![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In diagnosis of DM, random BG value?
|
200mg/dL
|
|
|
Diabetes: Fasting plasma glucose: (FPG)
|
≥ 126 mg/dL; confirmed with 2nd test
|
|
|
Diabetes: 2-hour blood glucose
|
200 mg/dL; confirmed with 2nd test
|
|
|
Diabetes: A1C
|
6.5% (Normal 4-5.6%); conformed with 2nd test
|
|
|
Pre-Diabetes: Fasting plasma glucose: (FPG)
|
100-125 mg/dL (impaired fasting glucose – IFG)
|
|
|
Pre-Diabetes: 2-hour blood glucose
|
140-199 mg/dL (impaired glucose tolerance – IGT)
|
|
|
Pre-Diabetes: A1C
|
5.7- 6.4% (Normal 4-5.6%)
|
|
|
Formulas for expressing A1c as average glucose
|
eAG = 28.7 X A1c- 46.7
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Preprandial glucose
|
70 - 130 mg/dL
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Postprandial glucose
|
<180 mg/dL
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: A1c
|
<7%
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Blood pressure
|
< 130/80
|
|
|
Drugs of choice in DM for lowering BP
|
CE inhibitor or ARB
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Lipid Levels: LDL
|
<100 mg/dL
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Lipid Levels: HDL, male
|
>40 mg/dL
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Lipid Levels: HDL, female
|
>50 mg/dL
|
|
|
Goals of DM therapy: Lipid Levels: Triglycerides
|
<150 mg/dL
|
|
|
Drugs of choice in DM for lowering lipids
|
Statins
|
|
|
What are the types of insulin for mealtime covereage
|
Rapid and short acting insulin
|
|
|
What are the types of insulin for basal control
|
Intermediate and long acting insulin
|
|
|
Algorithm for Type 2 DM: step 2 (well-validated)
|
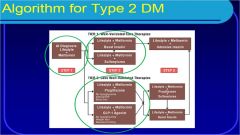
Lifestyle, metformin and basal insulin OR sulfonylurea
|
|
|
Accute complication of DM: too much glucose
|
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS)
|
|
|
Accute complication of DM: too little glucose
|
Hypoglycemia, Blood glucose < 60
|
|
|
What are the 4 Microvascular chrionic complications of DM
|
Peripheral neuropathy, Autonomic neuropathy, Retinopathy, Nephropathy
|
|
|
What are the 2 Macrovascular chronic complication of DM
|
Myocardial infarction and stroke
|
|
|
What is the effect of Peripheral neuropathy
|
Numbness, tingling, pain; can lead to foot damage
|
|
|
What is the effect of Autonomic neuropathy
|
Impotence, Diabetic gastroparesis, Neurogenic bladder, Hypoglycemic unawareness
|
|
|
What is the effect of Retinopathy
|
Leading cause of blindness
|
|
|
What is the effect of Nephropathy
|
Leading cause of kidney failure; Characterized by proteinuria
|
|
|
What are the treatments for Retinopathy
|
Photocoagulation, modify other risk factors, get regular eye exams
|
|
|
What are the treatments for Nephropathy
|
ACE inhibitors, ARBs, restrict protein intake
|
|
|
What is the treatment for the Macrovascular chronic complications
|
ASA therapy, 75-162 mg daily
|
|
|
know the insulin therapy for DM
|
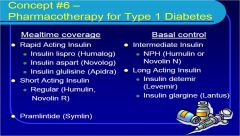
|
|
|
when should short acting insulin be given?
|
30 minutes before a meal
|
|
|
what is amylin?
|
Amylin is a hormone that is co-secreted w/ insulin from the cells of the pancreas
|
|
|
what is amylin release in DM 1 & 2?
|
w/ type II, we still have working of cells so we still have release of amylin but we don’t get that spike that we get in a normal person.
In type I, there is no release of amylin |
|
|
how can amylin work in treatment of DM? what is the SE?
|
So amylin would be a good treatment for type I DM or type II DM that requires insulin.
What amylin does when it is released w/ insulin is it reduces our emptying gastric time so we don’t empty the stomach as quickly. So glucagon is not released, it makes us feel full. The side effect of a slower emptying is nausea & it can also cause hypoglycemia. So it’s recommended that those who start on should decrease the rapid acting insulin or mealtime insulin by 50% |
|
|
What is synthetic analog of amylin?
|
symlin
|
|
|
A patient with Type 1 DM is found to have a high blood glucose during an office visit. Which of the following insulin preparations could be administered in the office to bring the blood glucose down in a timely manner?
A.Insulin detemir (Levemir) B.Insulin glargine (Lantus) C.Insulin lispro (Humalog) D.NPH insulin (Humulin or Novolin R) |
C is the correct answer
|
|
|
What is the effect of sulfonylureas on A1C?
|
reduces it by 1-2%
|
|
|
What are the 3 sulfonylureas covered in lecture?
|

Glimepiride, glipizide, glyburide,
|
|
|
This drug is given for newly diagnosed type 2 DM?
|
metformin
|
|
|
This drug could be considered for pre-diabetes?
|
Metformin
|
|
|
what SCr levels should not be given metformin?
|
SCr > 1.5 males; > 1.4 females
|
|
|
How are glinides different from sulfonyureas?
|
They have faster onset & shorter duration of action. They are dosed before a meal so if u skip a meal, u skip the dose whereas w/ sulfonylureas since they are long acting, if u skip a meal, a person will be hypoglycemic at the end of the day
|
|
|
MOA of glucosidase inhibitors?
|
Inhibit breakdown of complex CHO & decrease postprandial glucose
|
|
|
This drug should not be given to those w/ heart failure?
|
Thiazolidnediones
|
|
|
What are the thizoldinediones?
|
Pioglitazone & rosiglitazone
|
|
|
Adverse effects of thiazolidnediones?
|
Fluid retention, edema, bone fractures & cardiac risk
|
|
|
How do incretin hormones work?
|
Increase postprandial insulin & decrease postprandial glucagon. They also delay gastric emptying & enhance satiety
|
|
|
Incretin mimetics are aka what?
|
GLP-1 agonists
|
|
|
What are the 2 GLP-1 agonists?
|
GLP-1 agonists
Exenatide & liraglutide |
|
|
What are the adverse effects of GLP-1 agonists?
|
Nausea & vomiting, pancreatitis, & Ab can develop against them
|
|
|
What are the DPP-4 inhibitors?
|
Sitaglipitin & saxagliptin
|
|
|
MOA of DPP-4 inhibitors?
|
They inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzyme w/c is responsible for breaking down incretins
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of DPP-4 inhibitors?
|
Nasopharyngitis, headache
|
|
|
Too much glucose can lead to what 2 things?
|
DKA & hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS)
|
|
|
What complications occur w/ too little glucose?
|
Hypoglycemia w/ glucose <60
|

