![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Empiricism |
The view that knowledge comes from experience and observation. Pg. 9, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Epistemology |
Branch of philosophy concerned with the nature and origin of knowledge. Not in book; online definition (Dictionary.com) |
|
|
|
Critical thinking |
The process of assessing claims and making judgements based on well-supported evidence. Pg. 20, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Hypothesis |
In scientific research, a specific, testable proposition about a phenomenon. Pg. 23, Chapter 1 |
Example: EMDR treatment causes a significant reduction in anxiety. |
|
|
Operational definitions |
Statements that define phenomena or variables by describing the exact research operations or methods used in measuring or manipulating them. Pg. 23, Chapter 1 |
Example: EMDR treatment is a certain number of back-and-forth eye movements per second for a particular amount of time. |
|
|
Variables |
Specific factors or characteristics that can take on different numerical values in research. Pg. 23, Chapter 1 |
Example: the kind of treatment a client is given and the results of the treatment. |
|
|
Statistical reliability |
The degree to which test results or other research evidence occurs repeatedly. Pg. 23, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Statistical validity |
The degree to which evidence from a test or other research method measures what it is supposed to measure. Pg. 23, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Randomizing |
A procedure through which random variables are evenly distributed in an experiment by placing participants in experimental and control groups on the basis of a coin flip or some other random process. Pg. 31, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Random sampling |
A group of research participants selected from a population, each of whose members had an equal chance of being chosen. Pg. 32, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Confounding variables |
Any factor that affects the dependent variable along with, or instead of, the independent variable. Pg. 31, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Correlation |
The degree to which one variable is related to another. Pg. 26, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Dependent variable |
In an experiment, the factor affected by the independent variable. Pg. 28, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Placebo |
A treatment that contains no active ingredient but produces an effect because the person receiving it believes it will. |
|
|
|
Sampling |
The process of selecting participants who are members of the population that the researcher wishes to study. Pg. 32, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Experiment |
A situation in which the researcher manipulates one variable and observes the effect of that manipulation on another variable, while holding all other variables constant. Pg. 28, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Independent variable |
In an experiment, the variable manipulated by the researcher. Pg. 28, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Biased sampling |
A group of research participants selected from a population, each of whose members did not have an equal chance of being chosen. Pg. 32, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Behavioral genetics |
The study of how genes and environments interact to affect behavior and mental processes. Pg. 34, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Double-blind design |
A research design in which neither the experimenter nor the participants know who is in the experimental group and who is in the control group. Pg. 32, Chapter 1 |
|
|
|
Reification |
Treating hypothetical concept as if it was absolutely true. In-class notes 10/3 |
|
|
|
Hypothetical Concepts |
Made up term to describe/explain a relationship (like gender, gravity, etc). In-class notes 10/3 |
|
|
|
Hypothetical Construct |
Is an explanatory variable which is not directly observable. Wikipedia |
|
|
|
Critical Thinking Steps |
What am I being asked to believe or accept? Is evidence available to support the claim? Can that evidence be interpreted another way? What evidence would help to evaluate the alternatives? What conclusions are most reasonable? |
|
|
|
Anthropomorphize |
To ascribe human form or attributes to (an animal, plant, material object, etc.). Dictionary.com |
Example: when you talk about a thing as if it were human |
|
|
Theory |
An integrated set of propositions used to explain certain phenomena, including behavior and mental processes. Pg. 23, Chapter 1 |
Example: after examining research evidence, scientists may begin to favor certain explanations |
|
|
Mechanistic Worldview |
A belief that behavior and behavior change are predictable, lawful phenomena that can, theoretically, be fully understood through the use of systematic, objective empirical research methods. Social.jrank.org |
Example: natural wholes (principally living things) are like complicated machines or artifacts, composed of parts lacking any intrinsic relationship to each other. Wikipedia |
|
|
Ontology/Metaphysics |
Study of what is real |
Example: what the bleep do you know anyways? |
|
|
Neurons |
Specialized cells of the nervous system that send and receive messages. Pg. 46, Chapter 2 |
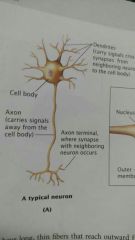
|
|
|
Glial cells |
Nervous system cells that hold neurons together and help them communicate with each other. Pg. 47, Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
Action potential |
The electrochemical impulse or message that is sent down an axon and simulates the release of a neurotransmitter. Pg. 48, Chapter 2 Speed of an action potential depends on thickness or diameter of the axon and on the presence of myelin. Myelin speeds up action potentials by wrapping around some axons like a stocking. |
Example: the communication signal between neurons begins with this electrochemical pulse, which shoots down the axon. |
|
|
Refractory period |
A short recovery time after cell firing, during which the cell cannot fire again. Pg. 48, Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
A chemical that transfers messages across synapses. Pg. 49, Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
Synapse |
The tiny gap between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another, across which they communicate (coordinate). Pg. 48, Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
Dendrites |
Fibers that receive signals from the axons of other neurons. Pg. 48, Chapter 2 |
|
|
|
Coordination between Neurons |
Action potential shoots down the axon, away from cell body. A neurotransmitter is released into the synapse, dendrites of neighboring neurons detect it. If there is a receptor for the neurotransmitter on the dendrites, neurotransmitter and receptor bind, creating electrochemical signal. If signal is strong enough, spreads down the dendrites and across the cell body of the next neuron and begins another action potential. Pg. 49, Chapter 2 |
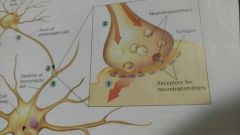
|
|
|
Associated behaviors of neurotransmitters |
Dopamine [DA]: finely coordinated movement, experience of a reward. Serotonin [5-Ht]: mood/arousal (alert or wakefulness) Norepinephrine [NE]: mood, mobilize the brain & body for action (released during fight-or-flight) Acetylcholine [Ach]: gross coordinated movement (legs while walking) Glutamate [Glu]: Gamma amino butyric acid [GABA]: sends signal to stop other neurons from sending signals (positive feedback loop prevention). Hormones: endorphins, melatonin, etc. |
|

