![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
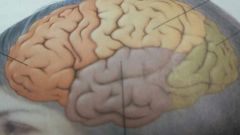
the orange lobe
|
frontal lobe
|
|
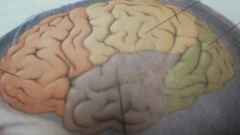
the yellow lobe
|
parietal lobe
|
|
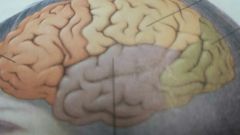
the brown lobe
|
temporal lobe
|
|
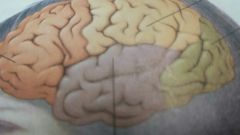
the green lobe
|
occipital lobe
|
|
|
medulla
|
a hind brain structure that extends directly from the spinal cord; regulates breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
|
|
|
pons
|
a hindbrain structure that serves as a bridge between lower brain regions and higher mid brain and forebrain activity.
|
|
|
cerebellum
|
a hindbrain structure involved in body movement, balance, coordination, gone motor skills and cognitive activities such as learning and language.
|
|
|
thalamus
|
a forebrain structure that receives information from the senses and relays it to the cerebral cortex for processing.
|
|
|
hypothalamus
|
a limbic structure; the master regulator of almost all major drives and motives we have, such as hunger, thirst, temperature, and sexual behavior; also controls the pituitary gland.
|
|
|
amygdala
|
small, almond shaped structure located directly in front of the hippocampus; has connections with many important brain regions and is important for processing emotional information, especially that related to fear.
|
|
|
hippocampus
|
a limbic structure that wraps itself around the thalamus; plays a vital role in learning and memory.
|
|
|
neuroplasicity
|
the brains ability to make new connections
|
|
|
neurogenesis
|
the development of new neurons
|
|
|
MRI magnetic resonance imaging
|
brain imaging technique that uses magnetic fields to produce detailed images of the structure of the brain and other soft tissue.
|
|
|
fMRI functional magnetic resonance imaging
|
brain imaging technique that uses magnetic fields to produce detailed images of activity in areas of the brain and other soft tissue.
|
|
|
PET positron emission tomography
|
brain imaging technique that measures blood flow to activate areas in the brain.
|
|
|
EEG electroencephalography
|
studies brain activity and facial expressions of emotion.
|

