![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hindbrain |
located above the base of the brain. includes pons, medulla and cerebellum. |
|
|
pons |
located above the medulla. involved with sleep, dreaming, arousal from sleep, breathing, coordination. relays messages between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum, and between the medulla and the midbrain. |
|
|
medulla |
controls vital functions such as swallowing, breathing, heart rate, blood rate, respiration, vomiting, salivating, coughing and sneezing. some parts are involved with sensations such as touch, pressure and vibration. |
|
|
cerebellum |
a cauliflower shaped structure located at the base of the brain. contains 80% of the brains neurone. coordinates fine movements, regulates posture and balance. associated with learning and memory and helps create seamless, automatic movement |
|
|
midbrain |
receives information from eyes and ears and connects upper and lower brain areas through neural pathways. involved in movement, processing of visual, auditory and tactile sensory information, sleep and arousal. |
|
|
reticular formation |
helps screen information, alerts higher brain centres to important information. helps maintain consciousness and regulars arousal and muscle tone, alertness and modifies muscles movement. |
|
|
forebrain |
located above midbrain, largest structure of brain. interact through neural pathways between midbrain and hindbrain. includes cerebrum, hypothalamus and thalamus. |
|
|
hypothalamus |
helps maintain brain's internal environment by regulating release of hormones and influences behaviour associated with basic biological needs. |
|
|
thalamus
|
relay station for sensory information, except taste. receives information from sensory organs and passes it to relevant pats of the brain for analysis. |
|
|
cerebrum |
cerebral cortex is its outer layer. involved in complex mental abilities. primarily responsible for cognitive processes such as learning, memory and thinking. |
|
|
cerebral cortex |
involved with complex mental abilities, such as perception, learning, memory, language, thinking and problem solving. |
|
|
cerebral hemispheres |
two almost symmetrical brain areas running from the front to the back of the brain. |
|
|
left hemisphere specialisations |
receives and processes sensations from right side of body. controls voluntary movements on right side of body. verbal tasks such as speech production, comprehension, reading, writing. analysis such as maths sequential tasks, evaluation. logical reasoning |
|
|
right hemisphere specialisations |
receives and processes sensations from left side of the body. controls voluntary movements from left side of body. non verbal tasks and processing the whole, rather than bits. spatial and visual thinking such as solving a jigsaw puzzle, map reading, visualising a location. creativity, fantasy, appreciation of art and music, recognising emotions. |
|
|
primary motor cortex |
coordination of movement |
|
|
primary somatosensory cortex |
receives tactile information from the body |
|
|
parietal lobe |
touch, detection of movement, pressure and pain |
|
|
frontal lobe |
reasoning, planning, speech production, emotions, personality, memory and problem solving |
|
|
occipital lobe |
vision |
|
|
primary visual cortex |
detection of visual stimuli damage can mean difficulty in processing visual information |
|
|
wernicke's area |
language comprehension damage can mean difficulty in comprehension of the language. |
|
|
broca's area |
speech production and articulation
damage will mean a lack of fluent speech 'broc-ken' speech |
|
|
primary auditory cortex |
detection of sound
damage can mean difficulty in processing auditory information |
|
|
temporal lobe |
hearing, recognition of faces damage to right temporal lobe can result in difficulty recognising faces |
|
|
what is missing from this table? CNS PNS Function satellite cell supportive ogliodendrocyte insulation,myelination microglia - |
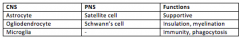
|
|
|
hippocampus |
development of long term memory |
|
|
amygdala |
production and regulation of emotions |
|
|
olfactory bulb |
interprets chemicals, smells and occurs can trigger memories due to location, which is near emotional centre |
|
|
corpus callosum |
connects left and right hemispheres of the brain, enabling them to communicate |

