![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Primary and secondary data |
Primary - data collected by yourself ✅ authentic ❌ time consuming Secondary - data collected by someone else ✅ easily accessible ❌ May be lacking valuable information |
|
|
Levels of measurement |
Nominal - frequency count for distinct categories (fail/pass a test, smokers/non smokers) Ordinal - ordered in some way like a scale rating (1-10) Interval data - numerical scale, where each difference between units is equal |
|
|
Measures of central tendency |
Mean - statistical average ✅ most sensitive as includes all scores/values ❌ easily distorted by extreme values Median - middle value ✅ not affected by extreme values ❌ not as sensitive as mean Mode - most often ✅ easiest measure to calculate and unaffected by extremes ❌ crude measure and can be unrepresentative |
|
|
Measures of dispersion |
Range - difference between highest and lowest values ✅ easiest to calculate ❌ only two extremes Standard deviation - statistical measure of how all values differ from the mean Large SD = lots of variation Small SD = not much variation ✅ precise measure ❌ doesn’t tell you full range and can be effected by extreme scores |
|
|
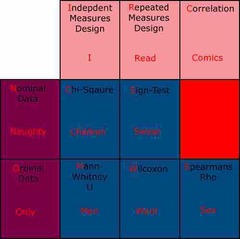
Inferential statistics |
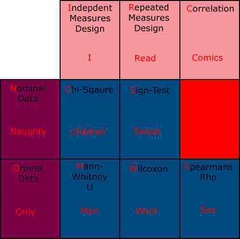
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Content analysis |
Indirect observation using catalogues to quantify the data Comes up with aim/hypothesis Select sample for content analysis (eg type of book) Create coding units of behaviours Researcher carefully goes through sample and coding unit marked down Total number of each coding unit counted |
|
|
Evaluation of content analysis |
✅ statistical analysis of data becomes possible ❌ can be argued to be reductionist ❌ subjective opinions may influence content analysis |
|
|
Thematic analysis |
Analysing patterns that occur in qualitative data Familiarise yourself with the data Produce coding units Look for emerging themes Define and name each desperate theme Write up the report |
|
|
Content VS Thematic analysis |
Content = converting from quantitative, thematic doesn’t Thematic = Themes ‘emerge’ whereas codes are predetermined in content |

