![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a cartilage covering of superior/inferior vertebral body that provides and attachment for IVD?
|
Endplates
|
|
|
How many fused vertebrae are in the sacrum?
|
5
|
|
|
How many fused vertebrae are in the coccyx?
|
4
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the sacrum?
|
Provide strength and stability
Occasional lumarization |
|
|
Which ligaments in the lumbar region are extrasegmental?
|
Anterior Longitudinal
Posterior Longitudinal Supraspinal |
|
|
Which ligaments in the lumbar spine are intersegmental?
|
Flavum
Interspinal Intertransverse |
|
|
What motion does the ligamentum flavum resist?
|
Lamia separation
|
|
|
What motion does the interspinal ligament resist?
|
Separation of vertebral bodies
|
|
|
What motion does the intertransverse ligament prevent?
|
Separation of t-processes
|
|
|
What motion does the anterior longitudinal ligament prevent?
|
Excessive Hyperextension
|
|
|
What motion does the posterior longitudinal ligament prevent?
|
Excessive Flexion
|
|
|
What motion the supraspinal ligament prevent?
|
Excessive Flexion
|
|
|
What motion does the iliolumbar ligament resist?
|
Most motions
|
|
|
What are purposes of the thoracolumbar fascia?
|
Connect with abdominal fascia:
Direct connection from anterior to posterior Multiple bony and muscle attachments |
|
|
What vertebral level is approximately at the iliac crest?
|
L4-L5
|
|
|
What vertebral level is approximately at the PSIS?
|
S2
|
|
|
What types of joints are the interbody joints of the lumbar spine?
|
Symphyses
Amphiarthroses |
|
|
What type of joint is the Z joint?
|
Synovial Planar
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the interbody joint?
|
Minimal deformity/translation
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the anulus fibrosis?
|
Tolerate high tensile loads
|
|
|
What composes the nucleus pulposus?
|
Mucopolysaccaride of about 70-90% water.
The rest is collagen, elastic fibers, and proteins |
|
|
What is the purpose of the nucleus pulposus?
|
Important for nutrition
Compression tolerance in conjuction with annulus |
|
|
What can change the shape of the IVD?
|
Hydration
Reduce or increase loading |
|
|
The IVD has potential to ______ ________ __________ during compression
|
store elastic energy
|
|
|
During side bending, where is compression of the disc?
|
Ipsilateral
|
|
|
What is the importance of the IVD and rotation?
|
Only a portion of oblique fibers under tension-thus reduced ability to resist torsion
|
|
|
During normal lordosis, what is the approximate intradiscal pressure?
|
400 N
|
|
|
During sitting unsupported, has much can the intradiscal pressure in the lumbar spine increase?
|
200-300 N
|
|
|
What type of motion does the Z joint resist?
|
Shear forces
|
|
|
Stability in the lumbar spine is a combination of what?
|
Bony congruency/architecture
Muscle activity/motor control Ligamentous/passive stabilizers Intraabdominal pressure |
|
|
What are the osteokinematics of the lumbar spine?
|
Flexion: 50-60 degrees
Extension: 15-30 degrees Lateral flexion: 15-25 degrees Rotation: up to 16 degrees |
|
|
What is the open pack position of the lumbar spine?
|
Neutral
|
|
|
What is the closed pack position of the lumbar spine?
|
Full extension
|
|
|
What is the capsular patter of the lumbar spine?
|
Side flexion and rotation equally limited, then extension
|
|
|
What are normal endfeels of the lumbar spine?
|
Firm
|
|
|
What is joint coupling in the lumbar spine is the neutral or extended position?
|
Contralateral
|
|
|
What is joint coupling in the lumbar spine in the flexed position?
|
Ipsilateral
|
|
|
What are muscle functions in the lumbar spine?
|
Movement
Stability Posture |
|
|
What are the normal maximum forces in the lumbar spine?
|
Compression: 10 kN
Shear: 1000 N |
|
|
What can assist the stability of the lumbar spine?
|
Distribution of load appropriately
|
|
|
During walking, what is the load distribution of the lumbar spine?
|
Relatively low load (Compressive up to 2.5 times body weight)
Mild shear |
|
|
During bending, what is the load distribution of the lumbar spine?
|
With maintenance of lordorsis:
Improved muscle ability to resist shear and distribute forces appropriately |
|
|
During sitting, what does an increased flexion in the lumbar spine influence?
|
Increase compression
|
|
|
What are the complications with respect to forces and moments with a slouched sitting posture?
|
Increased torque, compression, and shear force
|
|
|
What are important in stability of the lumbar spine?
|
Co-contraction
Lumbodorsal fascia Intraabdominal pressure Posture |
|
|
How might abdominal bracing decrease injury to posterior structures?
|
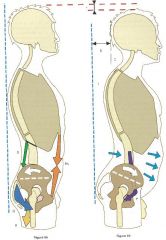
|
|
|
What is the main idea of the ball in a bowl model?
|
Useful for conceptualizing dynamic stability/instability
|
|
|
What exercises can help with spine stability?
|
Aerobic
Endurance with strength Core stability and abdominal bracing |
|
|
What are guidelines with developing lumbar exercises?
|
Start with motion
Strengthening Low load high rep Initial and maintenance Higher load lower rep to build bulk/power Curl ups Lateral stabilizers Extensors Dosing Daily preferably unless irritable Include cardio Be careful with positioning |
|
|
What are functions of the pelvic girdle?
|
Supports the weight of the body
Transmits ground forces upward to the vertebral column. Supports and protects pelvic viscera Muscle attachment Birth canal |
|
|
What is commonly known as the hip bone?
|
Os Coxae
|
|
|
What 3 bones compose the Os Coxa?
|
Ilium
Ischium Pubis |
|
|
The inlet superior of the pelvis oriented in which direction?
|
Vertically
|
|
|
The outlet inferior of the pelvis oriented in which direction?
|
Horizontally
|
|
|
What are the main bony landmarks of the ilium?
|
Iliac tuberosity
Auricular surface Iliac Crest Iliac fossa Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIS) Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) |
|
|
What are the main bony landmarks of the ischium?
|
Ischialbody
Ischialspine Ischialtuberosity Ramus |
|
|
What are the main bony landmarks of the sacrum and coccyx?
|
Base
Superior articularprocess Ala Foramina Auricular Surface Pelvic Surface |
|
|
What are main ligaments of the pelvis?
|
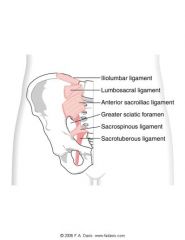
Anterior/ventral sacroiliac ligament
Posterior/dorsal sacroiliac ligament InterosseousSI ligament Sacrotuberousligament Sacrospinousligament Iliolumbarligament 2-3 bands (lower band “lumbosacralligament”) |
|
|
What is the lumbosacral angle?
|
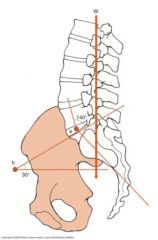
|
|
|
What influences the lumbosacral angle?
|
Anterior pelvic tilt increases the angle
Posterior pelvic tilt decreases the angle |
|
|
What are the two parts of the SI joint?
|
Synovial L-shaped
Fibrous Synarthrosis |
|
|
What are the key ligaments of the SI joint?
|
Ventral/dorsal SI
Interosseous SI |
|
|
What motions occur at the SI joint?
|
Nutation
Counternutation |
|
|
What are the arthrokinematics of the of the SI joint?
|
Rotation of either the sacrum on the ilium or vice versa
Base moves in opposite direction of apex Some translation accompanies rotation |
|
|
What are the two main ligaments of the pubic symphysis?
|
Superior pubic
Inferior pubic |
|
|
Why is the pubic symphysis important?
|
Balance of stability/mobility critical to the stability/mobility of the pelvis
|
|
|
Which muscles assist in anterior pelvic tilt?
|
Hip flexors
Back extensors |
|
|
Which muscles assist in posterior pelvic tilt?
|
Trunk flexors
Hip extensors |
|
|
Which muscles assist in lateral pelvic tilt?
|
Hip abductors
Lateral trunk flexors |
|
|
What are functions of the pelvic muscles?
|
Support for pelvic organs
Keep urogenitalorifices closed Unload other pelvic connective tissue Routine postural adjustments Support during increased intraabdominalpressure Control of functions such as micturition, defacation, sexual function, parturition |
|
|
What is the relative direction of the superior articular facet of the lumbar spine?
|
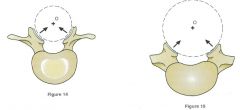
Facing medial like it would rotate around a cylinder
|
|
|
What are the extrasegmental ligaments of the lumbar spine?
|
Anterior Longitudinal
Posterior Longitudinal Supraspinal |
|
|
What are the intersegmental ligaments of the lumbar spine?
|
Ligamentum Flavum
Interspinal Intertransverse |
|
|
What motion does the iliolumbar ligament resist?
|
Most motions
|
|
|
What are implications of viscoelastic ligaments?
|
If I impart forces more quickly, the resistance is more stiff.
The time to return to original resting tension is usually slower than when it was stretched. |
|
|
What are implications to having a highly elastic ligamentum flavum?
|
It limits all sorts of motion, but still allows us to move and to be stable.
|
|
|
What are characteristics of the thoracolumbar fascia?
|
3 layers
Connect with abdominal fascia Multiple bony and muscle attachments |
|
|
What is the guideline to palpating L4-L5?
|
Iliac Crest
|
|
|
What is the guideline to palpating S2?
|
PSIS
|
|
|
What is the orientation of the fibers of the IVD in the lumbar spine?
|
Oblique orientation
|
|
|
What are characteristics of the IVD nucleus pulposus in the lumbar spine?
|
Mucopolysaccarideapprox 70-90% water
The rest is collagen, elastic fibers and proteins Important for nutrition Compression tolerance in conjunction with annulus |
|
|
What is the effect of hydration on the IVD?
|
Hydration can change the shape of the disc throughout the day-Change in height
|
|
|
What is a hoop stress?
|
The compression force on the disc actually creates a tension force
|
|
|
How is the lumbar IVD able to resist rotation?
|
Only a portion of oblique fibers under tension-thus reduced ability to resist torsion
|
|
|
What is the normal lordotic pressure in the lumbar disc?
|
400 N
|
|
|
What increases pressure in the lumbar disc?
|
Flexion
Increased muscle activity Lifting Sitting unsupported |
|
|
What is the innermost abdominal muscle?
|
Transverse Abdominis
|
|
|
What structure do the abs attach to that has an effect on the lumbar spine?
|
Thoracolumbar fascia
|
|
|
What motion does the rectus abdominis perform?
|
Trunk flexion
|
|
|
What does the quadratus lumborum perform?
|
Hiking the hip
|
|
|
Rotating to the right, was does the right facet joint do?
|
Gapping
|
|
|
How much load distribution is there in the lumbar spine in a neutral position?
|
400N
|
|
|
How much load distribution is there in the lumbar spine under max pressure?
|
10kN compression
1000 N shear |
|
|
What can assist the lumbar spine in stability?
|
Appropriately distributing loads
|
|
|
During flexion, what are the magnitudes of shear and compression forces in the lumbar spine?
|
1000 N shear
3000 N compression |

