![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition of isotropic:
|
handle stress the same way regardless of direction/orientation
|
|
|
Definition of anisotropic:
|
different properties related to stress depending on direction; potential multiple Young’s Moduli
|
|
|
Definition of orthotropic:
|
generally means that all properties are constant within a certain plane
|
|
|
What is an osteocyte?
|
Bone cell
|
|
|
What is an osteoblast?
|
Produces new bone
|
|
|
What is an osteoclast?
|
Breaks bone down and absorbs bone
|
|
|
What is an osteoprogenitor?
|
Derived from mesenchyme which produce other stem cell
|
|
|
What percent of bone tissue is collagen?
|
40%
|
|
|
Which type of bone hasn't completely mineralized yet?
|
Woven
|
|
|
What type of bone has a hard outer shell?
|
Cortical/Compact
|
|
|
What type of bone is porous and spongy?
|
Cancellous Bone
|
|
|
What is the metaphysis?
|
In long bones, the part and the ends that flare by the diaphysis
|
|
|
What is the endosteum?
|
Lines of the medullary canal
|
|
|
What is the periosteum?
|
Outermost covering of the bone
|
|
|
What is the diaphysis?
|
The main shaft of a bone; the center of the medullary canal
|
|
|
What are the 5 types of bones?
|
Long, Short, Flat, Sesamoid, Irregular
|
|
|
Which are example of long bones?
|
Femur, Humerus, Tibia
|
|
|
Which are examples of short bones?
|
Tarsals, Carpals
|
|
|
Which are examples of flat bones?
|
Ribs, Scapula, Skull
|
|
|
What is biomechanics?
|
Response of biological systems to mechanical forces
|
|
|
What is kinematics?
|
What happens when I do something to someone; without regard to forces that cause motion
|
|
|
What is kinetics?
|
Brings biomechanics and kinematics together
|
|
|
What is the minimum effective strain?
|
must have 10% of that stress needed to break the bone, as a stimulus to get bone to remodel/adapt
|
|
|
What are examples of fundamental measurement?
|
Length, mass, time, and temperature
|
|
|
What type of measurement is magnitude only?
|
Scalar
|
|
|
What type of measurement involves magnitude and orientation?
|
Vector
|
|
|
What is the push or pull which results in physical contact between two objects?
|
Force
|
|
|
What is a vector that is perpendicular to both the force and distance vectors?
|
Moment
|
|
|
What is the definition of force couple?
|
Whe the force and moment arm are in the same plane but in opposite direction
|
|
|
What is the distance perpendicular to the force vector?
|
Moment Arm
|
|
|
Which plane divides the body into left and right halves?
|
Sagittal
|
|
|
Which plane divides the body into front and back halves?
|
Coronal/Frontal
|
|
|
Which plane divides the body into top and bottom halves?
|
Transverse/Axial
|
|
|
What are the 3 main points when considering muscles forces?
|
Orientation, magnitude, and point of application
|
|
|
A pure force couple occurs only in which type of motion?
|
Rotational
|
|
|
What is the first law of newton?
|
An object remains at rest (or continues moving at constant velocity) unless acted upon by an unbalances external force
|
|
|
What is the second law of newton?
|
If there is an unbalanced force acting on an object, it produces an acceleration in the direction of the force, directly proportional to the force (f=ma)
|
|
|
What is the third law of newton?
|
For every action there is a reaction of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction
|
|
|
The mechanical advantage is the ratio of what?
|
Mam/Mar (muscles/resistive)
|
|
|
The center of mass in most adults is where?
|
S2
|
|
|
When considering base of support, which is important?
|
Side to side and front to back
|
|
|
What type of property depends on the amount of material?
|
Extensive
|
|
|
What are examples of extensive properties?
|
Mass, Volume, Internal Energy
|
|
|
What type of property doesn't depend on the amount of material?
|
Intensive
|
|
|
What are examples of intensive properties?
|
Density, Strength
|
|
|
What is the definition of stress?
|
Amount of force per given area
|
|
|
What is the definition of strain?
|
A normalized stretch or displacement of an object
|
|
|
Which type of force is linear motion?
|
Translatory
|
|
|
Which type of force is angular?
|
Rotational
|
|
|
Young's Modulus =
|
Slope of the line
|
|
|
Modulus of elasticity =
|
Stiffness
|
|
|
What is Poisson's Ratio?
|
Ratio of axial strain to lateral strain
|
|
|
What is the definition of work?
|
The force required to move an object a certain distance (Fxd)
|
|
|
What is the definition of power?
|
The rate that work is being done (work/time)
|
|
|
The ability of an object to permanently change shapes is what?
|
Plasticity
|
|
|
What is the ultimate tensile strength?
|
How strong the bone is before it breaks
|
|
|
_________ is something that will only change shape with a lot of pressure and then immediately breaks
|
Brittle
|
|
|
What is the definition of the ductile?
|
Ability to change shape fairly easy and allow for a change of length
|
|
|
What is a fatigue failure of a bone due to repetitive loading?
|
Stress Fracture
|
|
|
What is the ability to withstand further failure if a crack or flaw is already present?
|
Fracture Toughness
|
|
|
What is defined as: if loading on a particular bone increases, the bone will remodel to better deal with the heavier loads
|
Wolff's Law
|
|
|
Which are examples of stimuli for remodeling bone?
|
Magnitude of strain, rate of strain, distribution of strain, low serum calcium levels
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
|
Hyaline, Fibro, Elastic
|
|
|
What are the 3 main functions of cartilage?
|
Support soft tissue, Provide gliding surface at articulations where two bones meet, and Provide model for formation of most bones in the body
|
|
|
What is the first line of defense against loads?
|
Articular Cartilage
|
|
|
What makes up the extracellular matrix?
|
Collagen and Proteoglycans
|
|
|
What percent of articular cartilage is collagen?
|
70% dry weight (10-30% wet weight)
|
|
|
What percent of articular cartilage is proteoglycans?
|
30% dry weight
|
|
|
What percent of articular cartilage is water?
|
60-85% wet weight
|
|
|
What percent of articular cartilage are chondrocytes?
|
10% wet weight
|
|
|
Collagen is good at resisting _________, while proteoglycans are good at resisting __________.
|
tension, compression
|
|
|
What are the main functions of articular cartilage?
|
Allows nearly frictionless motion at joint, Distributes loads over a large area, Minimizes contact stresses, Dissipates energy
|
|
|
What is creep?
|
Deformation over time with a constant load
|
|
|
What is stress relaxation?
|
Holding stress for a period of time, the stress decreases because the object is stretching
|
|
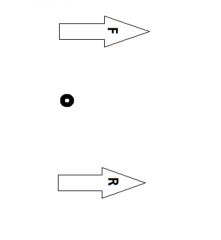
Which levers is this?
|
Type 1
|
|
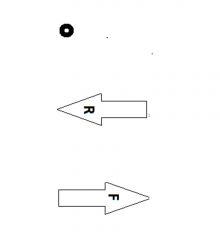
Which lever is this?
|
Type 2
|
|
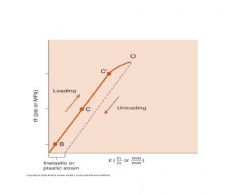
What is C'?
|
C’ is the yield point, or the point at which the stress begins to deform the object
|
|
|
What occurs at week 1 of the healing process?
|
Hematoma or Inflammation
|
|
|
What occurs at week 2-3 of the healing process?
|
Soft Callus
|
|
|
What occurs at week 4-16 of the healing process?
|
Hard Callus
|
|
|
What occurs at week 17+ of the healing process?
|
Remodeling
|
|
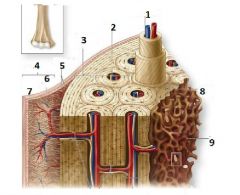
What is number 1?
|
Central Canal
|
|
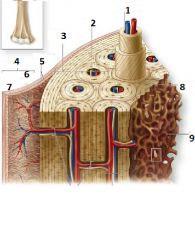
What is number 3?
|
External circumferential lamellae
|
|
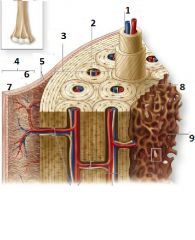
What is number 6?
|
Cellular Layer
|
|
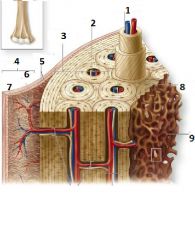
What is number 7?
|
Fibrous Layer
|
|
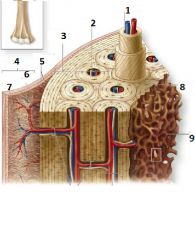
What is number 8?
|
Inerstial Lamellae
|
|
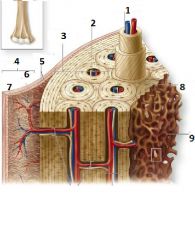
What is number 9?
|
Trabeculae of spongy bone
|

