![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is drug abuse?
|
Use of a drug in a manner that deviates fro the approved medical patterns within a given society
|
|
|
What are the forms / patterns of drug abuse?
|
- Experimental: pressured to try it
- Recreational: casual, modest use for pleasure - Circumstantial: help in particular situations (eg, amphetamines to stay awake or students to study) - Intensive: increased frequency and amounts of drug, however still can choose to take or not take - Compulsive: patterns of abuse that are perceived as detrimental to user and society |
|
|
If a patient is pressured to try a drug, what kind of drug use is this?
|
Experimental
|
|
|
If a patient uses a drug in modest amounts casually, what kind of drug use is this?
|
Recreational
|
|
|
If a patient is using a drug to help in particular situations (eg, amphetamines to stay awake or students to study), what kind of drug use is this?
|
Circumstantial
|
|
|
If a patient is using a drug in increased frequency and amounts of drug, however still can choose to take or not take, what kind of drug use is this?
|
Intensive
|
|
|
If a patient is using a drug with patterns of abuse that are perceived as detrimental to user and society, what kind of drug use is this?
|
Compulsive
|
|
|
What is tolerance?
|
Decreased response to a drug as a result of repeated treatment with drug
|
|
|
What are the types of tolerance?
|
- Dispositional: pharmacokinetic cause
- Pharmacodynamic: changes in target organ sensitivity - Behavioral: change in response to behavioral mechanisms - Cross-tolerance: between drugs of same class |
|
|
What type of tolerance is caused by pharmacokinetics?
|
Dispositional tolerance
|
|
|
What type of tolerance is caused by changes in target organ sensitivity?
|
Pharmacodynamic tolerance
|
|
|
What type of tolerance occurs when a patient tries to act normal after taking a substance so they don't get in trouble (often unsuccessfully)?
|
Behavioral tolerance
|
|
|
What type of tolerance occurs between drugs of the same class (eg, morphine and methadone)?
|
Cross-tolerance
|
|
|
What are the types of drug dependence?
|
- Physical: symptoms are produced by drug withdrawal
- Psychological: compulsive feelings of the need to take a particular drug |
|
|
What are the substance use disorders in DSM-5?
|
Substance Use Disorders (previously broken down into separate categories: substance abuse and substance dependence)
Substance-Induced Disorders - Substance intoxication - Substance withdrawal - Substance/medication-induced disorders included Non-substance related disorders/addictions - Gambling disorder |
|
|
What are the sedative/hypnotic/anxiolytic drugs that are abused?
|
- Barbiturates
- Benzodiazepines |
|
|
What are the opioid drugs that are abused?
|
- Heroin
- Prescription analgesics (eg, morphine, codeine, oxycodone) |
|
|
What are the stimulant drugs that are abused?
|
- Amphetamines
- Cocaine |
|
|
What are the hallucinogen drugs that are abused?
|
- Dissociative anesthetics: Ketamine, Phencyclidine (PCP)
- Entactogens: Ecstasy (MDMA) |
|
|
What are the general substance use disorder criteria?
|
A problematic pattern of substance use within a 12 month period manifested by two or more symptoms that cause impairment in functioning:
For example: - Taken in larger amounts or for longer than intended. - Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down use. - Great deal of time spent in activities necessary to obtain the substance, use the substance, or recover from it’s effects. - Important social, occupational, or recreational activities are reduced or given up because of substance use. - Craving or a strong desire or urge to use the substance. |
|
|
Which parts of the brain are activated by drugs of abuse to stimulate the reward pathway?
|
- Limbic system
- Nucleus accumbens |
|
|
What are the most commonly abused drugs in high school seniors?
|
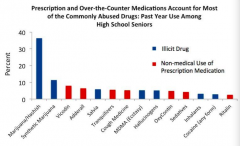
1. Marijuana / Hashish
2. Synthetic Marijuana 3. Vicodin 4. Adderall 5. Salvia |
|
|
How does the percentage of marijuana use compare across grades in high school?
|
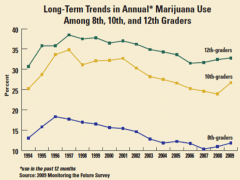
Increases with age
|
|
|
How does the use of marijuana compare in genders?
|
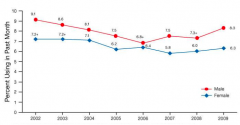
More common in males
|
|
|
What determines how high you will get from marijuana?
|
Δ9-THC content
|
|
|
What are the constituents of marijuana?
|
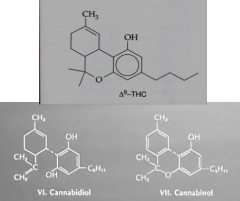
- Δ9-THC
- Cannabidiol - Cannabinol |
|
|
If you give a marijuana user Δ9-THC, what will they think?
|
They will think it is marijuana (most potent/active compound)
|
|
|
If you give a marijuana user cannabidiol or cannabinol, what will they think?
|
They don't think it is marijuana (not the same effects)
|
|
|
How is marijuana metabolized?
|
- In liver, rapid metabolism to 11-OH-Δ9-THC (highly active)
- Then metabolized to 9-nor-COOH-THC (inactive) |
|
|
What happens to the marijuana metabolites?
|
- Excreted in urine and feces (detectable in urine for many days)
- Redistributed in fat |
|
|
How quickly does marijuana get into the brain? Duration of action?
|
Smoked: reaches brain in 15-30 seconds
- 3-5x more potent smoked than ingested Oral: onset is about 30 minutes Duration of action: 1-6 hours (t1/2 in plasma = 20-50 hours); 20% remains in body after 5 days |
|
|
How long does it take for marijuana to be undetectable in body?
|
30 days
(only 20% remains after 5 days) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Δ9-THC?
|
CB1 receptor:
- High densities in cerebellum hippocampus and basal ganglia - Low in hypothalamus CB2 receptor: - Peripheral tissue (associated w/ immune system) Negatively coupled to Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) via Gi → generally inhibits transmitter release Affinity for receptor correlates with psychoactive potency of cannabinoid agonists |
|
|
What are the endogenous ligands for the CB1 receptor?
|
Endocannabinoids:
- 2-Arachidonylglycerol - Anandamide (both are derived from arachidonic acid - lipid constituent) CB1 antagonist: Rimonabant - reduces appetite but pulled off market for causing depression/suicide |
|
|
What are the effects of Marijuana (THC)?
|
- Euphoria
- Memory impairment - Perceptual-motor alterations - Cardiovascular - Pulmonary - Reproductive - Psychopathological effects |
|
|
What are the effects of Marijuana (THC) on memory?
|
- Digit symbol substitution
- Choice - reaction time - Digit span: how many numbers can you remember - Repeated subtractions: serial 7's - Recall of material learned while high is impaired |
|
|
What are the perceptual motor effects of Marijuana (THC)? Implications for driving?
|
Not as easy to test (like there is for alcohol to determine BAC), have to use behavioral test
All impaired: - Laboratory assessment of driving related skill - Driver - simulator studies - Test - course performance - Street - driver performance Studies of drivers involved in fatal accidents - Most common is alcohol - 2nd most common is THC |
|
|
What are the CV effects of Marijuana (THC)?
|
- Tachycardia
- Orthostatic Hypotension - Exacerbates Angina |
|
|
What are the Pulmonary effects of Marijuana (THC)?
|
- Bronchodilation (normals and asthmatics - not via beta receptors)
- Lung irritant - may cause bronchoconstriction (smoke has as much tar as cigarettes and as carcinogenic) - Decreased alveolar macrophage activity (possible risk of infections) - Decrease in ciliary function |
|
|
What are the Reproductive effects of Marijuana (THC)?
|
- Lowers T levels and sperm counts
- In rodents, gonadal weights are decreased - LHRH release is decreased, which decreases levels of FSH and LH - Prolactin release is decreased in females, greater incidence of abnormal menstrual cycles - Hazard to marginally fertile |
|
|
What are the Psychopathological effects of Marijuana (THC)?
|
- Acute anxiety reaction / panic attack (more common in naive users)
- Transient paranoid feelings - Exacerbation of schizophrenia - Diffuse acute brain syndrome w/ high doses - clouding of consciousness and memory, perceptual and sleep disorders - Amotivational syndrome (people who are stoned a lot do not want to work a lot) |
|
|
Does tolerance / dependence develop to Marijuana (THC)?
|
Yes - in frequent heavy users commonly reported symptoms associated with cessation of marijuana use include:
- Restlessness - Irritability and mild agitation - Sleep difficulties - Decreased appetite and nausea - Craving |
|
|
What are the therapeutic uses of Marijuana (THC)?
|
- Oral THC in sesame oil: control of nausea, AIDS wasting syndrome
- THC/cannabidiol mixture: MS pain treatment and cancer pain - CB1 antagonist: weight loss (removed from market) |
|
|
What are the other names for Synthetic Marijuana?
|
K2 or Spice or other names
|
|
|
What are the contents of Synthetic Marijuana?
|
- Contains synthetic compounds that have THC-like CB1 agonist activity
- Compounds that are not yet DEA scheduled are "legal" |
|
|
What are the hallucinogen dissociative anesthetics?
|
- Ketamine
- Phencyclidine (PCP) |
|
|
What are the absorption properties and t1/2 of Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP)?
|
- Rapid / complete absorption
- Plasma t1/2: 12-24 hours (in overdose t1/2, 72 hours) |
|
|
How are Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP) metabolized? Excreted?
|
Metabolized in liver:
- Hydroxylation - Conjugation Excreted in urine: - Primarily as biotransformation products |
|
|
What are the autonomic and CV effects of Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP)?
|
- Tachycardia
- Hypertension - Potentiation of catecholamines - Develops tolerance (but no dependence) |
|
|
What are the differences in effects of Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP)?
|
Complex and dose related
- Ketamine is less potent and has a shorter duration of action than PCP |
|
|
Which statement best describes the comparison between the effects of THC and phencyclidine on the cardiovascular system?
a) THC produces a dose-related tachycardia and can produce orthostatic hypotension. Phencyclidine also produces tachycardia, but can also produce a severe hypertension. b) Phencyclidine produces a dose-related tachycardia and can produce orthostatic hypotension. THC also produces tachycardia, but can also produce a severe hypertension. c) Both produce dose-related tachycardia and can produce orthostatic hypotension. d) Both produce tachycardia and can also cause severe hypertension. |
THC produces a dose-related tachycardia and can produce orthostatic hypotension. Phencyclidine also produces tachycardia, but can also produce a severe hypertension.
|
|
|
What happens when Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP) are taken in small doses?
|
"Drunken" state with numbness of extremities
|
|
|
What happens when Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP) are taken in moderate doses?
|
- Analgesia and anesthesia
- Psychic states crudely resemble sensory isolation except that sensory impulses reach neocortex - Cataleptoid motor phenomenon are observed |
|
|
What happens when Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP) are taken in large doses?
|
May produce convulsions
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Ketamine and Phencyclidine (PCP)?
|
Block NMDA receptors (non-competetive antagonists)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of overdose of Phencyclidine (PCP)?
|
CNS manifestations include:
- Anxiety - Aggression - Hallucinations - Dysphoria - Convulsions - Delirium Sympathomimetic manifestations include: - Tachycardia - Hypertensive crisis |
|
|
How do you treat an overdose of Phencyclidine (PCP)?
|
- Support vital signs
- Gastric suction (try to remove some of it) - Acidify urine (might increase excretion because it is a base) - Diazepam - Anti-HTN agent - Haloperidol (low anti-cholinergic anti-psychotic) |
|
|
What are the hallucinogens?
|
Indoleamines:
- LSD Phenethylamines: - MDMA (ecstasy) |
|
|
What are the pharmacological effects of LSD (how much penetrates the brain, onset, duration?)
|
- <1% crosses BBB
- Onset: 15-20 minutes - Duration: 12 hours |
|
|
What are the CV/autonomic effects of LSD?
|
- Tachycardia
- Increased BP - Psychomotor stimulation - Tolerance and cross tolerance (to psilocybin/mushrooms) |
|
|
What are the sensory and subjective effects of LSD? Mechanism?
|
- Altered perception, particularly visual
- Lability of mood - Impaired judgment - Mechanism: action at 5-HT2 receptors (agonist or partial agonist) |
|
|
What are the acute (<24 hours) toxic reactions to LSD? Treat?
|
- Hallucinations
- Anxiety - Panic - Depersonalization - Need quiet environment, benzos for sedation |
|
|
What are the long term toxic reactions to LSD?
|
- Flashbacks: days to years later, can be associated with drug use
- Neurotoxicity: 5-HT damage may be associated with -phenethylamine type drugs such as MDMA |
|
|
What is the other name for ecstasy?
|
MDMA
|
|
|
What are the pharmacological effects of LSD (onset, duration?)
|
- Onset: 20-40 minutes
- Duration: 3-4 hours |
|
|
What are the effects of MDMA/ecstasy?
|
- Induces feeling of "well-being and connection"
- Altered time perception - Psychomotor stimulation - Restlessness - Bruxism - Anorexia - Sweating - Tremor - Hangover: anhedonia - Neurotoxicity: serotonin neurons? |
|
|
Which of the following is an official FDA indication for delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol?
a) Asthma b) Bradycardia c) Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting d) Neuropathic pain e) None in Wisconsin |
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
|
|
|
Where is Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) found? What is it structurally similar to?
|
Found in brain - precursor and metabolite of GABA; may have its own receptor; can be made in body
|
|
|
How long do the effects of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) last?
|
Lasts about 3 hours
|
|
|
What are the effects of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB)?
|
- Primarily a depressant - induces a state of relaxation and tranquility
- Interacts with ethanol |
|
|
What are the characteristics of overdose of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB)?
|
- Drowsiness
- Ataxia - Nausea - Vomiting Higher doses: - Loss of bladder control - Temporary amnesia - Clonus - Seizures |
|
|
What drug is an inhalant? Where is it found? Bad effects?
|
Toluene
- Found in model airplane glue - led to glue sniffing - Contaminated with benzene which may cause aplastic anemia |
|
|
What kind of drug is a perennial herb grown in Mexico?
|
Salvia Divinorum - contains Salvinorin-A
|
|
|
What are the effects of Salvinorin-A?
|
- Extremely potent
- Psychedelic, dream-like experience w/ open and closed eyed visuals - High doses may cause dissociation with fear and perspiration (considered unpleasant by many) - Short duration of action: 20-45 minutes |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Salvia (Salvinorin-A)?
|
Kappa opioid AGONIST
|
|
|
Which receptor does phencyclidine produce its hallucinogenic effects at?
a) CB1 b) GABAa c) N-methyl-d-aspartate d) Norepinephrine – alpha2 e) Serotonin – 5-HT2 |
NMDA receptor
|
|
|
What OTC drug is abused?
|
Dextromethorphan (cough suppressant)
|
|
|
What is in "bath salts"?
|
Stimulants that may be related to those found in "khat" which is used recreationally in part of Africa
|
|
|
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) demonstrates cross tolerance with what other drug?
a) Atropine b) Cannabidiol c) Ketamine d) Mescaline e) Salvia divinorum |
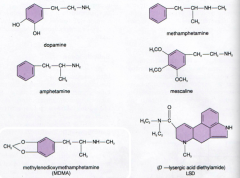
Mescaline
|

