![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Transient Exuberance |
▪temporary increase in # of dendrites in brain during first two years of life. ▪Unused dendrites wither to allow more space for more synapses and more complex thinking. |
|
|
Experience-dependent |
brain development is variable because circumstances vary. |
|
|
Experence-expectant |
brain development occurs because of circumstances that all human babies should have. |
|
|
Head-Sparing |
• A biological mechanism. • Protects the brain when malnutrition affects the body. •Brain is the last part of body to be damaged by malnutrition. |
|
|
R.E.M. |
Rapid Eye Movement |
|
|
neuron |
nerve cell in the central nervous system, especially the brain. |
|
|
• Axon (electrical) / (sends) • Dendrite (receives) • Synapse (gap) • Neurotransmitter (chemical). |
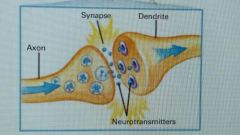
|
|
|
Axon (electrical) |
• fiber extending from a neuron • sends messages to neurons |
|
|
Dendrite (receives) |
• fiber extending from a neuron • receives messages from neurons |
|
|
Synapse (gap) |
• gab between neurons |
|
|
Myelin (cover) |
• covers axons • speeds transmission of impulses |
|
|
Neurotransmitters |
• carry info from one neuron to another |
|
|
SIDS |
▪Sudden Infant Death Syndrome |
|
|
Sensation |
▪response of a sensory system when it detects stimulus ▪eyes, ears, tongue, nose |
|
|
Perseption |
▪mental processing of sensory information |
|
|
S → P→C |
Sensation then Perception then Cognition |
|
|
Hearing (most mature) |
▪Develops during last trimester ▪Speech perception by 4 months |
|
|
Seeing (least mature) |
▪newborns focus between 4-30 inches away ▪Experience, maturation of visual cortex improve details ▪Binocular vision at 3 months |
|
|
Gross VS Fine Motor skills |
▪Gross: large body movement ▪Fine: small body movement |
|
|
Dynamic systems (3 types) |
▪Muscle strength ▪Brain Maturation ▪Practice |
|
|
Public Health Measures |
▪Clean Water ▪Nourishing food ▪Immunization ▪Medical Treatments |
|
|
Sensory Motor Intelligence |
▪Piaget's term to describe the way infants think-by using their senses and motor skills-during the first period of cognitive development
|
|
|
Circular Reactions |
Interaction of sensation, perception, and cognition |
|
|
Primary Circular Reactions |
▪Stage 1 (birth to 1 mo): Reflexes (ex: sucking, grasping) ▪Stage 2 (l to 4 mo): Habits (ex: sucking thumbs or pacifier) |
|
|
Secondary Circular Reactions |
▪Stage 3 (4-8mo): Attempt to make intresting things last (ex: Clapping hands to patty cakes) ▪Stage 4 (6-I2 mo): Initiate and anticipate (ex: putt moms hands together to make her start patty cakes) |
|
|
Tertiary Circular Reactions |
Stage 5 (12-18mo): Active Exploration ("little scientist'') Stage 6 (l8-24 mo): Mental combinations; intellectual experimentation via imagination (ex: toddlers can pretend, think of consequences) |
|
|
Object Permanence |
Realization that objects Ppl. continue to exsist when they are no longer in sight |
|
|
Holophrase |
Single words that express a complete thought |
|
|
Naming explosion |
▪many of words are nouns (person, place, things) ▪50-100 words/mo. |

