![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Coding in STM and LTM |
Baddeley - acoustically similar and semantically similar word lists STM was acoustic LTM semantic |
|
|
Capacity of STM |
Jacobs - ppts repeats digit lists 9.3 correct numbers 7.3 letters Miller - observations of everyday practice - many 7s Capacity of STM is 7+-2 items |
|
|
Duration of STM |
Peterson *2 Trigram then counting back from number After 18 second interval recall fell to 3% STM without rehearsal is 18 to 30 seconds |
|
|
Duration of LTM |
Bahrick et Al - 392 Americans aged 17 to 74 Recognition test of yearbook photos Free recall of names Ppts 70% accurate after 48 years |
|
|
Multi-store model |
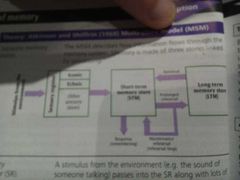
|
|
|
Evaluate Multi-store model |
Strength - research support Baddeley's coding research clearly shows the different stores through the different coding Limitation - more types of STM KF could recall written info not echoic Limitation - over simplifies LTM Evidenc eto show different types - episodic, semantic and procedural |
|
|
Episodic memory |
Time stamped events Consiscious effort needed for recall |
|
|
Semantic memory |
Knowledge of concepts and objects |
|
|
Procedural memory |
How to perform and action. Hard to explain with forced recall |
|
|
Working memory model |
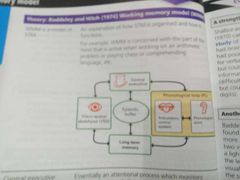
|
|
|
Evaluate the working memory model |
Strength - KF supports separate STM stores Strength - dual task experiments Baddeley found ppts to have more difficulties doing 2 visual task than 1 visual 1 verbal Strength - brain scans Activity in the prefrontal cortex when using the central executive Activity increased with task difficulty |
|
|
Proactive interference |
When and older memory interrupts a new one |
|
|
Retroactive interference |
When a new memory affects an old one |
|
|
Describe McGeoch and McDonald's 1931 similarity study |
Ppts asked to learn a word list to 100% then given another Synonyms, antonyms, unrelated, trigrams, 3digit numbers, no new list Worst recall with most similar material (synonyms) Show that interference strongest with similar memories |
|
|
Evaluated McGeoch and McDonald's 1931 study |
Limitation - artificial materials Not realistic so harder to generalise Limitation - time allowed between learning Research reduces the experience to very short time Not realistic so hard to generalise Limitation - affects overcome with cues When lists were organised into topics and topic names given recall was much higher Therefore using cues can overcome interference |
|
|
Encoding specificity principle |
Tulving suggested that cues present at encoding will help with retrieval if also present |
|
|
Describe Godden and Baddeley's 1975 context dependant forgetting study |
Divers learning a world list underwater or on land and than tested in a different condition Recall was 30% lower in not matching conditions Lack of cues leads to retrieval failure |
|
|
Evaluate retrieval failure for forgetting |
Strength - research support Baddeley's divers Argued this to be main reason for forgetting High validity of explanation Limitation - IRL effects weak Baddeley argues contexts have to be very different to cause effects So IRL this isn't very common Limitation - encoding cannot be tested When a cue doesn't help we assume it wasn't encoding but there is no way of testing this this leads to circular reasoning |
|
|
Context dependant forgetting |
Cue is a place or the weather |
|
|
State dependant forgetting |
Retival cue is a mental state e.g. Drunk or upset |
|
|
Describe Loftus and Palmer's 1974a car crash study |
45 ppts watched film of a car crash Asked how fast car speed at contact Caring the verbs to be:hit, contacted, bumped, collide, smashed Smashed produced a mean speed 10mph higher than hit did |
|
|
Post event discussion |
When witnessed discuss and event. This can cause memory contamination |
|
|
Memory conformity |
When witnesses go along with other's memories |
|
|
Describe Gabbert et Al's post event discussion study |
Paired ppts watched video of same crime from different view points They discussed their observations b4 completing and short test on the video 70% mistakenly recorded aspects from the other person |
|
|
Evaluate misleading information |
Limitation - artificial materials Studies use videos which is very different to witnessing the event Yuille and Cutshall found IRL robbery witnesses had very accurate recall 4months later Limitation - own age bias All age groups were more accurate when identifying their own group Studies often use young people to be identified Limitation - lack external validity Real eyewitnesses search their memory due to real world consequences |
|
|
Describe Johnson and Scott's 1976 anxiety study |
Ppts in waiting room for study when an argument is overheard. Man walks out either carrying a greasy pen or a bloody letter opener 50% could identify with low anxiety whereas only 33% in high anxiety |
|
|
Tunnel theory of memory |
Witnesses attention is on weapon because it is source of danger and anxiety |
|
|
Describe Yuille and Cutshall's gun shop robbery study |
13 witnesses to a gun shop robbery were interviewed at the time and 4-5 months later. Witnesses were very accurate and were more so with higher levels of self reported stress |
|
|
Yerkes - Dodson law |

|
|
|
Evaluated anxiety memory studies |
Limitation - surprise not anxiety Pickel's barbershop study Limitation - field studies lack variable control Extraneous variable will affect ppts recalll Limitation - ethical issues Creating anxiety in ppts is might cause harm This doesn't challenge finding but does question conduction of studies |
|
|
Cognitive interview |
Report everything Reinstate context Reverse order Change perspective Enhanced Focus on social dynamics Reducing anxiety and open questions |
|
|
Evaluate cognitive interview |
Strength - some elements best each element found to be equally valuable but report everything and context reinstatement combined was best Limitation - time consuming Limitation - variation All researchers and police used different variations so it is difficult to draw overall conclusions |

