![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Describe a swan neck deformity.
|
PIP hyperextension and flexion of the DIP
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of a Swan Neck deformity (SND)?
|
Overstretched palmar plate and bowstringing of the lateral bands of the extensor hood.
|
|
|
|
What are some post-operative precautions after correction of a Swan-neck deformity?
|
Limit PIP extension to 10 degrees of flexion during exercise and avoid extreme flexion of the DIP joint.
|
|
|
|
In what position should the PIP and DIP joints be splinted after corrective surgery for SND?
|
Maintain the PIP joint in 10-20 degrees of of flexion and the DIP join in full extensionwith static splinting
|
|
|
|
What are some post-op treatment guidelines associated with Swan-neck corrective surgery?
|
DIP extension exercises should be performed with the PIP joint in slight flexion, the DIP joint should be in neurtral during PIP ROM exercises and
|
|
|
|
When and what kind of exercsies should be done on post-op SND?
|
AROM should begin 10-14 days post-op. PIP flexion and DIP extensions exercises should be emphasized
|
|
|
|
Describe a Boutonniere deformity.
|
PIP flexion and DIP extension
|
|
|
|
What causes a Boutonniere deformity?
|
Rupture of the central band of the extensor hood
|
|
|
|
What are some post-operative precautions after correction of a Boutonniere deformity?
|
Avoid hyperextension of the DIP joint, avoid resistance exercises and stretching of the extensor mechanism of the PIP joint for 6-8 weeks
|
|
|
|
What is the goal of splinting after corrective surgery for a Boutonniere deformity?
|
Maintaining as much extension as possible of the PIP joint
|
|
|
|
How do you stretch the structures which make up the extensor hood?
|
MCP extension concurrent with PIP flexion (Extrinsic plus)
|
|
|
|
True or False: lacerations to the finger extensors is more common than lacerations to the finger flexors.
|
True
|
|
|
|
Felxor tendon injuries in what zone of the hand pose a particular challenge to hand surgeons and why?
|
Zone II because confined space for the extrinsic tendons and lack of vascularity makes injuries prone to excursion-restricting adhesions
|
|
|
|
Whare does scar tissue formation form that can interrupt tendon-gliding in flexor tendon injuries?
|
Synovial sheath
|
|
|
|
True or false: a direct tendon repair involves an end-to-end repair in which the tendon ends are re-opposed and sutured together.
|
True
|
|
|
|
How is dynamic splinting used to treat flexor tendon injuries?
|
The dynamic component protects the healing flexor tendon by passively flexing the involved digit but allows active extnsion to the limit of the dorsal block component.
|
|
|
|
What are the two basic approaches to management after flexion tendon repair?
|
Early controlled motion (active or passive) and Delayed motion
|
|
|
|
What is the rationale for early controlled motion after tendon repair?
|
Decreases edema, decreases the formation of adhesions that can limit excursion , increases synovial fluid for tissue nutrition, increases wound maturation and tensile strength of the repaired tendon, decreases gap formation at the repair site.
|
|
|
|
Name the three types of splints used after flexor tendon surgery.
|
Static dorsal blocking, Dorsal blocking with dynamic traction and Dorsal tenodesis with wrist hinge
|
|
|
|
What is the primary feature that distinguishes an early active motion from an early passive motion approach?
|
The early active uses minimium-tension, active contractions fo the repaired ms units in the acute stage of healing.
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for using prolonged immoblization and delayed motion on flexion tendon injuries?
|
Comprehension deficits, unmotivated patients, children, overzealous patients and other hand injuries that necessitates extended mobilization.
|
|
|
|
True or False: when treating flexor tendon repairs it is essential that the MCP joint is maintained in extension while performing passive ROM of the IP joints
|
False, MCP joints should be maintained in flexion. You want to avoid passive insufficieny of the finger flexor tendons.
|
|
|
|
Describe the funcitonal position of the hand used for splinting.
|
Wrist is in 15 degrees of EXT and the fingers are in full extension. A block along the ulnar border of the splint prevents ulnar deviation of the fingers.
|
Hand splints handout
|
|
|
What is the focus of treatments after surgical care of Dupuytren's contracture?
|
Maintaining hand and finger extension, controlling swelling, reducing scar tissue formation, and promoting active motion while enhancing static soft-tissue stretching using splints.
|
|
|
|
What is mallet finger?
|
Rupture or avulsion of the extensor tendon.
|
|
|
|
What deformity results from a mallet finger?
|
DIP joint flexion contracture
|
|
|
|
What are the post-op precautions associated with extensor tendon reconstructions in patients with RA?
|
In the early phase of rehab avoid commensing MCP extension from full MCP flexion, avoid stretching to increase MCP flexion if a active extension deficit is present, avoid postures which combine finger flexion or thumb flexion and adduction with wrist flexion, and avoid vigorous grasping activities.
|
|
|
|
What factors contribute to adhesion formation after tendon injury or repair?
|
Location of the injury, extent of trauma, reduced blood supply, excessive handling of damaged tissues during surgery, tendon sheath damage, prolonged immobilization, ineffective surturing technique and gapping of the repaired tendon ends.
|
|
|
|
What is the typical position of immobilization for flexor tendon repairs located in the distal part of the hand?
|
MCP flexion with PIP and DIP extension (this position prevents full lengthening and undue stress on the FDP and FDS while minimizing the risk of IP flexion contractures)
|
|
|
|
Describe the position of the wrist, MCP and IP joints that would cause passive insufficiency to the finger flexors.
|
Wrist extension, MCP ext, PIP and DIP extension.
|
|
|
|
Why is it impossible to actively extend the DIP joint of fingers 2-5 when the MCP and PIP are maximally passevely flexed?
|
The oblique retinacular ligament links these joints so that:
1. When the DIP joint flexes it pulls on the ligament and flexes the PIP joint. 2. When the PIP joint extends it pulls on the ligament and extends the DIP joint |
For more detail go to: http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/
hfa213/week5/lec5finger.pdf |
|
|
True or False: Imbalance from weak intrinsic muscles leads to an ape hand.
|
False, claw hand
|
|
|
|
Describe how to perform differential gliding of the EDC.
|
Move each digit into flexion while stabilizing the other digits in extension.
|
|
|
|
Increasing extensor tendon-gliding
|
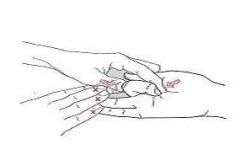
What is this exercise used for?
|
|
|
|
What is Allen's test used for?
|
Detect vascular problems in the radial and ulnar artery.
|
|
|
|
True or False: Froment's sign is used assess the radial nerve.
|
False, ulnar nerve
|
|
|
|
True or False: Heberden’s nodes are commonly seen in patients with OA.
|
True
|
|
|
|
True or False: De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is associated with motions that require repetitive radial deviation.
|
False, UD (for those who attended today's lab, we talked about RD, however Shankman says it is UD)
|
Shankman page 439
|
|
|
Describe a Bennett's fracture.
|
Fx-dislocation of the 1st metacarpal
|
|
|
|
Skier's thumb involves what ligament?
|
Ulnar collateral at the 1st metacarpal joint
|
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of injury associated with a skier's thumb?
|
Abd and hyperextension of the 1st MCP joint
|
Lecture notes
|
|
|
What direction do the fingers drift with RA?
|
In an ulnar direction
|
lecture notes
|
|
|
The carpal tunnel questions can be found with the elbow and wrist questions
|
See PTA 201 Elbow and Wrist cards
|
|
|
|
What does the Bunnel-Littler test detect?
|
It differentiates capsular tightness from shortened intrinsic muscles at the PIP joint when there is loss of flexion
|
Elbow, wrist, finger special test lab handout
|
|
|
What tissue is involved with Dupuytrens' contracture.
|
Palmar Fascia
|
Shankman page 445
|
|
|
What digits are most commonly involved with Dupuytrens' contracture?
|
4th and 5th
|
Shankman page 445
|
|
|
What adverse effect can occur with flexor tendon injuries if appropriate stress and directed motion is not applied after surgery?
|
Scar tissue forms in a random pattern and does not attain normal intact tendon strength.
|
Shankman page 447
|
|
|
What are the most salient (important)features of rehab after flexor tendon repair?
|
The interrelationship between immobilization and application of early, protected, limited PROM.
|
Shankman page 447
|
|
|
In the MinPP of a MCP implant arthroplasty, what kind of motion is allowed?
|
Active
|
Colby page 606
|
|
|
In what phase of rehab can isometric exercises be performed after MCP implant arthoplasty?
|
ModPP
|
Colby page 607
|
|
|
Place-and-Hold exercises are classified as what kind of strengthening exercise?
|
Isometric
|
Colby page 623
|
|
|
In what phase of rehab can Tendon-gliding and and blocking exercises be performed after a flexor tendon repair?
|
ModPP
|
Colby page 623
|
|
|
When initiating Tendon-gliding exercises what position should the wrist be placed?
|
Neutral
|
Colby page 631
|
|
|
Decribe the sequance of Tendon-gliding exercises.
|
Straight hand, hook fist, full fist, table top (intrinsic plus) and straight fist
|
Colby page 631
|
|
|
True or False, place and hold exercises are only used with flexor tendon injuries.
|
False, they can be used for extensor injuries as well.
|
Colby page 631
|
|
|
What's the main difference between static and dynamic hand splints?
|
Dynamic splints have an Elastic component which provides a dynamic traction force to mobilize joints and soft tissues
|
Hand Splint handout
|

