![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 4 unique characteristics of muscle tissue?
|
Excitability
Contractility Elasticity Extensibility |
|
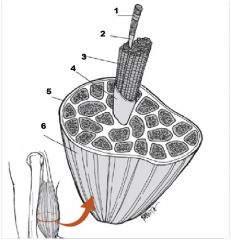
What is number 1?
|
Muscle Fiber
|
|
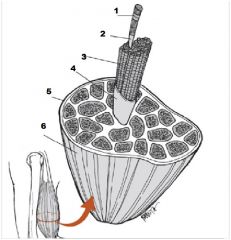
What us number 2?
|
Endomysium
|
|
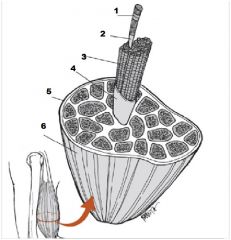
What is number 3?
|
Fascicle
|
|
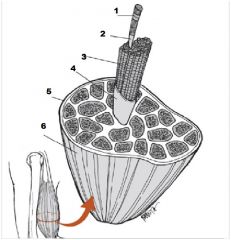
What is number 4?
|
Perimysium
|
|
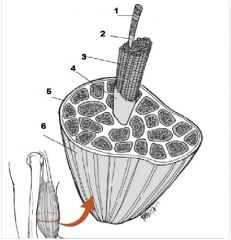
What is number 5?
|
Epimysium
|
|
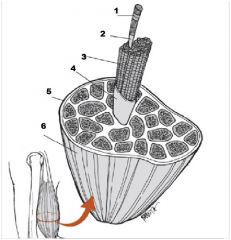
What is number 6?
|
Muscle
|
|
|
What is the innermost layer of connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber?
|
Endomysium
|
|
|
What connective tissue surrounds bundles of fascicles?
|
Perimysium
|
|
|
What is a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the whole skeletal muscle?
|
Epimysium
|
|
|
What is an expansive sheet of dense irregular connective tissue?
|
Deep Fascia
|
|
|
What is Synonymous with hypodermis, subcutaneous layer?
|
Superficial Fascia
|
|
|
What are the dark bands of a muscle called?
|
A Bands
|
|
|
What are the light bands of a muscle called?
|
I Bands
|
|
|
From z-disc to z-disc is called what?
|
Sarcomere
|
|
|
The neurons that stimulate muscle contraction are called __________.
|
Motor Neurons
|
|
|
What transmits a nerve impulse to a muscle fiber?
|
Axon
|
|
|
What is the sliding filament theory?
|
The thin filaments of actin slide over the myosin
|
|
|
What shortens during a muscle contraction?
|
Sarcomere
|
|
|
Each motor neuron has a __________ with each muscle fiber it controls
|
Neuromuscular Junction
|
|
|
A single motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates is called what?
|
Motor Unit
|
|
|
What is the all or none principle?
|
A muscle fiber either contracts completely or does not contract at all.
When a motor unit is stimulated, all its fibers contract at the same time |
|
|
What are the 3 types of muscles?
|
Slow Twitch
Intermediate Fast Twitch |
|
|
What are the 3 organizational patterns of muscle fascicles?
|
Circular
Parallel Pennate |
|
|
Muscle where all fibers are on the same side of the tendon
|
Unipennate
|
|
|
Muscles where muscle fibers are on both sides of the tendon
|
Bipennate
|
|
|
Muscle where the tendon extends into the muscle
|
Multipennate
|
|
|
What are two main factors that relate to a muscle's ability to create motion?
|
Length of Fibers
Length of Moment Arm |
|
|
The larger the moment the ______ amount of motion that is produced.
|
smaller
|
|
|
What are important factors related to muscle strength?
|
Muscle Size
Muscle Moment Arm Stretch Contraction Velocity Fiber Recruitment Fiber Types |
|
|
In vivo, where do we tend to function in the length-tension curve?
|
The middle part of the curve, or the middle part of our range.
|
|
|
What is the inability of a muscle that spans two or more joints to be stretched sufficiently to produce a full range of motion in all the joints simultaneously?
|
Passive Insufficiency
|
|
|
What is defined when a muscle reaches a point where it cannot shorten any farther it is has reached?
|
Active Insufficiency
|
|
|
What are important factors related to muscle strength?
|
Contraction Velocity
Fiber Recruitment Fiber Types |
|
|
What is defined when the length of the muscle does not change because the tension produced never exceeds the resistance (load)
|
Isometric
|
|
|
What is defined when tension is produced in response to a relatively constant load, and the muscle fibers change length, resulting in movement
|
Isotonic
|
|
|
What are the two types of isotonic contraction?
|
Concentric
Eccentric |
|
|
What is a contraction where the speed stays the same?
|
Isokinetic
|
|
|
What will potentially happen if a muscle is put on prolonged stretch?
|
Hypertrophy (Addition of sarcomeres)
|
|
|
What will potentially happen if a muscle is put on prolonged shortening?
|
Atrophy (Loss of sarcomeres)
|
|
|
What are different types of connective tissue?
|
Proper- loose, dense
Supporting- bone, cartilage Fluid- blood |
|
|
What are the components of connective tissue?
|
Cells- fibroblasts
Protein Fibers- Collagen, etc. Ground Substances- water, protein, other chemicals |
|
|
Tendon and ligaments are primary what type of connective tissue?
|
Dense Regular
|
|
|
What is the primary fiber in tendons and ligaments?
|
Type I Collagen
|
|
|
What are the 5 stages of response of tendons/ligaments to tension?
|
1. Straightening of collagen (toe region of Stress strain curve)
2.Elastic region-Partner discussion what this means 3.Plastic region-discuss what this means 4. Major failure 5. Rupture |
|
|
What are reasons for tendon failure?
|
Rupture
Enthesis Failure Avulsion |
|
|
What are different phases of healing?
|
Hemorrhagic (Day 1)
Inflammatory (Day 1-5) Proliferation (Through 2-3 weeks) Remodeling (Weeks-Months) |
|
|
What is the branch of anatomy related to the study of joints?
|
Arthrology
|
|
|
Structure of a joint determine both mobility and ________.
More Mobile= |
Stability
Less Stable |
|
|
When classifying joints, what two things are considered?
|
Type of connective tissue
Whether a space occurs |
|
|
What type of joint occurs where bones are held together by dense regular (fibrous) connective tissue?
|
Fibrous
|
|
|
What type of joint has:
1. a fluid-filled synovial cavity 2. bones are enclosed within a capsule 3. bones are joined by various ligaments |
Synovial
|
|
|
What type of joint is:
1. Immovable 2. Slightly movable 3. Freely movable |
1. Synarthrosis
2. Amphiarthrosis 3. Diarthrosis |
|
|
What are 2 types of synarthrotic joints?
|
Gomphoses
Sutures |
|
|
What is a syndesmoses joint classified as?
|
Amphiarthroses
|
|
|
What are two types of cartilaginous joints?
What is their classification? |
Synchondroses
Symphysis Amphiarthroses |
|
|
What are the parts of a synovial joint?
|
Bone
Joint Capsule Hyaline Cartilage Synovial Membrane Synovial Fluid Ligaments *Meniscus |
|
|
What describes movement between two bone around a joint axis?
|
Osteokinematics
|
|
|
What type of movement is often described in degrees of freedom (number of planes a movement can occur in)?
|
Planar movement
|
|
|
What is bony end feel?
|
Hard end
|
|
|
What is capsular end feel?
|
Firm, leather like limitation, and slight give
|
|
|
What is empty end feel?
|
Lack of mechanical constraint
Limited by pain |
|
|
What is a rebound movement, seen with torn cartilage, or some derangement of a joint?
|
Springy block
|
|
|
What is a reflex muscle spam during motion, common in acute injuries?
|
Muscle guarding
|
|
|
What are 3 types of movement of a joint?
|
Roll
Spin Glide |
|
|
When a concave joint surface moves, it is in the _______ direction as the body segment.
|
Same
|
|
|
When a convex joint surface moves, it is in the _______ direction as the body segment.
|
Opposite
|
|
|
When the moving joint is concave, roll and glide occur _______.
|
In the same direction
|
|
|
What does the pelvic girdle refer to?
|
Left and right coxae only
|
|
|
What is commonly refered to the innominate bone?
|
Hip
|
|
|
What are charcteristic of the true pelvis?
|
Lies inferior to the pelvic brim
Encloses the pelvic cavity and forms a deep bowl that contains the pelvic organs |
|
|
What are characteristics of the false pelvis?
|
Lies superior to the pelvic brim
Enclosed by the ala of the iliac bones Forms the inferior region of the abdominal cavity and houses the inferior abdominal organs |
|
|
What is coxa valga?
|
>125
|
|
|
What is coxa vara?
|
<125
|
|
|
What is angle of torsion?
|
Head and neck rotated outward from the shaft 15-25 degrees
|
|
|
What is femoral anteversion?
Femoral retroversion? |
Increased angle of torsion
Decreased angle of torsion |
|
|
What condition at the hip is associated with toe in?
|
Femoral Anteversion
|
|
|
What condition at the hip is associated with femoral retroversion?
|
Toe-out
|
|
|
What condition at the hip is associated with femoral retroversion?
|
Toe-out
|
|
|
What is the open pack position of the hip?
|
Slight flexion
Slight external rotation Slight abduction |
|
|
What is functional ROM for the following motions?
Flexion: ER: Abduction: |
Flexion: 120
ER: 20 Abduction: 0 |
|
|
Iliofemoral, pubofemoral, ischiofemoral, and ligamentum teres all prevent what motion?
|
Hyperextension
|
|
|
During single limb stance, how great is the abductor force? The joint reaction force?
|
Abductor: 2x body mass
Joint Reaction Force: 2.5x mass |
|
|
During Gait, how great is the JRF and MPa forces?
|
JRF: 2-3x body weight
MPa forces: 4-6 |
|
|
Congenital hip dislocation (dysplasia) is associated with what condition?
|
Shallow acetabulum
|
|
|
Leg-Calve-Perthes disease (coxa plana) is associated with what condition?
|
Necrosis of femoral head
|

