![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two sleep states?
|
- REM (rapid eye movement)
- Non-REM sleep |
|
|
What are the primary sleep NTs?
|
- ACh - REM
- Serotonin - NREM |
|
|
What are the two brain structures involved in REM and Non-REM sleep?
|
Deep brainstem structures: median raphe and ____
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Normal Sleep Architecture?
|
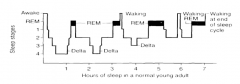
- Transitions from one stage of sleep to the other through the night
- Alternating stages of REM-1-2-3-4- |
|
|
What is the EEG pattern during awake state?
|
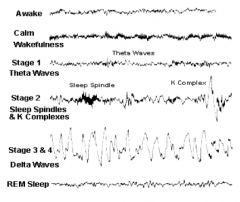
Beta waves
|
|
|
What is the EEG pattern during relaxed state?
|
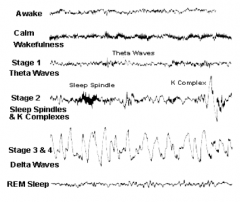
Alpha waves
|
|
|
What is the EEG pattern during stage 1 sleep?
|
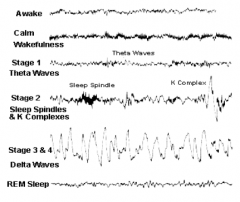
Theta waves
|
|
|
What is the EEG pattern during stage 2 sleep?
|
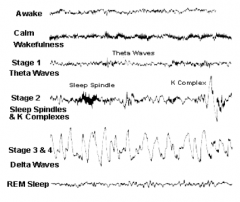
Sleep spindles and K complexes
|
|
|
What is the EEG pattern during stage 3/4 sleep?
|
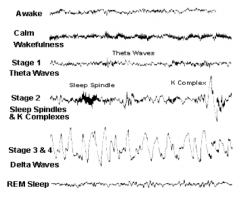
Delta waves
|
|
|
What is the EEG pattern during REM sleep?
|
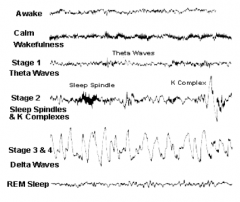
Beta waves, sawtooth waves
|
|
|
What is the normal human circadian cycle?
|
25 hours
|
|
|
What is the EEG pattern while awake?
|
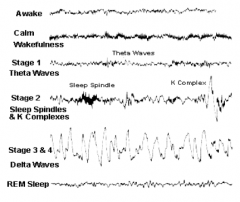
- Alert: beta waves
- Relaxed: alpha waves |
|
|
What is sleep latency? Normal?
|
- Time it takes to fall asleep
- <10 minutes |
|
|
What is sleep efficiency? Normal?
|
- Time spent sleeping / time spent trying to sleep
- Should be close to 100% |
|
|
How many hours of sleep are required for:
- Newborns - Adolescents - Adults - Older adults |
- Newborns: 16-18 hours
- Adolescents: 9-10 hours - Adults: 8 hours - Older adults: 7-8 hours |
|
|
What percent of sleep is spent in REM sleep? How frequently does REM sleep occur? How long does each episode last?
|
- 25% of all sleep
- Every 90 minutes - Episodes last 10-40 minutes (longer episodes during second half of night) |
|
|
What changes occur during REM sleep?
|
- Increased: BP, HR, and RR
- Penile and clitoral erection - Skeletal muscle paralysis (this is when dreaming occurs) - EEG: small irregular brain waves (beta waves) |
|
|
What percent of sleep is spent in each stage of non-REM sleep?
|
- Stage 1: 5%
- Stage 2: 45% - Stage 3/4: 25% |
|
|
When does the most deep sleep occur?
|
During first half of the night (Stages 3 and 4 - 25% of total sleep)
|
|
|
What percent of sleep is spent in Stage 1 NREM sleep? How long does each episode last?
|
- 5% of total sleep
- Lasts about 10 minutes |
|
|
What changes occur during Stage 1 NREM sleep? Can someone be awoken during this stage?
|
- Breathing: slow and even
- HR: regular - Decrease: BP, T, blood flow to brain - EEG: brain waves smaller, slower, irregular - Sleeper easily awoken |
|
|
What percent of sleep is spent in Stage 1 NREM sleep? How long does each episode last?
|
- 45% of total sleep
- Lasts about 20 minutes |
|
|
What changes occur during Stage 2 NREM sleep? Can someone be awoken during this stage?
|
- Bodily functions continue to slow
- Even if eyes are opened, sleeper cannot see - EEG: larger brain waves, occasional quick bursts of activity - Sleeper can be awakened by sounds |
|
|
What percent of sleep is spent in Stage 3 NREM sleep? When does it get initiated?
|
- 25% of total sleep (3 & 4)
- Begins about 30-45 minutes after sleep is initiated |
|
|
What changes occur during Stage 3 NREM sleep? Can someone be awoken during this stage?
|
- EEG: brain waves are slow and large (up to 5x as large as in stage 2)
- Sleeper is much less easy to awake, requiring loud noise or active attempts to wake |
|
|
What changes occur during Stage 4 NREM sleep? Can someone be awoken during this stage?
|
- Bodily functions decline to deepest state of rest
- EEG: brain waves are large, slow, and make a jagged pattern - Sleeper experiences oblivion: if awakened, very disoriented |
|
|
What are the changes to sleep that occur with aging?
|
- Decreased REM
- Decreased stage 3 & 4 sleep - Increased night-time awakenings - Decreased sleep efficiency |
|
|
What are the changes to sleep that occur with depression?
|
- Frequent awakenings / decreased sleep efficiency
- Early morning awakening - Decreased REM latency - first REM within 45 minutes total - Increased total REM - Decreased stage 3 & 4 sleep |
|
|
How can be sleep disorders be classified?
|
- Dyssomnias: abnormal timing, quality, and amount of sleep
- Parasomnias: abnormal behaviors associated with sleep |
|
|
What sleep disorder classification is characterized by abnormal timing, quality, and amount of sleep?
|
Dyssomnias
|
|
|
What sleep disorder classification is characterized by abnormal behaviors associated with sleep?
|
Parasomnias
|
|
|
What are the types of Dyssomias?
|
Categorized based on abnormal timing, quality, and amount
Timing: - Narcolepsy - Circadian rhythm sleep disorder Quality: - Restless leg - Sleep apnea Amount: - Insomnia - Hypersomnia |
|
|
What are the types of Parasomnias?
|
Abnormal behaviors associated with sleep
- Bruxism (tooth grinding) - Night terrors - Sleepwalking - REM sleep behavior disorder |
|
|
What are the key features of Narcolepsy?
|
- Sleep attacks
- Hypnogogic / hypnopompic hallucinations - Cataplexy - Sleep paralysis |
|
|
What happens to the sleep architecture in Narcolepsy?
|
- Decreased sleep latency
- Decreased REM latency (<10 minutes) - Less REM overall |
|
|
What may cause Narcolepsy? When is it commonly diagnosed?
|
- Narcolepsy is associated wit hypocretin (orexin) deficiency
- Usually diagnosed in adolescence - Significant genetic component |
|
|
How do you treat Narcolepsy?
|
- Scheduled daytime naps
- Psychostimulants: Methylphenidate and Modafinil |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Restless Leg Syndrome?
|
- Uncomfortable sensation in the legs
- Repetitive limb jerking - Frequent night-time awakenings |
|
|
When does Restless Leg Syndrome more commonly occur?
|
Usually occurs in older adults
|
|
|
How do you treat Restless Leg Syndrome?
|
Anti-parkinsonian agents:
- Levodopa - Carbidopa / Levodopa - Ropinirole |
|
|
What are the features of Sleep Apnea?
|
- Cessation of breathing
- Carbon dioxide increases - Frequent awakenings - Increased rate of sudden death |
|
|
What are the associated features of Sleep Apnea?
|
- Snoring (if obstructive variant)
- Daytime sleepiness - Morning headache - Lab: respiratory acidosis |
|
|
What lab findings are associated with Sleep Apnea?
|
Respiratory acidosis
|
|
|
What are the types of Sleep Apnea? How are they distinguished?
|
1. Central apnea - decreased respiratory effort
2. Obstructive apnea - normal respiratory effort but airway obstruction |
|
|
What are the types of Sleep Apnea more common epidemiologically?
|
1. Central apnea - usually older adults
2. Obstructive apnea - middle-aged adults, far more common in mean, associated with obesity |
|
|
How do you treat Sleep Apnea?
|
- Weight loss (if obesity present)
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) - Medroxyprogesterone acetate - Uvulopalatoplasty / Tracheostomy |
|
|
What are the features of Insomnia?
|
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- 3x/week or more - Duration for at least one month - Daytime sleepiness |
|
|
How common is Insomnia?
|
At least 30% of the population
|
|
|
What is Insomnia associated with?
|
Cognitive impairment and accidents
|
|
|
How do you treat Insomnia?
|
- Avoid caffeine, especially in evenings
- AM exercise - Develop sleep routine - Relaxation techniques - Hypnotic medication (may however, decrease REM and delta/stages 3/4 sleep) |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Bruxism? When does it happen?
|
- Tooth-grinding - may cause tooth damage and jaw pain
- Occurs during stage 2 sleep |
|
|
How do you treat Bruxism?
|
Dental appliance worn at night
|
|
|
What are the features of sleep terrors? When does it occur?
|
- Repetitive experiences of fright
- Not easily awakened - No memory upon awakening - Occurs during stage 3 and 4 sleep, usually in children |
|
|
What are the features of sleep walking? When does it occur?
|
- Repetitive walking
- Can be injured - No memory upon awakening - Occurs in stage 3 and 4 of sleep, usually in children |
|
|
How do you treat sleep walking?
|
Manipulate environment - safety
|
|
|
What stage of sleep takes up the largest percentage of sleep time in young, healthy adults?
a) Stage 1 b) Stage 2 c) Stages 3 and 4 d) REM |
Stage 2
|
|
|
During a sleep study, a patient’s EEG shows primarily sawtooth waves. What sleep stage is the patient in?
a) Stage 1 b) Stage 2 c) Stage 3 and 4 d) REM |
REM
|
|
|
3: A healthy five-year-old girl has recently exhibited several night time episodes of loud screaming that awaken her parents. She is found sitting up, with eyes wide open, and unresponsive to her parents’ attempts to awaken her. What would the girl’s EEG most likely show during these episodes?
a) Alpha waves b) Delta waves c) Theta waves d) Sawtooth waves |
Delta waves
|
|
|
A young woman presents with jaw pain and minor tooth damage. What would this patient’s EEG most likely show during episodes of tooth grinding?
a) Alpha waves b) Delta waves c) K complexes and sleep spindles d) Theta waves |
K complexes and sleep spindles (stage 2)
|
|
|
A patient has been taking moderate doses of a diazepam for years. What changes in sleep architecture is most likely to be present?
a) Decreased delta, decreased REM b) Decreased delta, increased REM c) Increased delta, decreased REM d) Increased delta, increased REM |
Decreased delta, decreased REM sleep
(more time is spent in Stage 2 NREM sleep) |
|
|
As compared with young adults, elderly adults demonstrate what changes in sleep architecture?
a) Decreased delta, decreased REM b) Decreased delta, increased REM c) Increased delta, decreased REM d) Increased delta, increased REM |
Decreased delta, decreased REM sleep
(more time is spent in Stage 2 NREM sleep) (Same as patient on a benzodiazepine) |
|
|
A patient with major depression is likely to demonstrate which of the following changes in sleep architecture?
a) Decreased delta, decreased REM b) Decreased delta, increased REM c) Increased delta, decreased REM d) Increased delta, increased REM |
Decreased delta, increased REM
|
|
|
A 55-year-old, overweight male presents with a complaint of significant daytime fatigue and morning headaches. He sleeps eight hours each night. His wife states that his snoring keeps her awake. What is his most likely diagnosis?
a) Central sleep apnea b) Circadian rhythm sleep disorder c) Kleine-Levin syndrome d) Narcolepsy e) Obstructive sleep apnea |
Obstructive sleep apnea
|
|
|
In addition to weight loss, what is the best treatment for the previous patient?
a) Antidepressant b) CNS depressant c) CNS stimulant d) Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) e) Sleep hygiene techniques |
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
|
|
|
A 20-year-old college student falls asleep suddenly in spite of sleeping 8 hours a night. The student also describes unusual visions while falling asleep and an occasional inability move his body for a few seconds upon awakening. What is EEG changes are most likely?
a) Decreased REM latency, decreased sleep latency b) Decreased REM latency, increased sleep latency c) Increased REM latency, decreased sleep latency d) Increased REM latency, increased sleep latency |
Decreased REM latency, decreased sleep latency
|

