![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
neurobiology of depression: reduced ____ volume commong among depressed patients and directly correlates w/ freuqnecy and length of depressive episodes |
hippocampal |
|
|
|
neurobiology of depression: ___ & ___ areas demonstrate differential metabolic rates, reflecting aberrant neural activity thought to contribute to depressive symptomatology |
prefrontal; limbic |
|
|
|
Neurobiology of depression: reduced GM volume noted in the ___-___ regions and functional alterations in the temporal regions and cerebellym in patients w/ MDD |
parietal; temporal |
|
|
|
The Monoamine Hypothesis: The structure and function of these brain regions are modulated by ___ ___ |
monoaminergic neurotransmission |
|
|
|
Monoaminergic neurotransmission is the neural basis for what 5 things? |
Mood, reward, pleasure, motivation, and executive functions |
|
|
|
The Monoamine hypothesis: 3 neurotransmitters associated w/ the hypothesis? |
serotnonin, norepinephrine, dopamine |
|
|
|
What neurotransmitters associated with motivation and deficits in EF? |
DA and NE |
|
|
|
Impaired neurotransmitter ___ associated with anhedonia, guilt, and similar negative affects of depression |
5HT (serotonin) |
|
|
|
Serotonin and norepinephrine have descending ___ pathways. |
Spinal |
|
|
|
Descending spinal pathways of 5HT and NE mediate ___ and related ___ sx. |
Physical fatigue; somatic |
|
|
|
What 3 behavioral sxs is serotonin involved in? |
appetite & weight changes; guilt and feelings of worthlessness; SI |
|
|
|
What 3 things are dopamine and norepinephrine involved in? |
apathy, EF deficits, fatigue |
|
|
|
What 3 sxs are serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine involved in? |
depressed mood, sleep disturbances, psychomotor disturbances |
|
|
|
6 types of SSRIs? |
Citalopram, Escitalopram, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxemine, Paroxetine, Sertraline |
Consumer Electrical Show for Final Fantasy People |
|
|
SSRI: SSRI works by preventing the reuptake of serotnin back into the ___ nerve. This results in ___ sertonin being available in the synapse and thus an amplified transmission |
presynaptic; more |
|
|
|
The action of antidepressants in neurotransmission is almost ___, but clinical response is usually more gradual. Patient's may see clinical improvements witin ___ weeks, with further improvements in symptoms over several weeks |
immediate; 2 |
|
|
|
Common side effects of SSRIs: 4 main areas? |
Gastrointestinal, psychomotor agitation, sleep changes, sexual side effects |
|
|
|
SSRI common side effects for gastrointestinal? Sleep? psychomotor agitation/retardation? |
nausea, vomiting, indigestion, diarrhea; insomnia or fatigue; jitteriness, nervouness, excessive sweating, headaches |
|
|
|
SSRI common side effects for sexual side effects? |
decreased libido, ejaculatory disturbance, ED, difficulty achieving orgasm. |
|
|
|
SSRIs can trigger a ___ episode in patients with bipolar disorder |
manic |
|
|
|
2 other adverse reactions to SSRI? |
Serotonin syndrome; Syndrome of inappropriate antiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) |
|
|
|
serotonin syndrome: always a risk when multiple ___ medications are combined |
serotonergic |
|
|
|
Serotonin syndrome: occurs due to ___ serotonin in CNS |
excessive |
|
|
|
serotonin syndrome: can be ___-___; must STOP offending medications immediately and go to ED |
life-threatening |
|
|
|
Symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome: 7 |
lethargy, confusion, restlessness, flushing, profuse sweating, tremor, and uncontrollable muscular twitching/ jerking |
Lee Could Really Flex Strong Tree Tops |
|
|
What happens if sertonin syndrome is untreated? 7 step process? |
elevated temperature and blood pressure, excessive muscle tension, muscle breakdown, kidney failure, coma, death |
Tell BP not to be Tense, can lead to muscle tension, breakdown, KF, coma, and death |
|
|
SIADH: what are the 5 steps? |
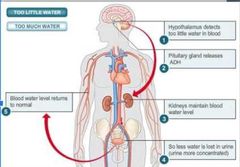
|
|
|
|
SIADH: Antiduetic hormone is released by the ___ and stored where? |
hypothalamus, posterior pituitary |
|
|
|
When is ADH released? |
Changes in blood volume (dehydration) |
|
|
|
What does ADH react on? |
Kidneys, leads to retain/reabsorb more water. |
|
|
|
When blood volume returns to equilibirium, this is sensed by the ___, which then decreases secretion of ADH |
hypothalamus |
|
|
|
SIADH: ___ and other meds can induce excessive release of ADH leading to excessive reabsorption and rention of water by the kidneys |
citalopram |
|
|
|
Excessive release od ADH can lead to higher blood volume (___) |
hypervolemia |
|
|
|
SIADH: having excess water can also lead to a dilutional lowering of the blood's volume concentration (___). |
hypoatremia |
|
|
|
SIADH: sxs associated w/ mild vs. severe hypoatremia? |
mild: loss of appetite, headache, nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, fatigue, cramps; severe: irritability, restlessness, confusions, seizures, LOC, coma, death |
|
|
|
Hypoatremia signs and sxs? |

|
SALTLOSS |
|
|
SSRIs: if discontinuing, the medication should NOT be stopped abruptly, as this will result in ____ ___ |
discontinuation syndrome |
|
|
|
Withdrawals sxs from SSRIs |
headaches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, insomnia, tremors, paresthesia |
HINT, it's not DVP |
|
|
antidepressants may increase risk SI and behavior in children and adolescnce |
SI |
|
|
|
SSRIs: Babies exposed to SSRI antidepressants late in ___ trimester of pregnancy may develop complications after birth. What sxs affected by it? |
third; respiratory distress, cyanosis (bluish skin tone from lack of oxygen), irritability, tremors, constant crying, feeding difficultty). |
|
|
|
SSRIs w/ pregnancy and breast feeding: may be caused by toxicity of the antidepressant or may be a manifestation of ___ sxs following materal exposure in utero |
discontinuation |
|
|
|
SSRIs pregnancy/breast feeding: SSRIs pass into ___ ___, |
breast milk, if patient cannot stop emdication, breast-feeding should not be started |
|
|
|
SSRIS: potential drug interactions: ___ and the antibiotic ___ are contraindicated |
MAOIs; linezolide |
|
|
|
The ____ actions of MAOIs and the antibiotic linezolide greatly increase the risk of what? |
serotonergic; serotonin syndrome |
|
|
|
How long does washout period last for potential drug interaction |
14 |
|
|
|
What are other sertonergic drugs that may interaction w/ SSRIs? |
triptans used for migraines, tramadol, tricyclics |
Mr. Triple T |
|
|
Citalopram: Brand name? |
Celexa |
|
|
|
Citalopram FDA approved for ___ |
depression |
|
|
|
Off-label use Citalopram for what? 6 dxs |
OCD, panic dx, GAD, SAD, PTSD, premenstrual dysphoric dx |
|
|
|
potential drug interactions of citalopram? (3) |
oral antifungals; anti-HIV drugs, some antibiotics |
|
|
|
citalopram metabolized in the ___; dose may need to be decreased to prevent ___ |
liver; toxicity |
|
|
|
citalopram: safer than ___ & ___. (TRUE FOR ALL SSRIs) |
tricyclics and MAOIs. |
|
|
|
fatalities are ___ w/ SSRIs, most cases of fatalaties result from combining w/ other drugs. Effects of overdose depends on ___. TRUE FOR ALL SSRIs |
rare; amount |
|
|
|
___ is purified form of citalopram (celexa) |
escitalopram |
|
|
|
Escitalopram brand name? |
Lexapro? |
|
|
|
Escitalopram FDA approved what what? |
Depression and Anxiety |
|
|
|
Offlabel use of escitalopram? 5 dx |
OCD, Panic dx, SAD, PTSD, premenstrual dysphoric dx |
|
|
|
escitalopram; approved for what special group / age? |
children, ages 12 - 17 |
|
|
|
Fluoxetine: Brand names? (3) |
Prozac, Prozac Weekly, and Sarafem |
|
|
|
Fluoxetine FDA indicated for what? 6 dx |
depression, OCD, panic dx, eating dx (bulimia), premenstrual dysphoric dx, depressive episodes w/ bipolar I dx |
|
|
|
Off-label use for fluoxetine: 5 dx |
anxiety dxs, PTSD, fibromyalgia, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic nerve pain |
|
|
|
Side effects of fluoxetine? |
decreases appetite, may led to weight loss |
|
|
|
Fluoxetine is one of the more ___ SSRIs |
activating |
|
|
|
4 medications that can interfere with breakdown of fluoxetine in the liver? |
Bupropion, duloxetine, quinidine, and cimetidine |
|
|
|
Fluoxetine can also inhibit the metabolism of what other 3 drugs? |
antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, beta-blockers |
|
|
|
Fluoxetine has a ___duration of action; an overdose may involve ___ serious complications than with other SSRIs |
long; more |
|
|
|
Sxs of fluoxetine overdose? |
somnolence, confusion, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, and seizures. In severe cases, serotonin syndrome, mania, arrhythmia, low blood pressure, elevated temperature, and coma |
|
|
|
FDA approval for Fluvoxemine? |
OCD |
|
|
|
Off-label use of Fluvoxemine? |
depressive dx, panic dx, anxiety dx, PTSD, and eating disorders (bulimia) |
|
|
|
Brand name for Fluvoxemine? |
Luvox |
|
|
|
Fluvoxemine can inhibit breakdowns of what 7 other medications? |
tricyclic antidepressants, clozapine, theophylline, propranolol, alprazolam, diazepam, and warfarin |
|
|
|
Paroxetine brand names (4) |
Paxil, Paxil CR, Brisdelle, Pexeva |
|
|
|
What is Paroxetine FDA approved for (6)? |
MDD, OCD, panic dx, PTSD, premestrual dysphoric dx, and SAD |
|
|
|
Off-label use for Paroxetine? |
OCD and Anxiety dx in peds; aggression after TBI |
|
|
|
Paroxetine is one of the more ___ SSRIs. |
activating |
|
|
|
Use of paroxetine in first trimester of pregnancy associated with increased risk of what? |
Teratogenicity (congenital malformations) |
|
|
|
Paroxetine w/ other drug metabolisms? (4) |
tricyclic antidepressants, antiarrhytmic drugs, antipsychotics, beta-blockers |
|
|
|
Sertraline brand name? |
Zoloft |
|
|
|
Sertraline FDA approved for what 6 things? |
Depression, OCD, SAD, panic dx, PTSD, premenstrual dysphoric dx |
|
|
|
sertraline is approved for ___ in children 6 years or older |
OCD |
|
|
|
Off-label use of sertraline? (4) |
GAD, aggression in TBI, smoking cessation, children w/ depression |
|
|
|
Sertraline: patients who are taking what may be predisposed to risk of bleeding? |
Warfarin (Coumadin) |
|
|
|
3 broad categories of Mixed Action Antidepressants? |
SNRIs (Serotonin, Norepinephrine, Reuptake Inhibitors), Atypical Agents, and Serotonin Modulators |
|
|
|
4 types of SNRIs? |
Desvenlafaxine, Duloxetine, Levomilnacipran, Venlafaxine |
|
|
|
2 types of atypical agents? |
bupropion; mirtazapine |
|
|
|
3 types of serotonin modulators? |
trazadone; vilazodone; vortioxetine |
|
|
|
SNRIs: work by preventuing reuptake of ____ & ___ back into the presynaptic nerve |
serotnin; norepinephrine |
|
|
|
SNRIs: this results in more serotonin and norepinephrine being available in the synapse and thus an ___ transmission |
amplified |
|
|
|
Babies exposed to SNRIs late in the ___ trimester may develop complications at birth |
third |
|
|
|
Drug interactions: ____ and the antibiotic ___ are CONTRAINDICATED |
MAIOs and linezolide |
|

