![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why do Research?
|
To establish a body of knowledge for a profession
To determine the efficacy of programs or treatments To improve patient/client care To make more intelligent, logical, sound clinical decisions “Outcomes” Research “Evidence-Based Practice” |
|
|
What is EBP?
|
EBP is the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values
The science of the art of medicine |
|
|
What is defined as beliefs, judgments, and intuitions that cannot be explained?
|
Art
|
|
|
What is defined as knowledge, logic, and prior experience that can be explained?
|
Science
|
|
|
What is best research evidence?
|
Clinically relevant research, often from patient-centered clinical research into the accuracy and precision of diagnostic tests, the power of prognostic markers, and the efficacy and safety of therapeutic, rehabilitative, and preventive regimens
|
|
|
What is clinical expertise?
|
Ability to use clinical skills and past experience to rapidly identify each patient’s unique health state and diagnosis, their individual risks and benefits of potential interventions, and their personal values and expectations.
|
|
|
What patient values?
|
Unique preferences, concerns and expectations each patient brings to a clinical encounter and which must be integrated into clinical decisions if they are to serve the patient
|
|
|
How do you evaluate the evidence using EBP?
|
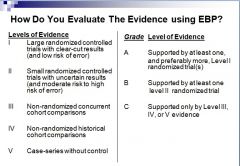
|
|
|
What are 5 reasons why we need EBP?
|
1. New evidence is being generated
When known and understood, this evidence creates frequent & major changes in patient care 2. We need the new evidence daily, but fail to get it 3. Our up-to-date knowledge and clinical performance deteriorate with time 4. Evidence suggests traditional CME DOESN’T improve our clinical performance 5. Evidence suggests that 3 EBM strategies CAN improve our clinical performance |
|
|
What is the definition of research?
|
Organized, systemic investigation of a question
|
|
|
What are 5 approaches for clinical decision making and research?
|
1. Tradition
2. Authority 3. Trial and Error 4. Logical Reasoning 5. Scientific Method |
|
|
What type of research generally has very small sample sizes and is focused on why or how?
|
Qualitative
|
|
|
What are two types of quantitative research?
|
Experimental
Non-experimental |
|
|
What are ethical principles that guide research?
|
Principle of non-maleficence
Principle of beneficence Principle of utility Principle of autonomy |
|
|
What should be in a well-constructed informed consent?
|
Special consideration given to vulnerable populations
Purpose & Description of study Informed if alternative treatments are available Description of foreseeable risks or discomforts Management/Compensation of Injury Potential benefits of participation Confidentiality and anonymity Understood (language and reading level) Researcher must be able to answer questions at any time Consent must be voluntary and free to withdraw without penalty |
|
|
What are components of the research process?
|
Theory
Identify the research question Literature review Revise research question Hypothesis Design Study IRB approval Data collection Analyze data Draw Conclusions from Study/Report findings |
|
|
What are the purposes of a theory?
|
Summarize
Predict Develop new knowledge |
|
|
What is the purpose of the literature review?
|
Helps provide theoretical framework for your study
Justify your study Provides an understanding of what already has been done (Strengths & Weaknesses of the studies) Will help inform your research design Help to establish research hypothesis Provide information regarding potential for successful outcomes, assumptions and limitations |
|
|
What are key points for literature review?
|
Begin broadly, then focus
In general, peer-reviewed manuscripts (original reference) of actual study more powerful than review papers or articles written in textbook chapter References generally should be in last 10 years, preferably last 5 years Should find “landmark” papers Okay if >10 years |
|
|
What does the acronym "finer" stand for?
|
Feasible
Interesting Novel Ethical Relevant |
|
|
What are different types of research questions?
|
Descriptive
Difference Relationship Risk |
|
|
What is defined as assigning numerals to objects to represent quantities of characteristics according to certain rules?
|
Measurement
|
|
|
What is an observable and measurable characteristic or even that can assume a range of values on some dimension that can be manipulated?
|
Variable
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of variables?
|
Independent
Dependent Confounding |
|
|
What does the acronym NOIR stand for?
|
Nominal- categorizing group data (e.g. gender, name of states)
Ordinal- add magnitude, ranking order (e.g. MMT, professor: associate) Interval-Increments, zero is arbitrary Ratio- includes levels of interval but also includes zero (e.g. kelvin scale of temperature) |
|
|
What are the two types of reliability?
|
Intratester
Intertester |
|
|
Which errors are "better"?
|
Systemic
|
|
|
What is the relationship between validity and reliability?
|
+ Reliability + Validity
+ Reliability - Validity - Reliability - Validity |
|
|
What are the types of validity?
|
Face
Content Criterion Concurrently Predictive Construct |
|
|
What is defined as a statement of the relationship between dependent and independent variables in order to test a construct and/or questions derived from a theory; specifying a specific population
|
Hypothesis
|
|
|
What is commonly known as the statistical hypothesis?
Alternative hypothesis? |
Null
Research |
|
|
A significant value would reflect a p value of what?
|
0.05
|
|
|
A type I error has what characteristics?
|
Null is true and you reject the null
Type I error= alpha level of stats significance |
|
|
A type II error has what characteristics?
|
Failing to reject the null when it is actually false
Want a power of 0.80 or beta=0.20 which means you'll reject 80% |
|
|
What is the purpose of the experimental design?
|
To rule out rival hypotheses as possible explanations for the observed response through the researcher’s manipulation and control of variables and measurements
|
|
|
What are 3 essential features to a true experiment?
|
Random Assignment
Control Group Researcher has control of independent variables |
|
|
What are 4 essential concepts of repeated measures?
|
Stability of Measures
Trend Magnitude Slope of trend |
|
|
What are characteristics of quasi-experimental designs?
|
Doesn't use random assignment for comparisons
May or may not use separate control group May involve non-equivalent groups Conclusions must take into account research design |
|
|
What is defined as the study of the distribution and determinants of diseases and injuries in human populations?
|
Epidemiology
|
|
|
What is defined as a study (usually a health study) conducted at a single point in time by taking a “slice” (a cross section) of a population at a particular time. All measures made at once.
|
Epidemiology Cross-sectional study
|
|
|
What are two major classifications of disease frequency?
|
Prevalence
Incidence |
|
|
What is defined as the = proportion of individuals in a population who have the disease at a specific instant and provides and estimate of the probability (risk) that an individual will be ill (or particular disorder) at a point in time
|
Prevalence
|
|
|
What are designs are studies that allow testing of hypotheses about the association of specific risk factors and outcomes?
|
Observational analytic designs
|
|
|
What is a study in which a subgroup of a population that is exposed to a risk factor and another subgroup that is unexposed to the risk factor are followed forward in time and the incidence rate of the disease in each group is determined.
|
Epidemiology: Cohort (Prospective) Study
|
|
|
What is : a study that starts with the identification of diseased and appropriate controls, then retrospectively assesses exposure to the risk factor/predictor?
|
Epidemiology: Case-control study
|
|
|
What are the comparison between prospective and retrospective studies?
|

|
|
|
What are the comparisons between retrospective cohort vs. case control?
|

|
|
|
How do you set up a 2x2 table?
|
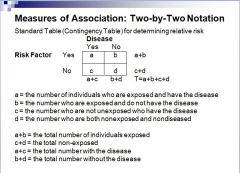
|
|
|
What estimates the magnitude of an association between the exposure and disease and indicates the likelihood of developing the disease in the exposed group relative to those who are not exposed?
|
Relative
|
|
|
Relative risk is associated with ________ while odd ratio is associated with _________.
|
Cohort
Case-control |
|
|
What represents the range within which the true magnitude of effect lies in the population with a certain degree of assurance?
|
Confidence interval
|
|
|
What are the 3 main types of biases?
|
Systemic
Selection Information |
|
|
What is an “extraneous or third” variable that is (1) associated with the exposure, (2) is a risk factor for the disease independent of the exposure, and (3) is not part of the casual link between the exposure and the disease?
|
Confounder
|
|
|
What are the 5 causation criteria?
|
Strength of association: size of the relative risk found. The greater the relative risk the more convincing it is that the association is causal. If a dose-response model can be demonstrated, the likelihood the exposure is causal increases.
Consistency of association: different studies result in same association Specificity of association: measures the degree to which one particular exposure produces one specific disease. Temporal relationship: means exposure to the factor must precede development of disease. Biological plausibility: means coherence with the current body of biological knowledge, which may have been established in animal models. |
|
|
What is the proportion or percentage of individuals with a particular diagnosis who are correctly identified as positive by the test?
|
Sensitivity
|
|
|
What is the proportion or percentage of individuals without a particular diagnosis who are correctly identified as negative by the test?
|
Specificity
|
|
|
What is an example of sensitivity and specificity?
|
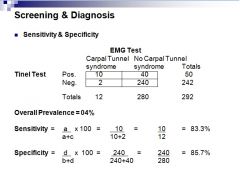
|
|
|
What is the proportion or percentage of individuals identified by the test as positive who actually have the diagnosis?
|
Positive Predictive Value
|
|
|
What is the proportion or percentage of individuals identified by the test as negative who actually do not have the disease?
|
Negative Predictive Value
|
|
|
What is defined as the truthfulness of a study as a whole?
|
Internal Validity
|
|
|
What are characteristics a control?
|
Task of ensuring constancy in the research environment
Task of controlling extraneous variables that can affect the outcome of the study Concept of Internal Validity Concept of External Validity |
|
|
What are threats to internal validity?
|
Chance
Bias Research Design Measurement Threats Temporal Threats |
|
|
What is defined as The extent to which the results of a study can be generalized beyond the internal specifications of the study?
|
External Validity
|
|
|
What are characteristics of external validity?
|
The extent to which the results of a study can be generalized beyond the internal specifications of the study
Concerned with usefulness of the information Increased by Random selection of subjects Good internal validity is a perquisite before good external validity |
|
|
What are threats to external validity?
|
Sampling Threats
Design Measurement/Treatment Sampling Bias Research Design Measurement |

