![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the frontal lobe responsible for? |
Executive functioning - reasoning, planning, problem solving, decision making, symbolic thinking etc. |
|
|
What does the primary motor cortex do? |
It initiates and controls voluntary movements. |
|
|
What does Broca's area do? |
It is in charge of articulate speech production. |
|
|
What does the Parietal Lobe do? |
It receives and processes bodily or somatosensory information such as touch, temperature, information about muscle movement and the body's position in space. |
|
|
What does the Primary Somatosensory Cortex do? |
Receives and processes senseory information from the skin and body parts. |
|
|
What is the occipital lobe devoted to? |
The sense and processing of visual stimulants. |
|
|
What is the primary visual cortex in charge of? |
The destination of visual infomration from our eyes. thee information comes from visual sensory receptors located on the retina at the back of each eye. |
|
|
What does the temporal lobe do? |
Involved with auditory perception, memory, visual perception and emotional responses. |
|
|
Primary auditory cortex? |
receives and processes sounds from both ears. |
|
|
WHat does wernicke's area do? |
Critical function in processing and making sense of speech, comprehension. |
|
|
Identifythe 4 different lobes of the brain |
Parietal, Frontal, Occipital and temporal. |
|
|
Whatis the relationship between the CNS & PNS? |
The PNS gathers information from receptorsin the skin, muscles, organs and sends it to the CNS which then takes theinformation, processes it and acts on it |
|
|
Name all different parts of the NS |
|
|
|
What is a neuron? |
A neuron is an individual nerve cell in the human nervous sytem. |
|
|
What is the differencebetween the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system? |
The central nervous system comprises of thebrain and the spinal cord however, the peripheral nervous system comprises ofthe autonomic and somatic nervous system. The CNS also handles involuntaryinformation and the PNS handles voluntary information. |
|
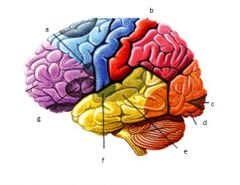
What are different areas in this pic? |
a) frontal lobe b) primary motor cortex b1)somatosensory cortex c)visual cortex d)occipital lobe e)temporal lobe f)auditory cortex g)brocas area |
|
|
What does the spinal cord do? |
connects the brain and peripheral nervous system. |
|
|
The brain area involved in regulating bodily activities is? |
Hindbrain |
|
|
What does the autonomic nervous system do? |
It is the self regulating n/s, it is incharge of doing things that we are not in control of. Parasympathetic and Sympathetic nervous systems are a group of this nervous system. |
|
|
What is the pons |
Regulation of breathing etc |
|
|
What is the hindbrain? |
Cerebellum, pons and medulla |
|
|
What is the medulla? |
Reflexes like coughing and vomiting. |
|
|
What is the corpus collosum? |
|
|
|
What is the reticular formation? |
Arousal, sleep, attention Goes through the core of medulla, pons etc |
|
|
What is the midbrain? |
|
|
|
What is physical development? |
Changes to the body and its various systems, such as development of the brain and nervous system, bones and muscles, motor skills and the hormonal chanes of puberty and menopause. |
|
|
Social development involves what? |
Changes in an indivisual's relationships with other people, and their skills in interacting with others, such as the ability to form close relationships and interact with others in a group situation. |
|
|
WHat is cognitive development? |
Changes in an individual's mental abilities, such as perception, thinking etc. |
|
|
What is emotional development? |
How someone reacts to something or interprets something and how their feelings are expressed. |
|
|
What is continuous development? |
Development involves gradual andongoing changes thoroughout the lifespan without sidden shifts/ |
|
|
Discontinuous development? |
Development involves seperate stages with different kinds of abilities occurring in each stage. |
|
|
What does environment mean in psychology? |
All the experiences, objects and events to which we are exposed throughout our entire lifetime. |
|
|
What is the nature vs nurture debate? |
How we are bought up may affect us and how our genes may affect us. Instead of debating which one is more influential, researchers now focus more on trying to understand how hereditary & environmental factors combine to interact in influencing our thoughts, feelings & behaviour. |
|
|
What does maturation refer to? |
The orderly and sequential developmental changes which occur in the nervous system and other bodily structures controlled by our genes. |
|
|
What is the principle of readiness? |
States that unless the necessary bodily structures are sufficiently mature, then no amount of practice will produce the particular behaviour. |
|
|
Describe infancy. |
Birth - 2 years Infants are dependent on adults. Bond between infant and primary caregiver important for later emotional development. Many psychological abilities are rapidly devloping. |
|
|
Describe childhood. |
2-10 years of age Children become more independent form parents They gain scholarly skills Spend lots of time playing Develop a sense of right and wrong |
|
|
Adolesence. |
10-20 years of age Marked by the onset of puberty. Dominated by seeking independent from parents. Heavily influenced by friends Thought processes are more logical. |
|
|
Early adulthood. |
20-40 years Establishing a life Making babies |
|
|
Middle age |
40-65 years advancing career supporting offspring |
|
|
old age |
65+ years retires decrese in stamina. |
|
|
What is a sensitive period in development |
sensitive periods are periods of rapid change when individuals seem to be more vulnerable or responsive to influences from their environement. Outside this period of time, the same environmental influences need to be stronger to produce the same effects. |
|
|
WHat is a critical period in development? |
A specific period in development which an organism is most vulnerable to the deprivation or absense of certain environmental stimuli or experiences. |
|
|
What is a monozygotic twin? |
They are identical and are formed with one egg which has split into two after a few days. |
|
|
Dizygotic twins are? |
Fraternal, they are basically brothers/sisters born at the same time. |
|
|
What is the attachment theory? |
Human infants need a secure relationship with an adult caregiver in order for healthy emotional and social development to occur. |
|
|
What are the three types of attachement? |
Secure attachment. Insecure resistant attachment Insecure avoidant attachment |
|
|
What is secure attachment? |
This infant shows a balance between dependent and exploration, the infant uses the care giver as a safe base for which to venture out and explore an unfamiliar environment, but shows distress and decreases exploration when the caregiver departs. |
|
|
What is insecue avoidant addachment? |
The infant does not seek closeness or contact with the caregiver and treats them much like a stranger. The infant rarely creis when the caregiver leaves the room and ignores them when they return. |
|
|
What is insecure resistant attachment? |
The infant appears anxious when they are near When the caregiver returns, they want to be picked up but cry until they are put down. |
|
|
Who is harry harlow? |
that guy who made those monkeys |
|
|
What is assimilation? |
The process of taking in new information and fitting it into an dmkaing it part of and existing idea. |
|
|
Accomodation? |
When we cannot assimilate information, we are forced to change or accomodate an existing mental idea to fit the new object or experience. Changing an existing mental idea in order to fit new information. |
|
|
What are the four stages to piagets theory? |
Sensorimotor Pre operational Concrete operational Formal |
|
|
What is the sensorimotor stage? |
Object permanence Goal directed behavour 0-2 years |
|
|
What is the pre operational stage? |
Symbollic thinking and egocentrism animism and transfomation (understanding that one thing can change states.) Centration(when child can only focus on one thing at at time. |
|
|
What is the concrete operational stage? |
conservation classificaion |
|
|
formal operational stage? |
more complex thought processes become evident abstract thinking and logical thinking |
|
|
What is mental wellbeing? |
Use their abilities to reach their potential Cope with everyday life FOrm positive relationships. |

