![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
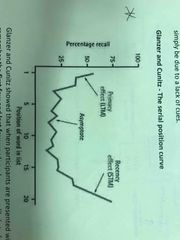
Glanzer and Cunitz - Serial position curve |
First and last few words are more likely to recall. First few words are rehearsed which means no attention paid to middle words. Last few words are recalled as they were the most recently heard. |
|
|
Sensory Register |
Duration - 1/4 to 1/2 second Capacity- potentially unlimited Forgetting - decay Encoding- sense specific |
|
|
Short-Term Memory |
Duration- 18 to 30 seconds Capacity - 7+/-2 items (Miller) Forgetting- displacement Encoding- phonologically Light maintenance rehearsal lon |
|
|
Long- Term Memory |
Duration- unlimited Capacity- unlimited Forgetting - interference Encoding - semantic Deep elaborative rehearsal |
|
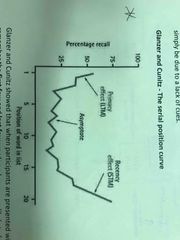
Glanzer and Cunitz - Serial position curve |
First and last few words are more likely to recall. First few words are rehearsed which means no attention paid to middle words. Last few words are recalled as they were the most recently heard. |
|
|
Evaluation |
✅ Jacobs (1887) - average digit span numbers = 9.3 and letters = 7.3. Type of information can affect capacity of STM. ✅Miller - lab based study, 7+/-2 items. ✅Peterson and Peterson- lab based experiment, 24 participants. After 18 seconds 10% of trigrams (meaningless 3 letter combinations) recalled and after 30 almost 0%. ✅supported by lab experiments- tight control over extraneous variables and standardised procedure + case studies eg: patient HM |
|
|
Evaluation 2 |
❌Artificial task - lacks mundane realism and ecological validity ❌too simple- MSM doesn’t account for different systems within the STM (visual and auditory) ❌nomothetic approach- assumes that processes are universal (don’t take individual differences into account) ❌ignores the idea of Flash bulb memories (Brown and Kulik)- shocking memory of event go straight to LTM. |

