![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Fill in the numbers-
a. The prevalence of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) in the US is estimated to be between ___% and ___% of the adult population, increasing to as much as 10% in those ___ years and older. b. As many as one-fourth of those with PAD will likely require amputation; ____ will die within ___ years of diagnosis; three-fourths will die within ____ years of diagnosis. |
a. The prevalence of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) in the US is estimated to be between __6_% and __3_% of the adult population, increasing to as much as 10% in those __65_ years and older.
b. As many as one-fourth of those with PAD will likely require amputation; _1/3___ will die within _5__ years of diagnosis; three-fourths will die within __10__ years of diagnosis. |
|
|
2. What are the 3 leading causes of traumatic amputation in the united states
|
a. Industrial and farming accidents
b. Motor vehicle accidents c. Injury during high risk sport/activity |
|
|
3. Describe the post op treatment for a toe amputation
|
• Initial dressing remains in place for up to 5 days
• After 5 days, patient instructed in NWB ambulation • Educate patient to keep limb elevated to reduce swelling • After 10 days, patient begin PWB • FWB allowed 2 to 3 weeks after sutures removed. |
|
|
4. What is a complete trans metatarsal amputation
a. Amputation of one metatarsal b. Amputation of one or more metatarsals c. Amputation of all 5 metatarsals |
c. Amputation of all 5 metatarsals
|
|
|
5. Very short matching
a. Lisfranc procedure b. Chopart procedure ______ Transmetatarsal disarticulation ______ Midtarsal disarticulation (between tarsal bones) |
5. Very short matching
a. Lisfranc procedure b. Chopart procedure __A____ Transmetatarsal disarticulation __B____ Midtarsal disarticulation (between tarsal bones) |
|
|
6. T/F-After a Lisfranc or Chopart procedure, a prosthetic is required.
|
T
|
|
|
7. What is a Syme amputation?
|
Disarticulates the talocrural, trims the malleoli to create a flat weight bearing surface, and repositions the heel pad under the distal tibia and fibula.
|
|
|
8. Comfort in prosthesis, quality of gait, energy costs are all enhanced when the amputation preserves ___to ___% of the tibia in a transtibial amputation.
a. 20-30% b. 30-40% c. 40-50% d. 50-60% |
c. 40-50%
|
|
|
9. T/F Knee Disarticulation was one of the first amputation surgeries due to simplicity of the technique & limited infection rates.
|
T
|
|
|
10. In an amputation for a child it is important to preserve the_____________?
|
Growth Plate
|
|
|
11. Function and prosthetic control improve as________?
|
Length of the residual limb increases
|
|
|
12. Myoplasty helps in knee disarticulations by
a. Preserving femoral length b. Preserving muscle mass c. Increasing the likelihood of having greater strength and control of the residual limb d. Increasing the likelihood of having a better shaped residual limb e. All of the above are correct |
e. All of the above are correct
|
|
|
13. Why are hemipelvectomy surgeries so difficult on the patient?
|
Individual is left without a bony case to support the abdominal contents on one side of the body.
|
|
|
14. As many as ____% of persons with new amputations have noticeable phantom limb sensation
a. 20% b. 40% c. 50% d. 70% |
d. 70%
|
|
|
15. T/F-Patients who experience dysvascular limb pain before surgery are less likely to experience phantom limb pain.
|
F
|
|
|
16. If you answered F on the previous question, you got it right. They are likely to feel fantom pain for up to____ year(s) after the surgery?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 |
b. 2
|
|
|
17. T/F-Actual limb length is measured from a bony land mark (proximal part of limb) to the end of the soft tissue at the distal end of the residual limb.
|
F
Actual limb length is measured to the end of the bone, and total limb length is measured to the end of the soft tissue. |
|
|
18. At least how many inches of the tibia are required to ensure a sufficient lever arm for effective prosthetic control?
a. 1-2 b. 3-4 c. 4-5 d. 5-6 |
d. 5-6
|
|
|
19. Less than ____ inches may be insufficient length for prosthetic control?
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. 6 |
b. 3
|
|
|
20. Referral for a prosthetic fitting is made when the distal limb circumference is equal to or no more than ___ inch greater than limb circumference?
a. ¼ b. ½ c. ¾ d. 1 |
a. ¼
|
|
|
21. With each dressing change, the wound is carefully examined and the ______ of the drainage is documented
a. Quality b. Quantity c. Color d. Consistency e. Both A and B f. Both C and D |
e. Both A and B
|
|
|
22. Within ___ weeks a person with an amputation due to trauma will have sufficient enough healing to begin using a prefabricated adjustable prosthesis.
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 6 |
a. 2
|
|
|
23. From the above question…If there is a vascular disease it could take_________
a. 4-6 weeks b. 6-8 weeks c. 2-4 months d. Up to a year |
b. 6-8 weeks
|
|
|
24. List 2 ways to assess circulation around an amputation
|
a. Palpation of peripheral pulse
b. Skin temperature |
|
|
25. What test is done to determine if there is a hip flexion contracture for a transtibial or transfemoral amputation?
|
a. Thomas Test
|
|
|
26. When assessing the aerobic capacity of an amputee, screen for __________________
|
a. Orthostatic Hypotension
|
|
|
27. T/F-Interventions for post operative amputation pain include anti-seizure medications; local steroid injections; relaxation techniques; therapeutic touch; TENs; therapeutic modalities
|
T
|
|
|
28. The effectiveness of an Ace Wrap depends on___________
|
a. Patient Education
|
|
|
29. What does every new amputee need to have before they are sent home?
|
a. A wheel chair
|
|
|
30. What 2 exercises should be done 1 week after a transtibial amputation?
|
a. Quad sets and short arc quads
|
|
|
31. What 2 exercises should be done 1 week after a transfemoral amputation?
|
a. Glut sets, and short arc hip extension and abduction
|
|
|
32. T/F-After an amputation, walkers are good for initial gait training, but they may teach abnormal gait patterns, hence use crutches whenever possible.
|
T
|
|
|
33. Amputations at the transtibial level (below the knee) occur at least _______ as often as amputations at other levels.
a. Half b. Twice c. 3 times d. 4 times |
b. Twice
|
|
|
34. Matching
a= K0, b= K1, c= K2, d= K3, e= K4 ____ The patient has the ability or potential to use a prosthesis for transfers or ambulation on level surfaces at a fixed cadence. With a prosthesis, the patient achieves limited or unlimited household ambulation status. _____ The patient has the ability or potential for prosthetic ambulation that exceeds basic ambulatory skills, exhibiting high impact, stress, or energy levels during activity. This category includes most children, active adults, or athletes with amputation. ______ The patient does not have the ability or potential to ambulate or transfer safely with or without assistance, and a prosthesis does not enhance quality of life or mobility. ______ The patient has the ability or potential for prosthetic ambulation that exceeds basic ambulatory skills, exhibiting high impact, stress, or energy levels during activity. This category includes most children, active adults, or athletes with amputation. ______ The patient has the ability or potential for ambulation, including the ability to traverse low-level environmental barriers such as curbs, stairs, or uneven surfaces. With a prosthesis, the patient is considered a limited community ambulator. |
34. Matching
a= K0, b= K1, c= K2, d= K3, e= K4 __B__ The patient has the ability or potential to use a prosthesis for transfers or ambulation on level surfaces at a fixed cadence. With a prosthesis, the patient achieves limited or unlimited household ambulation status. __D___ The patient has the ability or potential for prosthetic ambulation that exceeds basic ambulatory skills, exhibiting high impact, stress, or energy levels during activity. This category includes most children, active adults, or athletes with amputation. ___A___ The patient does not have the ability or potential to ambulate or transfer safely with or without assistance, and a prosthesis does not enhance quality of life or mobility. ___E___ The patient has the ability or potential for prosthetic ambulation that exceeds basic ambulatory skills, exhibiting high impact, stress, or energy levels during activity. This category includes most children, active adults, or athletes with amputation. ___C___ The patient has the ability or potential for ambulation, including the ability to traverse low-level environmental barriers such as curbs, stairs, or uneven surfaces. With a prosthesis, the patient is considered a limited community ambulator. |
|
|
35. The ______ is the portion of the prosthesis that makes contact with and disperses pressure around the residual limb.
a. Shank b. Suspension mechanism c. Prosthetic foot d. Socket |
d. Socket
|
|
|
36. What is the most commonly prescribed transtibial socket? And what does it do?
|
a. PTB=patellar tendon bearing.
b. Distributes the primary loading pressures of weight bearing over several surfaces of the residual limb. |
|
|
37. Which of the following is not a goal of prosthetic socks?
a. cushion forces applied to the residual limb during ambulation b. cosmetic appeal c. accommodate to changes in the volume of the residual limb d. absorb moisture and keeps it away from the skin |
b. cosmetic appeal
|
|
|
38. Once the layers of socks reach a ply of ___ or more, a new socket may be necessary.
a. 4 b. 6 c. 8 d. 10 |
d. 10
|
|
|
39. The residual limb will continue to shrink for up to_______ after amputation.
a. 6 weeks b. 3-6 months c. 6-8 months d. 1 year |
d. 1 year
|
|
|
40. The definitive prosthesis is made when…
a. The residual limb volume stabilizes b. When the patient uses the same amount of socks with the prosthesis c. When the patient has learned to successfully use the temporary prosthesis d. A and B e. All of the above |
d. A and B
|
|
|
41. The definitive prosthesis should last the patient…
a. 1-3 years b. 2-4 years c. 3-5 years d. 4-6 years |
c. 3-5 years
|
|
|
42. T/F-Visual evaluation of the stump should take place after a period of rest.
|
F
Should happen after prolonged weight bearing |
|
|
43. Areas on the residual limb that are blanched and quickly turn deep red often indicate…
a. Infection b. Excessive pressure c. A rash d. Edema |
b. Excessive pressure
|
|
|
44. Problems with limb circumference or shape can usually be corrected by
a. Increasing muscle mass b. Decreasing muscle mass c. Altering the number of socks d. Addition or subtraction of an ace wrap |
c. Altering the number of socks
|
|
|
45. The powder test, ball of clay test, and the lipstick tests are….
a. Used to determine if the socket is too large b. Used to determine if the socket is too small c. Used to determine the number of socks needed for proper socket fit d. Used to determine is a new socket is needed |
c. Used to determine the number of socks needed for proper socket fit
|
|
|
46. Explain how to perform the powder, ball of clay, and lipstick tests.
|
a. Powder Test - use baby power sprinkled on all sides and bottom of socket. Walk a short distance. Inspect the socket for powder remains. Very little powder should remain on the sides or bottom. Powder at the bottom indicates a loss of total contact and can be corrected by changing the number of socks
b. Ball of Clay Test - use a ball of clay (penny size) placed in the bottom of the socket. Have patient stand and walk. The clay should be compressed ¼ to of an inch. Change the number of socks to regain total contact c. Lipstick Test - mark painful area with lipstick on outer sock. Have patient stand and walk a short distance. The lipstick smudge should appear at the area of bony relief. If it is below or above the area of bony relief, change the number of socks |
|
|
47. Phantom limb pain can be controlled with all of the following except.
a. Heat modalities b. Firm pressure techniques c. Analgesics d. Consistent use of prosthetic e. All of the above |
e. All of the above
|
|
|
48. Diabetics amputees will undergo amputation of their sound limb ____% of the time within 1 year.
a. 10% b. 20% c. 30% d. 40% e. 50% |
b. 20%
|
|
|
49. From the previous question, what percent will lose their sound limb after 5 years?
a. 20% b. 30% c. 40% d. 50% e. 60% |
d. 50%
|
|
|
50. Which of the following devices is most recommended for transtibial amputee gait training?
a. Quad Cane b. Lofstrand crutches c. Standard walker d. All of the devices are equally effective |
b. Lofstrand crutches
|
|
|
51. T/F Wheeled walkers are preferred to standard walkers when teaching and amputee to walk with a new prosthetic
|
F
Standard walkers - impede development of reciprocal gait pattern. Use only when endurance or postural control are significantly compromised. Wheeled walker better to use. |
|
|
52. T/F Quad canes are not recommended because they are frequently misused as weight bearing devices, and the wide base can create a fall hazard.
|
T
|
|
|
53. A transfemoral amputation is done
a. Proximal to the anatomical knee joint b. The middle of the anatomical knee joint c. Distal to the anatomical knee joint d. All of the above e. False! There is no such thing as a transfemoral knee joint amputation |
a. Proximal to the anatomical knee joint
|
|
|
54. Which of the following is not a concern for increased energy expenditure for a transfemoral amputee?
a. Weight of prosthesis b. Quality of socket fit c. Accuracy of alignment of the prosthesis d. Number of socks being worn by the amputee e. Functional characteristics of the prosthetic component |
d. Number of socks being worn by the amputee
|
|
|
55. T/F-The energy cost of gait increases significantly as the length of the residual limb increases.
|
F
as the length decreases |
|
|
56. The anterior wall of the socket causes the socket to be
a. Of equal width on all 4 socket walls b. More narrow anterior to posterior c. More narrow medial to lateral d. Wide anteriorly and narrow posteriorly |
b. More narrow anterior to posterior
|
|
|
57. The anterior socket wall produces a _______ force which keeps the ischium on the ischial seat (where the ischium does its weight bearing in standing and gait)
a. Anterior b. Posterior c. Medial d. Lateral |
b. Posterior
|
|
|
58. The ischial ramal containment socket does all of the following except
a. Stabilizes the socket on the residual limb b. Controls socket rotation c. Distributes weight through the socket along the shaft of the femur d. Enhances muscle function by having a wider anteroposterior dimension e. All of the above are correct |
All of the above are correct
|
|
|
59. Matching-State whether the description fits a rigid or flexible socket
A= Rigid B= Flexible ____ Vacuum forme with thermoplastics ____ Less Bulky ____ More expensive ____ Easily modified ____ Easy to clean ____ Less expensive ____ Less durable ____ Harder to fit |
59. Matching-State whether the description fits a rigid or flexible socket
A= Rigid B= Flexible __B__ Vacuum forme with thermoplastics __A__ Less Bulky __B__ More expensive __B__ Easily modified __A__ Easy to clean __A__ Less expensive __B__ Less durable __A__ Harder to fit |
|
|
60. Matching-State whether the description fits an endoskeletal prosthesis or and exoskeletal prosthesis
A=Endo B=Exo ____ Easy to interchange or replace modular units ____ Durable ____ Requires little maintenance ____ Easily adjusts |
60. Matching-State whether the description fits an endoskeletal prosthesis or and exoskeletal prosthesis
A=Endo B=Exo __A__ Easy to interchange or replace modular units __B__ Durable __B__ Requires little maintenance __A__ Easily adjusts |
|
|
61. Matching- (Pretty easy, but it’ll still help)
a. Single axis knee b. Polycentric knee c. Weight activated stance control knee d. Manual locking knee e. Hydraulic knee f. Pneumatic knee g. Micro processor knee ____ Uses air pressure to control stability and cadence. ____ Center of rotation changes through the range of motion ____ Has a locking pin mechanism for added stability during stance ____ Simple hinge which allows the shank to swing through flexion/extension ____ Controlled with a microprocessor ____ Contains a braking mechanism that is activated when weight is applied during stance phase ____ Uses Hydraulic cylinder to control Stability and cadence. |
61. Matching- (Pretty easy, but it’ll still help)
a. Single axis knee b. Polycentric knee c. Weight activated stance control knee d. Manual locking knee e. Hydraulic knee f. Pneumatic knee g. Micro processor knee __F__ Uses air pressure to control stability and cadence. __B__ Center of rotation changes through the range of motion __D__ Has a locking pin mechanism for added stability during stance __A__ Simple hinge which allows the shank to swing through flexion/extension __G__ Controlled with a microprocessor __C__ Contains a braking mechanism that is activated when weight is applied during stance phase __E__ Uses Hydraulic cylinder to control Stability and cadence. |
|
|
62. Which of the following preoperative assessments does not help dictate the level of amputation in an upper extremity.
a. Pain b. Chronic scar tissue c. Muscle strength |
a. Pain
|
|
|
63. T/F-Amputation should never be performed to relieve pain.
|
T
|
|
|
64. According to the slides, the benefits of UE residual limb exercises are all of the following except…
a. Improved circulation b. Decreased chance of phantom pain c. Prevents scar tissue adhesion d. Reduced likely hood of psychological problems e. All of the above are correct |
d. Reduced likely hood of psychological problems
|
|
|
65. The most common device for an UE prosthetics is…
a. An artificial hand b. A hook c. No device (a stump) d. A weapon like a knife or some sort of laser gun !!!! |
b. A hook
|
|
|
66. The three classes of UE prosthetics are listed below, which one does not belong? Once you weed out the intruder, define each of the 3 classes of prosthetics.
a. Industrial b. Cosmetic c. Body Powered d. Electric Powered |
a. Industrial
Cosmetic= no true control; only used for appearance Body powered= Body movement used to control the device, not very cosmetic; but very functional. Electric powered= Battery operated motor can move hand, wrist and elbow |
|
|
67. In the case of a bilateral arm amputee, the patient may learn to use their feet to perform activities of daily living if they are under the age of_______?
a. 12 b. 15 c. 20 d. 25 |
c. 20
|
|
|
68. T/F-The definition of practical advice for an amputee is: advice given which is considered good for their entire lives.
|
T
|
|
|
69. Give two pieces of advice about proper care of a prosthesis.
|
1. Washing daily with mild soap; dried thoroughly; done at the end of the day (damp stump can cause problems if inserted into a socket).
2. Examine the skin signs of friction - use a mirror as needed; if exam is positive, then consult health care professional before wearing prosthesis. 3. No creams, oils or medications should be used unless advised by the primary care physician. 4. Proper donning of stump sock - no wrinkles!!!! |
|
|
70. What is exostosis?
|
a. Bony growth out from the main surface of the bone; can involve muscles or tendons.
|
|
|
71. According to the slides, how should an amputee break in new shoes?
a. Begin wearing them for 2 hour intervals b. Wear them every other day for the first 2 weeks c. Initially: do not use them at work or during physical activities d. Ask the neighbor boy if he’ll break them in for you… |
a. Begin wearing them for 2 hour intervals
|
|
|
72. All component parts need to be checked regularly for wear; especially the_______.
a. Joint component b. Socket c. Outer surface d. Feet |
d. Feet
|
|
|
73. T/F To clean the socket daily with a mild soap; dry thoroughly.
|
F
Cleaning - wipe socket with damp cloth; do not use soap; dry thoroughly |
|
|
74. The majority of Hip Disarticulation Amputations are due to
a. Malignant bone tumors b. Trauma c. Diabetes d. Birth defects |
a. Malignant bone tumors
|
|
|
75. Matching- A= Hind quarter amputation, B= Hip disarticulation
____ Head of the femur may be left intact in the acetabulum ____ Half of the Pelvis is removed |
75. Matching- A= Hind quarter amputation, B= Hip disarticulation
__B__ Head of the femur may be left intact in the acetabulum __A__ Half of the Pelvis is removed |
|
|
76. With a hip amputation, the most important thing regarding the socket is?
a. General fit b. Comfort c. Function d. Cosmetics |
b. Comfort
|
|
|
77. Prosthesis lift test -If the limb sags during hip hiking, then the socket is too ____.
a. Short b. Small c. Large d. Heavy |
c. Large
|
|
|
78. A hip prosthesis should be______
a. The same length as the sound limb b. Shorter than the sound limb c. Longer than he sound limb |
b. Shorter than the sound limb
|
|
|
79. After the prosthetist correctly aligns the prosthetic, it may appear_____
a. That the knee is slightly flexed b. That the knee is straight c. That the knee is slightly hyperextended |
c. That the knee is slightly hyperextended
|
|
|
80. The proper instructions for a hip amputee to use a ramp or go up a hill is…
a. Go up and down ramp leading with sound leg b. Go up and down ramp leading with prosthesis c. Go up ramps leading with prosthesis, and down with sound leg d. Go up ramps leading with sound leg, and down with prosthesis |
d. Go up ramps leading with sound leg, and down with prosthesis
|
|
|
81. 2 part question: Approximately ____% of unilateral amputees will lose their other leg within____ years.
a. 5% a. 1 b. 10% b. 2 c. 20% c. 3 d. 30% d. 4 |
d. 30%
c. 3 |
|
|
82. What are the two most important goals for patients with bilateral hip disarticulations?
|
a. Teach sitting balance and safe transfers.
|
|
|
83. T/F-In the case of a bilateral hip amputee: after several months of rehab, if no success is attained, it may be deemed unrealistic to continue.
|
T
|
|
|
84. T/F- In the case of a bilateral hip amputee: It is common to make both prosthesis shorter, thus making the person shorter.
|
T
The prosthesis are made shorter, making the person shorter. This lowers the center of gravity making the patient more stable |
|
|
85. T/F- In the case of a bilateral hip amputee: Ramps are easier to walk up than stairs.
|
F
|
|
|
86. T/F-Bilateral below the Knee amputees that are totally independent in ambulation often do not need wheel chairs.
|
F
|
|
|
87. T/f-Regarding a bilateral LE amputation: Always a good idea to take a cane when outside to announce your disability to others.
|
T
|
|
|
88. T/F- It may be good to encourage bi lateral amputees to avoid participating is sports
|
F
|
|
|
89. T/F- It is advisable that bilateral amputees use a treadmill when they go running.
|
T
|
|
|
90. What does SACH stand for?
|
Solid Ankle Cushion Heel
|
|
|
91. How do you teach a patient to fall backwards?
|
a. Attempt to jack-knife forward at the waist so that the buttocks will strike the mat first, then roll backwards onto the rounded back and shoulders.
|
|
|
92. Name one position or technique you could use to prevent hip flexion contractures with a patient that has a transfemoral amputation
|
Prone lying
|
|
|
93. T/F- Walking with a prosthesis is more energy efficient that single limb ambulation with crutches
|
T
|
|
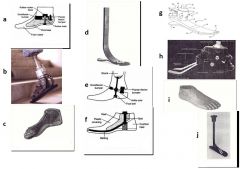
94. Name that foot
|
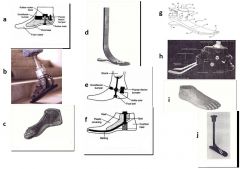
94. Name that foot…A= Multiple axis foot, B= STEN, C= SAFE, D= Flex foot, E= Single axis, F= SACH, G=Carbon copy II, H=College Park, I=Seattle, J= Springlite foot.
|

