotension
|
|
|
MOA of orlistat?
|
It’s an inhibitor of pancreatic & intestinal lipases present in the intestinal lumen so it prevents the breakdown of ingested TG into absorbable FA & monoacylglycerols.
|
|
|
What is the brand name of orlistat?
|
Xenical, alli
|
|
|
How should orlistat be taken?
|
Should be taken w/ meals 3x/day
|
|
|
What are the SE of orlistat?
|
Flatulence, steatorrhea, increased stool frequency, fecal incontinence, & oily rectal discharge. There is an associated malabsorption of DAKE vitamins
|
|
|
What should be given to patients who are taking orlistat?
|
Supplement enriched w/ DAKE w/c should be given at least 2 hours before or after each orlistat dose.
|
|
|
What should be measured before starting orlistat? Why?
|
Because of the higher rate of vitamin D deficiency in people with obesity and the associated risk of metabolic bone disease, vitamin D levels should be measured before starting orlistat and periodically (eg, every six months) during therapy.
|
|
|
What is the MOA of lorcaserin?
|
Selective agonist of the 5-HT2C serotonin R
|
|
|
MOA of naltrexone? Used for what?
|
Opioid R antagonist that has been used as an adjunctive therapy for substance abuse Tx & addiction
|
|
|
Naltrexone along w/ what other drug has been shown to have significan wt loss?
|
Along w/ bupropion
|
|
|
What other drug combo have been shown to have wt loss effects?
|
Phentermine & topiramate
|
|
|
What dosage has been given of the phentermine/ topiramate combo for wt loss?
|
Doses given were lower than the typical doses used for monotherapy w/ each drug.
|
|
|
What are some drugs that have been discredited for wt loss?
|
Fenfluramine & dexfenfluramine
|
|
|
brand name of dexfenfluramine
|
(Redux)
|
|
|
What were the major complications of ephedrine & pheylprpanolamine?
|
Increased risk of CV complications including strokes & life threatening arrhythmias
|
|
|
Name the drugs that are in the reading that are associated w/ wt gain?
|
Steroid hormones, thiazolidinediones, DM agents, psychotropic drugs
|
|
|
What are the psychotropic meds that cause wt gain?
|
Olanzapine, valproic acid, lithium, phenothiazine, AD
|
|
|
What drugs maybe used in conjunction w/ bypass gastric surgery? What should not be used?
|
Phentermine, sibutramine, & topiramate. Orlistat is not recommended
|
|
|
How much is lost after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass?
|
65-70% w/n 1-2yrs
|
|
|
Know the BMI & their classifications?
|
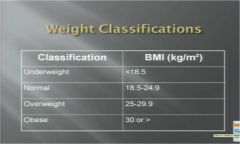
|
|
|
3. Know the BMI category for children?
|

|
|
|
How do you calculate BMI?
|
Pt’s wt in kg/height in meters squared
|
|
|
Define BMI for obesity?
|
BMI > or equal to 30
|
|
|
When looking at ethnic groups, who has the highest prevalence for being over wt?
|

native americans
|
|
|
W/c ethnic group has the lowest over wt prevalence?
|
Asian
|
|
|
Formula to calulate BMI
|
BMI = ( Weight in Pounds / ( Height in inche )2) x 703 OR Weight (kg) / (Height (m))2
|
|
|
How is weight calssified in infants
|
Weight for length; overweight is 95%
|
|
|
What are the contributing factors for obesity
|
genetic/in-utero; energy intake>expenditure, poor diet
|
|
|
What are the secondary causes for obesity
|
Hypothyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, Lesions of the hypothalamus, Medications (Diabetes treatment, Antipsychotics)
|
|
|
What are the complications of obesity
|
CV, diabetes, asthma, gallbladder disease, PCOD, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, fatty liver, psychological
|
|
|
What are the clinical criteria for pharmacologic therapy
|
BMI >30 or BMI>27 with medical complications , failure of behavioral approaches, no strong contraindications, 4-pound weight loss per month for each of the first 3 months, waist circumference (>35†in women, >40†in men)
|
|
|
At what stage in the treatment of children, is medication an option, what is the medication
|

Stage 4, Orlistat for 12+yo
|
|
|
Most common FDA approved medication for weight loss
|
Phentermine (Brand names: Adipex-P, Atti Plex P, Ionamin, Kraftobese, Panshape M, Phentercot, Phentride, Pro-Fast, Raphtre, Supramine, Tara-8, Teramine, Termene)
|
|
|
In phentermine therapy, what drug is contraindicated
|
MAO inhgibitors
|
|
|
Brand: Amphetamine/Dextroamphetamine
|
Adderall
|
|
|
Brand: Benzphetamin
|
Didrex
|
|
|
Brand: Phendimetrazine
|
Bontril
|
|
|
Brand: Diethylpropion
|
Tenuate
|
|
|
Brand: Methampetamin
|
Desoxyn
|
|
|
Brand: Dextroamphetamine
|
Dexadrine
|
|
|
Brand: Naltrexone-buropion
|
Contrave (not approved by FDA)
|
|
|
Brand: Phentermine-topiramate
|
Qnexa (not approved by FDA)
|
|
|
Brand: Sibutramine
|
Meridia
|
|
|
Why was Fenfluramine removed
|
cardiac valvular defects
|
|
|
Why was Ephedrine and phenylpropanolamine removed
|
increased risk of cardiovascular complications
|
|
|
Why was Sibutramine removed
|
increased risk of uncontrolled hypertension
|
|
|
What is currently in a SCOUT
|
Sibutramine; (Sibutramine Cardiovascular OUTcomes) trial
|
|
|
Brand and primary indication: Bupropion
|
Aplenzin, Budeprion., Buproban, Wellbutrin, Zyban; Depression
|
|
|
Brand and primary indication: Metformin
|
Fortamet, Glucophage, Glumetza; Type 2 Diabetes
|
|
|
Brand and primary indication: Exenatide
|
Byetta injection; Type 2 Diabetes
|
|
|
Brand and primary indication: Topiramate
|
Topamax, Topiragen; Seizure disorder, migraine headaches
|
|
|
Brand and primary indication: Zonisamide
|
Zonegran; seizure disorder
|
|
|
Steriod hormones associated with weight gain
|
Glucocorticoids, Progesteron
|
|
|
Neurotropic and psychotropic medication associated with weight gain
|
Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Clozapine (Clozaril), Valproid acid (Depakote), Lithium, Phenothiazines
|
|
|
Diabetes treatment associated with weight gain
|
Sulfonylureas, Insulin, Thiazolidinediones (Actos, Avandia)
|
|
|
OTC treatment of obesity; approved
|
Alli (Orlisatat ); 18+yo
|
|
|
OTC treatment of obesity; removed
|
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA), Ephedra (Ma Huang or Heartleaf)
|
|
|
OTC treatment of obesity; other (with minimal effect)
|
Fiber (Glucomannan and psyllium), caffiene (Methylxanthine, Dexatrim ephedra free formula), Green Tea (Dexatrim Green Tea Formula, Dexatrim ephedra free formula), Bitter orange, Chitosan, Chromium, laxatives, diuretics, hoodia gordonii
|
|
|
What product is typically abused by teenage girls for weight loss
|
Syrup of Ipecac
|
|
|
What is the future for development of new obesity drugs
|
Central Melanocotin Pathway, neurons which control appetite and energy expenditure
|
|
|
What is currently undergoing study fior the future of wieght loss medication
|
1. Ciliary Neutrophic Factor
2. Melanocortin-4 receptor agonist 3. Ghrelin 4. Neuropeptide Y antagonists 5. Melanin-concentrating hormone agonists 6. Peptide YY |
|

know the drugs associated w/ wt gain?
|

|
|
|
a combo of fenfluarmine & what other drug was shown to have improved wt loss effects?
|
phentermine
|
|
|
who needs to be treated for obesity?
|

|
|
|
what are the non PTX treatments that can be used for obesity?
|

|
|
|
Surgery for obesity is reserved for w/c group of people?
|
Surgery for people who have BMI >40
|
|
|
is there any drug interactions w/ orlistat?
|
Will interfere w/ DAKE vitamins & will decrease [ ] of cyclosporin
|
|
|
how can u treat the SE of orlistat?
|
w/ low fat meals & psyllium
|
|
|
What is the generic for Adipex-P?
|
phentermine
|
|
|
Adipex can suppress appetite for how many hours?
|
12-14 hours
|
|
|
Adipex P is considered what schedule drug?
|
Schedule IV
|
|
|
What are the DI for sibutramine?
|
SSRIs, MAOIs, dextromethorphan, sumatriptan, meperidine, fentanyl, lithium
|
|
|
What are the SE of sibutramine?
|
Insomnia, constipation, dry mouth, increase in BP & pulse
|
|
|
Sibutramine is CI in w/c group of people?
|
Those w/ uncontrolled HTN, seizure disorders, narrow angle glaucoma, severe renal & hepatic dysfunction, CHF, arrhythmias, stroke, Hx of substance abuse
|
|
|
Orlistat is approved by the FDA for what age of children?
|
12 years & older
|
|
|
what is the age group for Alli?
|
18 years & older
|
|
|
How does caffeine work in wt loss?
|
Increases lypolysis, circulating FA levels, & oxygen consumption.
|
|
|
This weight loss product may increase bleeding time?
|
Green tea so it should be stopped 24 hours before surgery
|
|
|
This product works in wt loss by increasing thermogenesis of brown adipose tissue?
|
Bitter orange
|

